Acne conglobata (AC) is a severe form of acne that disfigures the face. It is characterized by the formation of multiple extensive inflammatory papules, interconnecting pustules, multiple Polyporus comedones (black and white), cysts, and nodules on the face. This condition also involves the formation of multiple sinuses in the skin that contain serosanguineous fluid or pus.
What is Acne Conglobata?
Acne Conglobata is a rare inflammatory skin pathology in which painful cysts and nodules begin to form deeper below the skin. It is a form of nodulocystic acne that usually affects the face, neck, shoulders, thighs, and back.
Acne conglobata is a chronic inflammatory disorder that disfigures the face by forming a large number of cysts and nodules followed by multiple deep-pitted scars or hypertrophic keloid scars. It also causes cosmetic and psychological impairment.
Moreover, it occurs due to the worsening of acne vulgaris and can also occur due to the recrudescence of acne that remains dormant for many years.1Acne conglobata. (2024, January 1). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29083736/#:~:text=Acne%20conglobata%20(AC)%20is%20a,arms%2C%20buttocks%2C%20and%20thighs.
How Common is Acne Conglobata?
Acne conglobata is an uncommon disease. It usually affects people in puberty and can also occur late. The onset of this disease occurs between 18-30 years. It can also affect infants. It targets males more than females.2Hafsi, W., Arnold, D. L., & Kassardjian, M. (2023, June 1). Acne conglobata. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459219/
Causes of Acne Conglobata
The primary cause of acne conglobata is unknown. However, multiple factors can cause acne conglobata. These factors are the following:
Increase Sebum Production (Hormone-Induced)
Sebaceous glands are sensitive to androgen hormone secretion. These hormones are testosterone, 5-alpha dihydrotestosterone (5-alpha DHT), and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). The receptors of these hormones are present in sebaceous glands and the outer sheath of the hair follicles.
A high level of these hormones in your body triggers the receptors in sebaceous glands, causing excessive sebum production. This excessive sebum mixes with the dead cells of your skin and forms a plug, resulting in acne breakouts.
Hypercornification of Follicular Cells
Hypercornification can also occur due to high sebum and is associated with ductal hyperproliferation. It is an early feature of acne. It causes the formation of comedones that can be open or closed.
Open Comedones
These comedones are also known as blackheads. In them, the hyperkeratotic plug, which looks like a macule, is formed at the skin’s level.
Closed Comedones
Closed comedones are also named as white heads. It occurs due to the formation of a plug below the skin surface.3Silcock F. A. (1937). Acne Conglobata. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine, 31(2), 82–84.
Inflammation
Inflammation can occur due to the formation of keratin plugs. Chemicals and a low level of linoleic acid form keratin plugs. Due to the formation of the plug, sebum can not be secreted and induces inflammation that causes acne.
Increase Colonization of Bacteria
Bacteria are present on your skin and help combat foreign organisms. However, the colonization of bacteria on your skin causes acne. The most common bacteria involved in causing acne is propionibacterium. This bacteria is present deep inside the follicle and causes acne.
Genetics
Familial cases of acne conglobata have also been reported as being linked with chromosome 15q24-26 in the region of IL-16 and CRABP1 gene.
