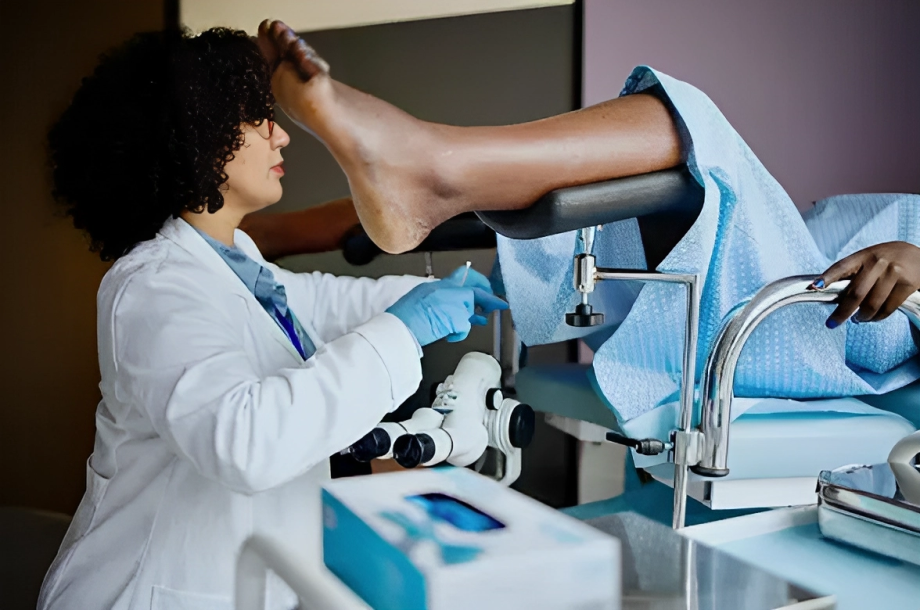
What is a Hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a medical procedure that allows the visualization of the interior of the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope. It is a tube-like device that has a light at the end and a camera to show a bigger picture of the uterus on a screen. The doctor carefully puts the hysteroscope into the vagina with a speculum. This procedure helps diagnose any issues in the uterus and endometrial cavity.1Petrozza, J. C., MD. (n.d.). Hysteroscopy: practice essentials, background, and history of the procedure. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/267021-overview#a6
What are the Indications of Hysteroscopy?
It is used for various diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes.
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy:
It is used to diagnose various problems of the uterine and endometrial cavity. These include:
1- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Abnormal uterine bleeding is an indication of hysteroscopy. Abnormal uterine bleeding includes bleeding more than regular days of your menstrual cycle, intermenstrual bleeding (bleeding between two menstrual cycles), or bleeding after intercourse. A doctor can diagnose the cause of AUB by using a hysteroscope. Causes of AUB can be fibroids, polyps, or endometriosis (It is the growth of abnormal tissue outside the lining of your uterus; this abnormal tissue resembles the tissue of the uterus)2Moore, J. F. (2023, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
2- Heavy Periods
Heavy periods are also known as menorrhagia. Basically, heavy periods are periods in which there is a need to change the tampon or pad every 1 to 2 hours, and you bleed for more than seven days. These symptoms may indicate the presence of any pathology. Certainly, it can diagnose the cause of heavy periods like fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease.
3- Repeated Miscarriages
Patients with recurrent miscarriages (loss of pregnancies) may have underlying diseases like uterine and cervical abnormalities. The hysteroscope visualizes structural abnormalities in the endometrial cavity that cause miscarriages. These structural abnormalities may include adhesions, endometriosis, or polyps. However, there are also other causes of repeated miscarriages, like chromosomal abnormalities.
4- Pelvic Pain
It helps in diagnosing the cause of acute or chronic pelvic pain. Pelvic pain occurs due to any urinary tract infection or gastrointestinal tract disease. These infections include urinary tract infections, appendicitis, kidney stones, or sexually transmitted diseases. Moreover, hysteroscopy also helps in diagnosing endometriosis or an ovarian cyst causing pelvic pain.
