Dental filling or restoration is a common dental procedure to restore the normal functions of the teeth. Teeth may need filling or restoration for various reasons, such as chipping of teeth, dental caries, which may cause a loss of considerable tooth structure, or dental fracture or trauma. Ignoring cavities or carious parts of the teeth can lead to sensitivity problems or, in severe cases, tooth loss. The most commonly used dental filling material nowadays is dental composite. Dentists also use other dental filling materials, such as dental amalgam and glass ionomer cement, depending on the patient’s needs.
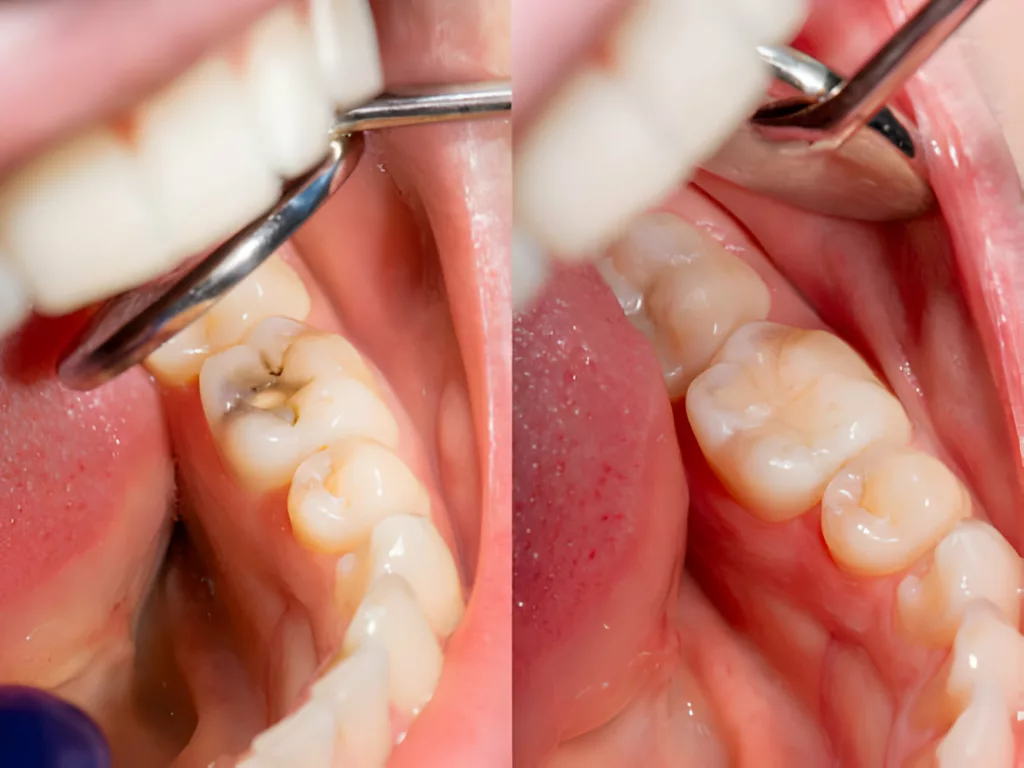
During a dental restoration, dentists remove and replace a decayed or damaged part of the teeth (not involving pulp) with dental filling material to rebuild the normal tooth structure and restore its normal function and shape.
Our mouth contains 32 teeth. The outermost layer of a tooth, known as enamel, is one of the body’s hardest substances. Dentin, the middle layer, is sensitive to irritants. The innermost layer is the pulp, which is a living tissue of the tooth. When a cavity reaches the dentin layer, or damage exposes it, a dental filling is necessary to restore the affected area. On the other hand, when pulp is damaged, dentists opt for root canal treatment.
Types OF Dental Fillings
There are various types of dental fillings. Some of these are mentioned below:
Glass Ionomer Cement
Glass ionomers have become materials often used in dental practice. They are preferred due to:
- Fluoride-releasing properties
- Good color stability
- They do not require strict isolation from the salivary environment.1Gherman, A.-M., (2023). Studies on the use of glass ionomer.Medicine and Pharmacy Reports, 96(1), 86–92. doi:10.15386/mpr-2351
Unfortunately, dentists often use it as a temporary restorative dental material due to its weaker strength.
