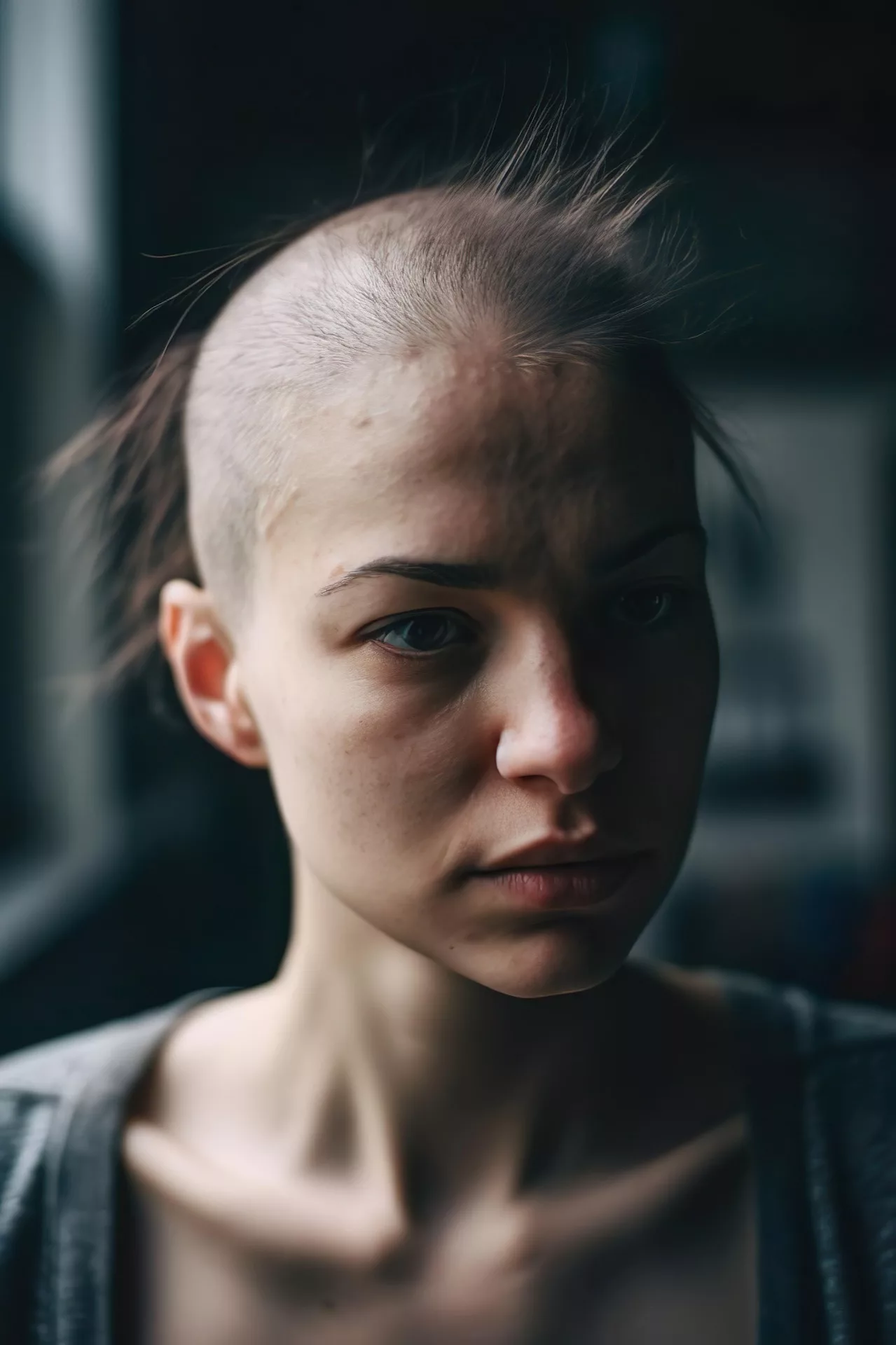
Hypotrichosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal deficiency of hair on the scalp or body. It may affect various areas, including the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes, and can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. Congenital hypotrichosis is often associated with genetic mutations and may occur as part of syndromic or non-syndromic conditions.