Predisposing Factors
Factors that cause or trigger the AC are called predisposing factors. These include:
- High level of testosterone in your body
- Anabolic steroids abuse
- Testosterone withdrawal
- Androgen secreting tumors
- Exposure to aromatic hydrocarbons and halogens
- Ingestion of thyroid medications
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Hidradenitis suppurativa4Mph, R. a. S. M. (n.d.). Acne conglobata differential diagnoses. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1072716-differential#1?form=fpf
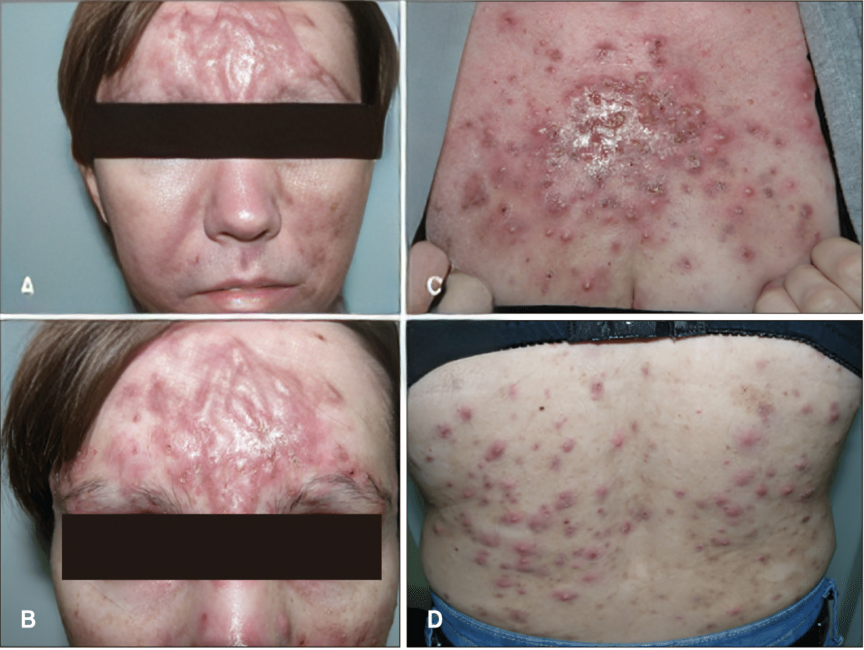
Symptoms of Acne Conglobata
The clinical features of acne conglobata depend upon the severity of the location. It usually affects the face, arm, shoulder, and thighs. The symptoms include:5Palmer, A. (2024, January 26). How to identify and treat acne conglobata. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/acne-conglobata-overview-4158219
- Multiple tender cysts and nodules in line that cause disfigurement
- Interconnecting pustules with sinuses
- Tenders Comedones with multiple openings
- Foul, smelly discharge from the sinuses
- Deep pitted scars or keloid formation
- Crusting of broken or inflamed tissues
How to Diagnose Acne Conglobata?
The diagnosis of acne conglobata is usually clinical. However, if the discharge is coming out through the pustules or nodules, then sensitivity and culture of the pus are advised. Start the antibiotics straight away; do not wait for the culture report.
Your doctor may advise you to have a skin biopsy if there is a suspicion of squamous cell carcinoma and to rule out other skin pathologies.6Gerd Plewig, & Kligman, A. M. (1975). Acne Conglobata. Springer EBooks, 168–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-96246-2_11
How to Treat Acne Conglobata?
The treatment of acne conglobata is mainly systemic, but your dermatologist can advise some topical agents as an adjunct. It includes:
Retinoids & Steroids
Retinoids are the treatment of choice for acne conglobata. Depending on the patient’s condition, treatment lasts 20-30 weeks or longer.
Prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day) is given with retinoids in case of acne flares or when there are systemic manifestations. Steroids are effective in treating acne conglobata. If acne flares occur after treatment with isotretinoin, it should be stopped, and prednisolone (1 mg/kg) should be continued (1 mg/kg) for 2-4 weeks.
Topical therapy with retinoids is not as effective as systemic therapy. However, it is critical to note that isotretinoin is unsuitable for pregnant women due to its teratogenic effects.
Minocycline & Doxycycline
These antibiotics (doxy and minocycline 100mg) are also used to treat acne but are not advised in combination with isotretinoin because they can cause pseudotumor cerebri.
Azithromycin
Azithromycin can also treat acne conglobata. Your doctor can advise you to use this antibiotic with a combination of isotretinoin.
Dapsone
If the above treatment fails, then your dermatologist may advise dapsone at a dose of 50-150 mg daily. However, lab monitoring is necessary because it causes methemoglobinemia, agranulocytosis, and G6PD deficiency.
TNF-Alpha Therapy
TNF-alpha therapy with infliximab and etanercept can be given in unresponsive patients. According to reports, there are also some positive responses in patients.