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide appears to be the material of choice for pediatric patients. They are employed if primary teeth are not near to shedding. It has:
- Excellent antibacterial properties
- It initiates the formation of dental tissues.
- It can be used as a therapeutic liner. A therapeutic liner regenerates tooth structure when the prepared tooth cavity is very close to the pulp, and pulp exposure is possible.
Despite multiple benefits, calcium hydroxide is weak and cannot provide a better barrier.
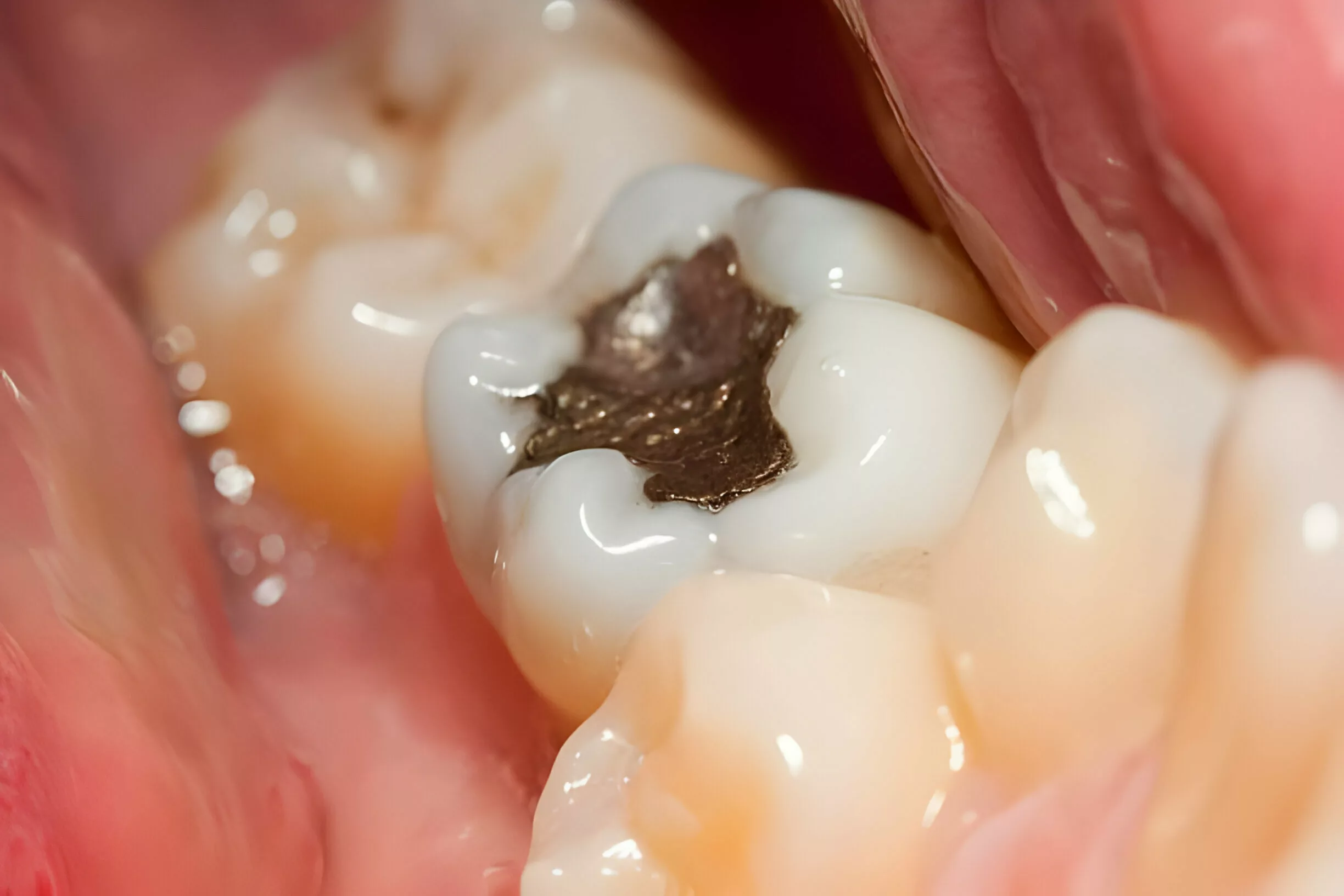
Dental Amalgam
The word amalgam means a combination of mercury with another metal. Dental amalgam, also called Silver filling, is a blend of metals made up of liquid elemental mercury combined with a powdered alloy of silver, tin, and copper. Due to its metallic color, amalgam is suitable only for posterior teeth. It is available in powder and liquid form. Mixing the metal powder with liquid mercury is called trituration.