Hypotrichosis Types
Dermatologists divide hypotrichosis into different types, including:
Autosomal Recessive Woolly Hair/Hypotrichosis (ARWH):
Babies born with this type have sparse and woolly scalp hair, which is usually lighter in color and very fragile. You can find weak hair in the eyebrows and eyelashes, too. The hair is sparse, and even the ones present can’t grow beyond a few inches. A high prevalence of the genetic mutation condition is found in Pakistan, Japan, and Russia.1Akiyama, M. (2021). Isolated autosomal recessive woolly hair/hypotrichosis: genetics, pathogenesis and therapies. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 35(9), 1788-1796. Patients may also experience associated symptoms like redness and itchiness. The disease can progress to complete loss of scalp hair (alopecia).
Hypotrichosis Simplex:
This type is also a rare, genetic disorder that involves hair loss primarily on the scalp. However, experts divide it into scalp-limited and generalized forms. Individuals affected with hereditary hypotrichosis simplex (HSS) usually have normal hair at birth but experience progressive hair thinning and loss. Most individuals notice thinning of the hair shaft during early childhood. The prevalence of the disease is less than 1 in 100000 individuals.2Kibtiar, M., Akther, R., Islam, M. M., & Rahman, S. A. (2019). Congenital hypotrichosis simplex: A case report. Bangladesh Journal of Child Health, 43(1), 59-61.
Marie Unna Hereditary Hypotrichosis:
In this type, patients experience alternating growth of hair. The autosomal dominant disorder is characterized by the presence of sparse hair (of scalp, eyelashes, and eyebrows) at birth. However, there is regrowth of hair (though coarse) during early childhood. But patients notice an eventual progressive loss of hair with age.
Hypotrichosis Symptoms
Sparse Body Hair:
As already mentioned, body hair is sparse. There are a few strands present on the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
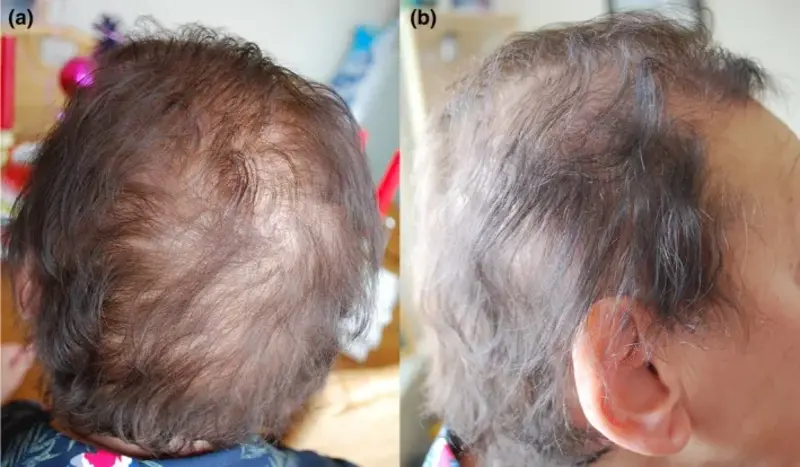
Hair Fragility:
The hair present on the scalp is fragile and prone to breaking. The hair shaft is abnormal and weak in such cases.3Olsen, E. A., & Iorizzo, M. (2019). Hair disorders. Harper’s textbook of pediatric dermatology, 2103-2138.
Light Hair Color:
Infants have light-colored hair. Studies show that the hair color of children is usually lighter than that of their unaffected peers.4Ahmed, A., Almohanna, H., Griggs, J., & Tosti, A. (2019). Genetic hair disorders: a review. Dermatology and therapy, 9, 421-448.
Skin Presentations:
In addition to low hair density, patients encounter skin issues like erythema (redness) and pruritus (itchiness).
Hypotrichosis Causes
Researchers believe that mutations in the following genes cause the hair disorder. The autosomal recessive type develops as a result of mutations in the following genes:
- LPAR6
- LIPH
- DSG4
These genes instruct proteins involved in hair follicle proliferation and differentiation. Mutations produce abnormal genes that can not properly support hair follicle development, leading to underdeveloped, woolly hair.