5- Fibroids or Polyps
A hysteroscopy can confirm the presence of fibroids and polyps. A doctor inserts the hysteroscope into the vagina, and the light source of a hysteroscope helps to visualize the uterine cavity.
Therapeutic Hysteroscopy:
Therapeutic hysteroscopy is used to treat certain problems of uterine and endometrial origin, and diagnostic hysteroscopy helps diagnose those diseases.
Indications of therapeutic hysteroscopy are:
1- Polyps
Polyps are outgrowths of tissue projecting from the mucosa. A doctor can diagnose the presence of uterine polyps and remove them using a hysteroscope. The procedure for removing polyps through hysteroscopy is known as hysteroscopic polypectomy.
2- Fibroids
A hysteroscopy can easily remove small fibroids present in the uterine cavity. This procedure is called hysteroscopic myomectomy.
3- Adhesions
The formation of scar tissue (adhesions) in the uterine cavity is called Asherman’s syndrome. Any previous surgery or pelvic infection forms adhesions in the uterus. Therefore, hysteroscopy helps to remove these adhesions.
4- Misplaced Intrauterine Device
Using Hysteroscopy, a doctor can visualize and remove a misplaced intrauterine device (IUD). This procedure is a viable option for IUD removal, even if you are pregnant.3Moore, J. F. (2023b, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
What to expect before Hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is typically scheduled in the first week after the cessation of bleeding for those with regular menstrual cycles to ensure optimal visibility inside the uterus. If you have irregular cycles, coordination with your surgeon will be necessary to determine the most suitable timing. However, the procedure can be performed at any time for individuals who have undergone menopause. Before undergoing a hysteroscopy, you can anticipate the following preparations:
1- Complete Medical History
Your doctor will take your recent medical and surgical history. If you’re taking anticoagulant drugs, the surgeon may advise you to discontinue them for a few weeks before the procedure.
Your doctor may inquire about various aspects, including:
- The normal duration of your menstrual cycle.
- Is there any history of irregular bleeding?
- Any history of previous surgery?
- Any history of pelvic infection?
- Is there a history of taking any vitamins or other supplements?
- Any history of pelvic or abdominal pain?
- What type of contraception method are you using?
- Is there a family history of any gynecological condition or cancer?
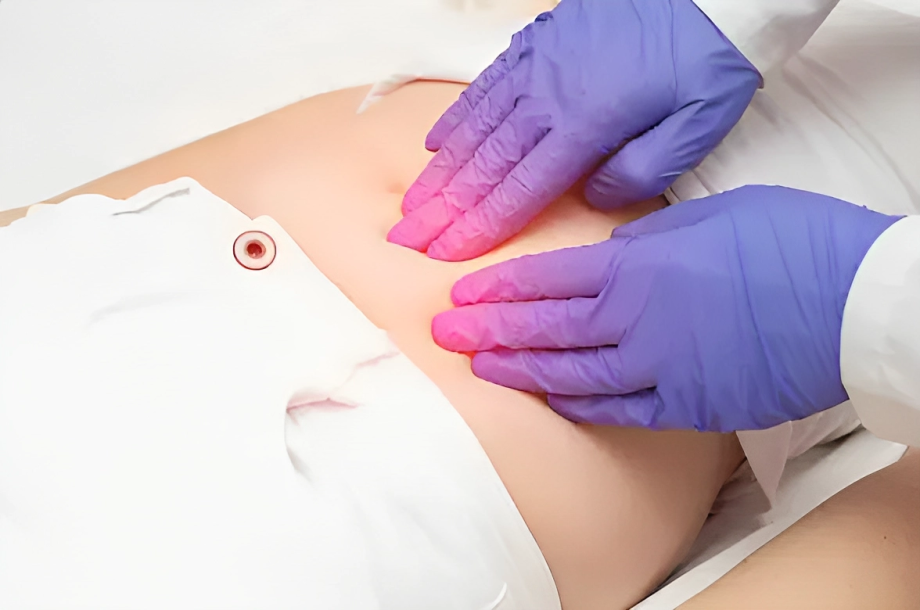
2- Abdominal and pelvic Examination
Although it is not necessary before doing hysteroscopy, your doctor may do an abdominal and pelvic examination to rule out any pathology if needed. A doctor may do superficial and deep palpation of the abdomen to rule out any gastrointestinal mass or disease. Furthermore, a doctor uses a speculum to do the necessary pelvic examination.
3- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
CBC provides basic knowledge of the patient’s condition, including information about hemoglobin levels. Your doctor may order a CBC if they have specific concerns or if there are reasons to assess your overall health, such as checking for anemia or other blood-related conditions.
4- Pregnancy Test
Your doctor will prescribe a pregnancy test, either a blood test or a urine test. This is important to ensure a safe procedure without any risk.
5- Pap-Smear
A doctor may use a pap smear to check for any cervical abnormality or cancer. A pap smear is important as injury can happen during the procedure.
6- Cervical Culture
Symptoms of vaginal discharge indicate the presence of an infection. Your doctor may take a cervical swab to do a cervical culture before doing a hysteroscopy.
7- Hysterosalpingogram
A doctor may do an HSG before hysteroscopy to confirm the presence of fibroids, polyps, or any other abnormality in the uterine cavity. A therapeutic hysteroscopy can remove any mass, like fibroids or polyps.4Petrozza, J. C., MD. (n.d.-b). Hysteroscopy WorkUp: laboratory studies, imaging studies, diagnostic procedures. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/267021-workup?form=fpf#c6
What is the Procedure of a Hysteroscopy?
Firstly, the patient is put into a lithotomy position, where a patient lies on their back with flexed hips and knees. The doctor may administer anesthesia or a sedative to help you relax. After that, the bladder is emptied using a catheter, and the cervix is dilated with a speculum. The hysteroscope is then carefully inserted into the uterine cavity, providing the surgeon with a real-time visual on a screen. The hysteroscope is equipped with a light source at one end and a camera at the other, and it can be either rigid or flexible.

A liquid solution, such as normal saline, is introduced into the uterine cavity through the hysteroscope to clear any blood or mucus. Surgical instruments are utilized to address issues like polyps and fibroids within the uterus.5Moore, J. F. (2023c, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
Is Hysteroscopy Painful?
The pain associated with hysteroscopy depends upon the individual’s capacity to bear it. Some women feel more pain than others, so you should inform your surgeon if you experience pain or severe irritation. In that case, your doctor will apply a numbing cream or local anesthetic on your cervix and vagina. If the hysteroscopy is therapeutic, like a hysteroscopy polypectomy or myomectomy, your doctor may offer you general anesthesia to avoid pain.6Pegoraro, A., Santos, M. E., Takamori, J. T., De Almeida Pereira De Carvalho, W., De Oliveira, R., Bianco, B., & Van Nimwegen, Â. (2019). Prevalence and intensity of pain during diagnostic hysteroscopy in women attending an infertility clinic: analysis of 489 cases. Einstein (São Paulo), 18. https://doi.org/10.31744/einstein_journal/2020ao4916
What are the Precautions of a Hysteroscopy?
After hysteroscopy, you don’t need extra precautions as it is a safe procedure. However, if therapeutic hysteroscopy involves general anesthesia, you may experience dizziness. In such cases, your doctor may advise staying in the recovery area for a few hours or even a day if necessary. It is normal to experience slight irritation and bleeding after the procedure. If you feel unwell, you can rest at home for a few days.