Although it seems advantageous over other dental fillings in terms of strength and longevity, allegations of effects caused by amalgams have involved many diseases.
Mercury in Dental Amalgam
Dentists have used dental amalgam fillings containing mercury for almost 200 years, and they have been controversial for almost the same time. Small amounts of mercury vapor are released from these fillings, which can be inhaled and absorbed by the lungs.2Bates, M. N. (2006a). Mercury amalgam dental fillings: An epidemiologic assessment. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 209(4), 309–316. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2005.11.006. This exposure may cause adverse effects on the brain and kidneys, particularly in high-exposure settings. Vulnerable groups include pregnant women, fetuses, young children, and individuals with pre-existing neurological or kidney conditions. Limited data on long-term health effects in these groups suggest consulting a dentist for alternative treatments if concerned. Those with allergies to amalgam components should also seek other options.3U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). Dental Amalgam Fillings. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/dental-devices/dental-amalgam-fillings#:~:text=Dental%20amalgam%20is%20a%20dental,silver%2C%20tin%2C%20and%20copper.

Composite Resin
Dental composite resin materials are an aesthetic alternative to mercury-containing fillings, and their mechanical properties have developed sufficiently to make them suitable for restoring posterior teeth. Nevertheless, composite resin materials may have the potential for toxicity to human health and the environment.4Worthington, H. V., Khangura, S., Seal, K., Mierzwinski-Urban, M., Veitz-Keenan, A., Sahrmann, P., … Rasines Alcaraz, M. G. (2021b). Direct composite resin fillings versus amalgam fillings for permanent posterior teeth. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 8(8), CD005620. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005620.pub3
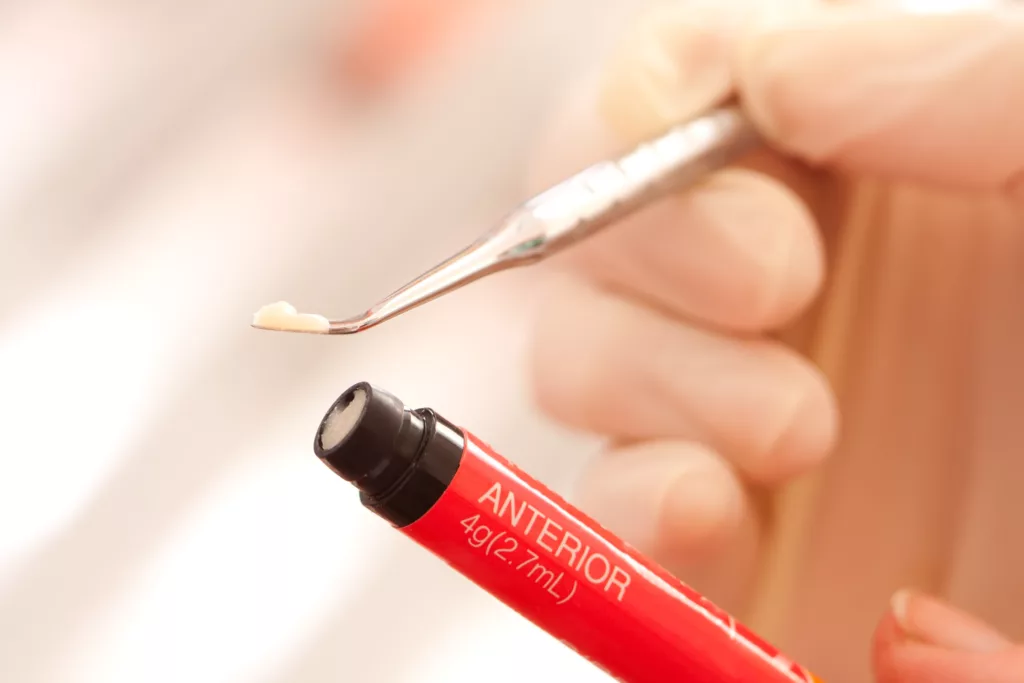

Advantages & Disadvantages of Composite
Composite filling materials, which come in different shades and tints, enable dentists to use them in esthetic areas. They bind with tooth structure, providing a good seal. Due to their strength, aesthetics, and ease of handling, dentists widely use them as dental filling materials in the modern day.