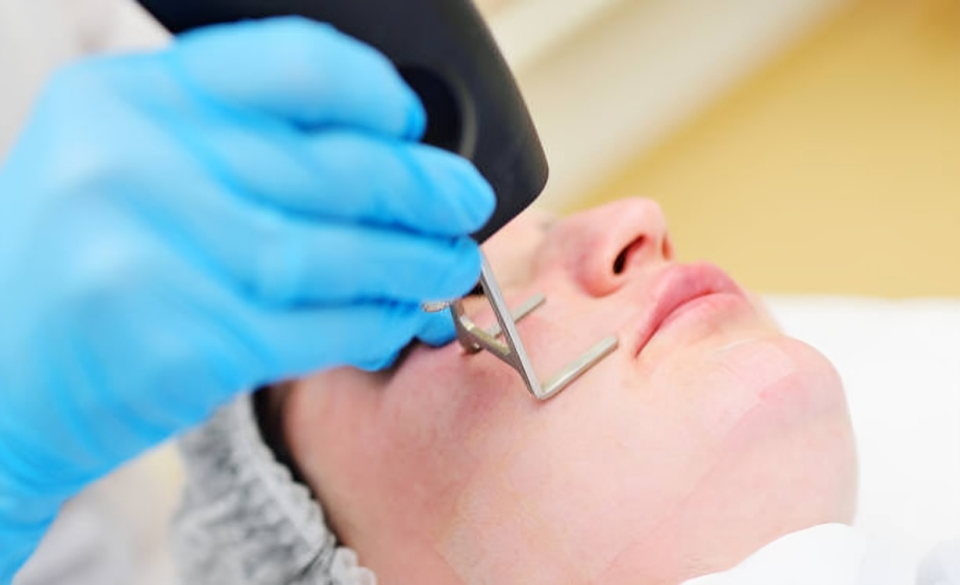
Laser Therapy
Lasers show significant improvement in patients with acne conglobata. Laser therapy includes:
- Fractional laser
- Ablative carbon dioxide laser
- YAG laser
- Vascular laser
In severe cases where medical and physical therapy fails to treat acne, your doctor may advise external beam radiation therapy.
Surgery
Surgery is the last option for patients. It is preferable when the nodules are hard, fluctuating, and contain pus or fluid. In surgery, your doctor will aspirate these nodules with a needle.
Intralesional injection with triamcinolone can also help reduce the lesions’ size. Cryotherapy can also help to treat the lesions. Afterwards, your doctor will excise these nodules surgically.
Postoperative recurrence can occur in some cases; therefore, surgical and medical therapy are combined to avoid recurrence.
Physical Modalities to Treat Acne
Some physical modalities can also treat acne conglobata. These are:
- Intralesional corticosteroid injection
- Chemotherapy
- Laser therapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Dermabrasion
- Fillers
- Chemical peeling
Alternative Treatment
Some Chinese therapies can treat acne conglobata. The Chinese author reported that the acupuncture technique with ventouse and cupping effectively reduced the level of IL-6 (pro-inflammatory cytokine). The acupuncture effect in lowering IL-6 levels is greater than isotretinoin level.7Canpolat, F., Kurmuş, G. I., & Gönül, M. (2018). Acne conglobata. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324532340_Acne_Conglobata
How To Treat Scars Of Acne Conglobata?
Acne conglobata disfigures the face. When large nodulocystic acne heals, it leaves a large, deep, pitted scar or keloid on the face. Skin grafting can also be suitable for treating deep scars.
Your doctor may inject fillers in the area of scars to fill these scars and give your skin a smoother look. Triamcinolone injection is suitable for large and pitted scars.
Your dermatologist may advise surgical excision to treat the big scar. In this procedure, your doctor will cut the scars surgically and suture them together.
How To Prevent Acne?