On the other hand, HSS arises primarily due to mutations in the LSS and CDSN genes. Other gene mutations that may be linked to hypotrichosis include:
- APCDD1
- KRT25
Risk Factors:
Exposure to negative environmental factors like harsh chemicals and UV radiation can increase your risk of experiencing hair fall. While genetics is the main cause of hypotrichosis, environmental factors can aggravate the condition.
Hypotrichosis Diagnosis
Doctors take a complete history of hair sparsity. As it is a congenital condition, patients present with hair problems since birth. Health professionals thoroughly examine the child’s hair strength, size, and color. The doctor may also look for signs of redness and itchy patches on the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Questions about the family history of baldness and hypotrichosis are crucial. Usually, genetic testing is done to reach a conclusive diagnosis of hypotrichosis.
Differential Diagnosis:
Hypotrichosis Vs Alopecia
Both conditions are similar in many ways. However, hypotrichosis is characterized by sparse hair due to a lack of healthy hair follicles, but alopecia is a condition of hair loss that can present with a complete absence of hair.
Hypotrichosis Treatment
There is no definitive cure for this genetic anomaly. However, certain strategies can help improve the hair density and volume. Dermatologists offer the following treatment plans for hypotrichosis:
Topical Minoxidil:
Minoxidil is a commonly used drug to treat hair loss. Multiple studies advocate the use of topical minoxidil in managing congenital hypotrichosis. In one study, topical 1% minoxidil improved hair growth in a family with multiple autosomal recessive hypotrichosis patients.5Taki, T., Tanahashi, K., Takeichi, T., Yoshikawa, T., Murase, Y., Sugiura, K., & Akiyama, M. (2020). Association of topical minoxidil with autosomal recessive woolly hair/hypotrichosis caused by LIPH pathogenic variants. JAMA dermatology, 156(10), 1132-1134. Astonishingly, when used in hypotrichosis-prevalent areas like Japan, minoxidil showed excellent results. 1% and 5% preparations of minoxidil significantly improved hair growth in hypotrichosis patients with LIPH mutations.6Tanahashi, K., Sugiura, K., & Akiyama, M. (2015). Topical minoxidil improves congenital hypotrichosis caused by LIPH mutations. British Journal of Dermatology, 173(3), 865-866.
Moreover, as per a 2025 study, the combination of minoxidil with botanical extracts results in significant hair growth in hypotrichosis simplex cases.7Zhuang, M., Xu, Y., Zhong, S., Tian, Z., Liu, Q., & Yang, D. (2025). Treatment of hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp with the combination of botanic extracts and minoxidil: a case report. Frontiers in Genetics, 15, 1491870.
Platelet-Rich Plasma:
PRP or platelet-rich plasma is being readily used in the field of healthcare because of its rejuvenating powers. This process of injecting the patient’s own plasma (with concentrated platelets and growth factor) into diseased areas boosts natural healing and has minimal to no side effects. PRP injection with 2% minoxidil has proven to be an effective treatment strategy for hypotrichosis. 8Ramadan, W. M., Hassan, A. M., El-Hawary, E. E., & Gomaa, N. S. (2023). Successful treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex by platelet rich plasma injection with topical minoxidil 2%. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 34(1), 2169575.
Isotretinoin:
It is a type of retinoid (derivative of vitamin A) medication used to treat acne. Its use in hair-related disorders is limited. However, a study showed that isotretinoin therapy induced long-lasting hair growth in cases with hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp. The vitamin A derivative was used after minoxidil application failed to provide permanent hair growth. Isotretinoin showed promising results and can be used as an effective modality in the future.9AlMudimeegh, A., & Nagshabandi, K. N. (2024). Isotretinoin-induced hair growth in a case of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp: A promising therapeutic approach. JAAD Case Reports, 51, 75-78.
Topical Gentamycin:
The application of this topical gentamycin can be a beneficial leap forward in the treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex (HSS). Modern research now focuses on the impact of topical gentamycin on hair growth and finds it as a potential therapeutic modality for HSS.10Peled, A., Samuelov, L., Sarig, O., Bochner, R., Malki, L., Pavlovsky, M., … & Sprecher, E. (2020). Treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp with topical gentamicin. British Journal of Dermatology, 183(1), 114-120.