Among many other advantages, it also has some disadvantages. During the setting of the composite, it may undergo shrinkage, which creates leakage and, hence, increases the chances of secondary caries. Moreover, strict isolation from the salivary environment is required for proper settings.
Indications of Dental Filling
It is always better to visit the dentist twice yearly for routine dental checkups. Your oral health will be maintained through those appointments. The indications of dental filling include:
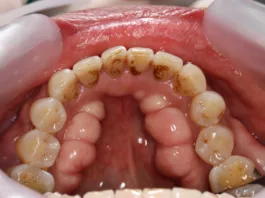
- Any black or brown spots on your teeth surfaces. Any carious lesion or attack on the tooth structure initially appears as a brown or black spot. Negligence causes this to spread. As soon as this caries reaches the middle layer of the tooth, i.e., dentin, the tooth becomes sensitive to hot and cold beverages.
- Damaged or decayed part of the tooth.
- Food impaction between your teeth.
- Changing the shape of the teeth for aesthetic concerns
- If your old filling becomes discolored or decayed, it can be replaced with a new filling.
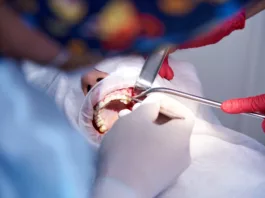
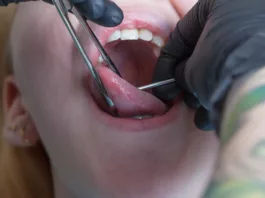
Procedure of Dental Filling
All dental filling materials follow different guidelines for their placement into the cavity. There are general steps in every dental filling procedure which are stated as:
- The dentist will use a numbing gel and a local anesthetic to numb the area.
- Dentists use dental instruments to remove all damaged or carious tooth structures and prepare a cavity design.
- They isolate the working tooth to prevent any salivary contamination.
- After drying the cavity surface, they place the dental filling material.
- Some dental filling material undergoes setting chemically, while some dental filling material, such as dental composite, requires an external light source5Price R. B. T. (2017). Light Curing in Dentistry. Dental Clinics of North America, 61(4), 751–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2017.06.008 to undergo setting.
- Amalgam filling sets after mechanical condensation.
- After completing the dental filling, the dentist guides the patient to follow aftercare instructions according to the type of filling performed.
Aftercare
After the placement of dental filling material, there are certain guidelines to follow concerning every dental filling material.
- For amalgam, avoid eating hard or sticky things from the restored site for 24 hours, as dental amalgam filling takes time to develop maximum strength.
- The composite hardens immediately after curing, so there is no waiting time to eat.
- Patients should postpone elective dental procedures, such as veneers and braces, unless they have a dental emergency.
- Maintain good oral hygiene and brush your teeth twice a day.
- Use fluoride-containing mouthwash and toothpaste.
- Consult your dentist as soon as you experience any problem.
Is the filling procedure painful?
Dental fillings typically do not cause pain during the procedure because dentists use local anesthesia to numb the area around the affected tooth. You might feel a brief pinch when the anesthetic is injected, but this quickly subsides. During the procedure, you may experience some pressure or vibration as the dentist removes the decayed part of the tooth and prepares it for the filling, but this should not be painful. After the procedure, once the anesthesia wears off, you might experience minor sensitivity or discomfort, especially to hot or cold temperatures, but this usually resolves within a few days.6Porto, Isabel. (2012). Post-operative sensitivity on direct resin composite restorations: clinical practice guidelines. Indian Journal of Restorative Dentistry. 1. 1-12. If you experience significant pain or prolonged discomfort, it’s important to contact your dentist for further evaluation.