Also, maintain a healthy diet for a few days, and you can shower on the same day unless advised otherwise. Your doctor may instruct you to avoid sexual intercourse for a specified period after the procedure.7Pegoraro, A., Santos, M. E., Takamori, J. T., De Almeida Pereira De Carvalho, W., De Oliveira, R., Bianco, B., & Van Nimwegen, Â. (2019c). Prevalence and intensity of pain during diagnostic hysteroscopy in women attending an infertility clinic: analysis of 489 cases. Einstein (São Paulo), 18. https://doi.org/10.31744/einstein_journal/2020ao4916
What are the Benefits of a Hysteroscopy?
The benefits of hysteroscopy include the following:
- Safe to use due to fewer complications
- Less time taking (almost 30 minutes)
- For diagnostic hysteroscopy, there is no need for general anesthesia
- Patients typically recover within a few days after the procedure
- Hysteroscopy serves as a secure method for the removal of polyps and fibroids
What are the Complications of a Hysteroscopy?
Although it is a safe procedure, it still has some side effects.
These include:
Intraoperative Complications:
Uterine Perforation
Perforation of the uterus can occur if the procedure is not done accurately by the surgeon. The incidence of uterine perforation by hysteroscopy is about 0.8 to 1.5%, making it the most common complication of this process.8Elahmedawy, H., & Snook, N. J. (2021). Complications of operative hysteroscopy: an anesthetist’s perspective. BJA Education, 21(7), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjae.2021.03.001
Injury to your Bowel & Bladder
Injury to the bladder can lead to complications of the urinary tract, like urinary incontinence and urinary tract infections. Damage to the bowel can cause bowel perforation. That is why it is important to do a safe insertion of the hysteroscope inside the uterus to avoid these problems.
Reaction to the Distension Media
During this process, a fluid or a gas is used to distend the uterine cavity. Distension of the cavity gives a better image of the cavity. Sometimes, it can lead to fluid overload or hyponatremia.9Elahmedawy, H., & Snook, N. J. (2021b). Complications of operative hysteroscopy: an anesthetist’s perspective. BJA Education, 21(7), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjae.2021.03.001
Hemorrhage
Damage to the cervix, vagina, or uterine cavity during the insertion of hysteroscopy can cause hemorrhage, and in some cases, it can cause severe bleeding. This is also a common side effect of hysteroscopy.
Gas Embolism
The gas used to distend the uterine cavity during hysteroscopy is mainly carbon dioxide. However, in some cases, this gas enters into the vessels, causing embolism.10Moore, J. F. (2023, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide. was found in 34% of the patients.
Postoperative Complications:
Postoperative complications occur days, weeks, or years after the hysteroscopy. These include:
Infections
Infection of the cervix, vagina, or uterine cavity can occur. Symptoms of infection present a few days after the procedure. These are vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, or bleeding in some cases. The use of a sterile hysteroscope is necessary to avoid the risk of any infection.
Intrauterine Adhesions
The procedure can result in the formation of adhesions if any part of the genital tract sustains damage. Adhesions typically develop a few days or weeks after the procedure. A skilled surgeon should perform this procedure to mitigate the risk of complications.
Formation of Hematometra
Hematometra is the accumulation of blood inside the uterus. Improperly performed procedures can cause injury to the uterine cavity and lead to the accumulation of blood.
What are the Contraindications of Hysteroscopy?
Following are a few contraindications:
- Ongoing pelvic infection
- Pregnancy (although safe for removing IUD or retained products of conception)
- Vaginal bleeding
- Cervical cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Active genital herpes
- Lack of appropriate equipment
- Lack of informed consent
What is the Prognosis of a Hysteroscopy?
The prognosis of hysteroscopy is good as it is a safe procedure. The risk associated with diagnostic hysteroscopy is 0.28%, and the risk of therapeutic hysteroscopy is 0.22 %.11The use of hysteroscopy to diagnose and treat intrauterine pathology. (n.d.). ACOG. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2020/03/the-use-of-hysteroscopy-for-the-diagnosis-and-treatment-of-intrauterine-pathology
Is Hysteroscopy and D&C the same?