Bimatoprost:
This medication is prescribed for eyelash hypotrichosis. The non-invasive treatment is effective in promoting eyebrow hair. The good thing is that the bimatoprost is well tolerated by patients.11Chanasumon, N., Sriphojanart, T., & Suchonwanit, P. (2018). Therapeutic potential of bimatoprost for the treatment of eyebrow hypotrichosis. Drug design, development and therapy, 365-372. Moreover, 0.03% ophthalmic solution of bimatoprost effectively enhances eyelash growth in patients. 12Fagien, S. (2015). Management of hypotrichosis of the eyelashes: focus on bimatoprost. Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing, 35(2), 82-91.
Hair transplant is the treatment of choice for patients who experience a complete loss of hair. ARWH has the potential to progress into alopecia. Therefore, skin/hair specialists transplant hair to improve patients’ appearance.
Wrapping Up
Hypotrichosis is a condition of sparse hair that is present at birth. It mainly affects the scalp, the eyebrows, and the eyelashes and is the result of genetic mutations (in the LIPH, LPAR6, LSS, and CDSN genes, etc.). There are three types of the condition, i.e., autosomal recessive, simplex type, and Marie Unna. Infants suffering from the condition have little hair that is weak, fragile, and of lighter color. Skin symptoms like erythema and pruritus may accompany hair fall. A confirmed diagnosis is made with genetic testing. There is no definitive treatment for the disorder. However, PRP therapy, topical minoxidil, topical gentamycin, isotretinoin, and bimatoprost application have shown superb results. Hypotrichosis can progress to alopecia (complete hair loss), for which doctors perform hair transplants.
Refrences
- 1Akiyama, M. (2021). Isolated autosomal recessive woolly hair/hypotrichosis: genetics, pathogenesis and therapies. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 35(9), 1788-1796.
- 2Kibtiar, M., Akther, R., Islam, M. M., & Rahman, S. A. (2019). Congenital hypotrichosis simplex: A case report. Bangladesh Journal of Child Health, 43(1), 59-61.
- 3Olsen, E. A., & Iorizzo, M. (2019). Hair disorders. Harper’s textbook of pediatric dermatology, 2103-2138.
- 4Ahmed, A., Almohanna, H., Griggs, J., & Tosti, A. (2019). Genetic hair disorders: a review. Dermatology and therapy, 9, 421-448.
- 5Taki, T., Tanahashi, K., Takeichi, T., Yoshikawa, T., Murase, Y., Sugiura, K., & Akiyama, M. (2020). Association of topical minoxidil with autosomal recessive woolly hair/hypotrichosis caused by LIPH pathogenic variants. JAMA dermatology, 156(10), 1132-1134.
- 6Tanahashi, K., Sugiura, K., & Akiyama, M. (2015). Topical minoxidil improves congenital hypotrichosis caused by LIPH mutations. British Journal of Dermatology, 173(3), 865-866.
- 7Zhuang, M., Xu, Y., Zhong, S., Tian, Z., Liu, Q., & Yang, D. (2025). Treatment of hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp with the combination of botanic extracts and minoxidil: a case report. Frontiers in Genetics, 15, 1491870.
- 8Ramadan, W. M., Hassan, A. M., El-Hawary, E. E., & Gomaa, N. S. (2023). Successful treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex by platelet rich plasma injection with topical minoxidil 2%. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 34(1), 2169575.
- 9AlMudimeegh, A., & Nagshabandi, K. N. (2024). Isotretinoin-induced hair growth in a case of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp: A promising therapeutic approach. JAAD Case Reports, 51, 75-78.
- 10Peled, A., Samuelov, L., Sarig, O., Bochner, R., Malki, L., Pavlovsky, M., … & Sprecher, E. (2020). Treatment of hereditary hypotrichosis simplex of the scalp with topical gentamicin. British Journal of Dermatology, 183(1), 114-120.
- 11Chanasumon, N., Sriphojanart, T., & Suchonwanit, P. (2018). Therapeutic potential of bimatoprost for the treatment of eyebrow hypotrichosis. Drug design, development and therapy, 365-372.
- 12Fagien, S. (2015). Management of hypotrichosis of the eyelashes: focus on bimatoprost. Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing, 35(2), 82-91.