Pediatric Dental Filling Materials
Dentists usually select dental filling materials for primary teeth, considering various factors such as the size and location of the cavity, the child’s age, oral health issues, and the dentist’s preferences.
Common pediatric filling materials are:
- Composite Resin: The dentist may use them for small to medium-sized cavities in primary teeth.
- Glass Ionomers: GIC releases fluoride and prevents further decay or damage.
- Stainless Steel Crowns: Dentists use stainless steel crowns for large cavities in primary molars.
- Zinc Oxide Eugenol: It has pain-relieving and antibacterial properties.
Dental Filling during Pregnancy
The physiological changes that occur in the mouth during pregnancy are widely documented. The lack of routine dental check-ups exposes the pregnant patient to a greater risk of dental caries.7Favero, V., Bacci, C., Volpato, A., Bandiera, M., Favero, L., & Zanette, G. (2021). Pregnancy and dentistry: A literature review on risk management during dental surgical procedures. Dentistry Journal, 9(4), 46. doi:10.3390/dj9040046
Patients should postpone elective dental procedures, such as veneers and braces, unless they have a dental emergency.
If the patient needs any dental fillings, the second trimester is recommended for non-emergency dental work, as it may be difficult to lie on your back for extended periods during the third trimester.
Mercury from dental amalgam can cause neurological problems if used during pregnancy.8Favero, V., Bacci, C., Volpato, A., Bandiera, M., Favero, L., & Zanette, G. (2021). Pregnancy and dentistry: A literature review on risk management during dental surgical procedures. Dentistry Journal, 9(4), 46. doi:10.3390/dj9040046
Dental Filling Materials Vs. Root Canal Filling Materials
Dentists utilize dental filling materials to restore the part of the tooth that caries and trauma have affected, and they use root canal filling materials to fill the clean root spaces after they remove the central living dental tissue known as the pulp.
In conclusion, Dental fillings are essential for preserving oral health because they fill dental cavities and stop additional decay. Furthermore, the longevity of dental fillings and general oral health depend on practicing good oral hygiene and seeing the dentist regularly. With the right maintenance, dental fillings can contribute to maintaining the health of your smile.
Refrences
- 1Gherman, A.-M., (2023). Studies on the use of glass ionomer.Medicine and Pharmacy Reports, 96(1), 86–92. doi:10.15386/mpr-2351
- 2Bates, M. N. (2006a). Mercury amalgam dental fillings: An epidemiologic assessment. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 209(4), 309–316. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2005.11.006
- 3U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). Dental Amalgam Fillings. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/dental-devices/dental-amalgam-fillings#:~:text=Dental%20amalgam%20is%20a%20dental,silver%2C%20tin%2C%20and%20copper.
- 4Worthington, H. V., Khangura, S., Seal, K., Mierzwinski-Urban, M., Veitz-Keenan, A., Sahrmann, P., … Rasines Alcaraz, M. G. (2021b). Direct composite resin fillings versus amalgam fillings for permanent posterior teeth. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 8(8), CD005620. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005620.pub3
- 5Price R. B. T. (2017). Light Curing in Dentistry. Dental Clinics of North America, 61(4), 751–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2017.06.008
- 6Porto, Isabel. (2012). Post-operative sensitivity on direct resin composite restorations: clinical practice guidelines. Indian Journal of Restorative Dentistry. 1. 1-12.
- 7Favero, V., Bacci, C., Volpato, A., Bandiera, M., Favero, L., & Zanette, G. (2021). Pregnancy and dentistry: A literature review on risk management during dental surgical procedures. Dentistry Journal, 9(4), 46. doi:10.3390/dj9040046
- 8Favero, V., Bacci, C., Volpato, A., Bandiera, M., Favero, L., & Zanette, G. (2021). Pregnancy and dentistry: A literature review on risk management during dental surgical procedures. Dentistry Journal, 9(4), 46. doi:10.3390/dj9040046