No, they are distinct procedures. Dilation and Curettage (D&C) are utilized to remove retained products of conception from the uterus, and a sample may be taken using a spoon-shaped instrument. On the other hand, hysteroscopy involves the insertion of a hysteroscope through the cervix, allowing the doctor to visualize the uterine cavity and diagnose any pathology.
What is MyoSure Hysteroscopy?
MyoSure is a compact, telescope-like device doctors utilize for a hysteroscopic procedure. The device is carefully placed into the uterine cavity by inserting a hysteroscope. MyoSure is designed to visualize and safely remove small polyps and fibroids from the uterus.
This procedure is relatively safe when compared to alternative gynecological interventions. The MyoSure hysteroscopy typically takes approximately 15 to 20 minutes to efficiently remove any identified abnormal tissue.12Yong, J., Guo, X., Lan, H., Yuan, J., Zeng, D., Zeng, X., Yi, S., & Xiao, S. (2021). Clinical analysis of the MyoSure hysteroscopic tissue removal system of endometrial polyps in women with an intact hymen. BMC Women’s Health, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-021-01362-w
When should you see a Doctor after a Hysteroscopy?
A scheduled visit is not necessary unless advised by your healthcare provider. However, if you notice the following symptoms after hysteroscopy, consult your doctor immediately:
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Fever
Conclusion
In conclusion, doctors employ hysteroscopy for both the diagnosis and treatment of uterine diseases, particularly addressing fibroids and polyps. If you are experiencing the gynecological issues mentioned above, consulting with a surgeon is advisable for proper evaluation and guidance.
Refrences
- 1Petrozza, J. C., MD. (n.d.). Hysteroscopy: practice essentials, background, and history of the procedure. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/267021-overview#a6
- 2Moore, J. F. (2023, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
- 3Moore, J. F. (2023b, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
- 4Petrozza, J. C., MD. (n.d.-b). Hysteroscopy WorkUp: laboratory studies, imaging studies, diagnostic procedures. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/267021-workup?form=fpf#c6
- 5Moore, J. F. (2023c, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide.
- 6Pegoraro, A., Santos, M. E., Takamori, J. T., De Almeida Pereira De Carvalho, W., De Oliveira, R., Bianco, B., & Van Nimwegen, Â. (2019). Prevalence and intensity of pain during diagnostic hysteroscopy in women attending an infertility clinic: analysis of 489 cases. Einstein (São Paulo), 18. https://doi.org/10.31744/einstein_journal/2020ao4916
- 7Pegoraro, A., Santos, M. E., Takamori, J. T., De Almeida Pereira De Carvalho, W., De Oliveira, R., Bianco, B., & Van Nimwegen, Â. (2019c). Prevalence and intensity of pain during diagnostic hysteroscopy in women attending an infertility clinic: analysis of 489 cases. Einstein (São Paulo), 18. https://doi.org/10.31744/einstein_journal/2020ao4916
- 8Elahmedawy, H., & Snook, N. J. (2021). Complications of operative hysteroscopy: an anesthetist’s perspective. BJA Education, 21(7), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjae.2021.03.001
- 9Elahmedawy, H., & Snook, N. J. (2021b). Complications of operative hysteroscopy: an anesthetist’s perspective. BJA Education, 21(7), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjae.2021.03.001
- 10Moore, J. F. (2023, July 18). Hysteroscopy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564345/#:~:text=Hysteroscopy%20can%20result%20in%20carbon,the%20use%20of%20carbon%20dioxide. was found in 34% of the patients.
- 11The use of hysteroscopy to diagnose and treat intrauterine pathology. (n.d.). ACOG. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2020/03/the-use-of-hysteroscopy-for-the-diagnosis-and-treatment-of-intrauterine-pathology
- 12Yong, J., Guo, X., Lan, H., Yuan, J., Zeng, D., Zeng, X., Yi, S., & Xiao, S. (2021). Clinical analysis of the MyoSure hysteroscopic tissue removal system of endometrial polyps in women with an intact hymen. BMC Women’s Health, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-021-01362-w