Besides medical treatment, preventive measures can also help with acne conglobata. These preventive measures include:
- Wash your face three times a day with good soap or face wash
- Avoid using products that your doctor does not recommend
- Remove your makeup before going to bed
- Avoid picking or touching your skin
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid eating spicy and high-sugar diets

Prognosis of Acne Conglobata
Acne conglobata is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder. Therefore, it takes time to heal and form a deep, pitted scar that causes disfigurement. Severe disfigurement can affect your daily lifestyle and cause psychological impairment. It is also responsible for anxiety and depression in multiple patients.
Squamous cell carcinoma is a rare complication of AC with a poor prognosis.8Camisa C. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in acne conglobata. Cutis. 1984 Feb;33(2):185-7, 190. PMID: 6230214. Therefore, patients with severe acne conglobata need careful monitoring.
What type of food aggravates my Acne?
Research suggests that some foods contribute to acne breakouts. These are:
High Sugar Diet
If you consume too many carbohydrates and have oily skin, you might have acne. A high-carbohydrate diet increases glucose levels in your body, resulting in insulin production. Androgen hormones are sensitive to insulin. Therefore, too much insulin increases your androgen secretion, which causes acne. A high-sugar or carbohydrate diet includes chocolates, beverages, cane sugar, and honey.
Spicy Foods
Acne eruption is mainly linked to spicy, high-calorie, and fatty foods. The exact mechanism of this food is unknown, but it is reported that spicy food alters hormone levels, which causes acne. Spicy foods include burgers, nuggets, hot dogs, French fries, pizzas, and pasta.
Whey Protein Powder
Most people nowadays use whey protein to meet their protein requirements. According to research studies, the amino acids in whey protein can change skin cells and contribute to acne.
What type of food can I eat if I have acne?
Some foods make your skin clear and acne-free. These foods are:
Probiotics
Gut microbes may also contribute to your acne. Therefore, using probiotics can reduce your acne problems because probiotics make your gut healthy and help reduce inflammation.
Omega-3-Fatty Acids
Some studies report that omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that reduce skin inflammation and acne eruption.
Green Tea
Green tea contains polyphenols that have anti-sebum properties. Excessive sebum production causes acne, and green tea helps control and reduce sebum.
Multivitamins
Multivitamins like vitamins A, D, E, and zinc help nourish skin. Retinoic acid, a vitamin A derivative, treats acne vulgaris.
Turmeric
Turmeric is also an anti-inflammatory agent that can regulate the insulin level in your body. It lowers your body’s insulin level and helps reduce your acne.
Vegetable Diet
A high-vegetable diet can effectively reduce acne. Therefore, if you have acne-prone skin, follow a vegetarian diet.
Acne Conglobata Vs. Acne Fulminans
Acne conglobata is a severe inflammatory disorder that manifests as multiple erythematous papules, polyporus comedones, tender nodules, and pustules. Its systemic features are rare.
However, acne fulminans is a severe and destructive form of acne that primarily affects adult males. It usually involves the trunk but can also involve the face. It presents with the formation of crusted ulcerative lesions on the face, along with fever, muscle pain, and bone pain.
Acne Conglobata Vs. Sweating
Acne conglobata is a severe form of acne in which the sebaceous glands produce more sebum. You may confuse sebum with sweating. Sweating is the secretion of waste products from your body’s sweat glands, not from sebaceous glands. Sweat contains salt, while sebum contains fat.
Conclusion
To conclude, this is a severe form of acne that causes disfigurement of your skin.
It presents as pitted scars, pustules, foul-smelling discharge from sinuses, tender cysts, and broken or inflamed tissues. It tends to leave scars on your skin. Multiple treatment options include medical treatments, lasers like fractional and YAG lasers, and physical modalities as described above. Your doctor may advise a skin graft for deep pitted scars with skin disfigurement. A good skincare routine can prevent advanced stages of acne conglobata.
Refrences
- 1Acne conglobata. (2024, January 1). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29083736/#:~:text=Acne%20conglobata%20(AC)%20is%20a,arms%2C%20buttocks%2C%20and%20thighs.
- 2Hafsi, W., Arnold, D. L., & Kassardjian, M. (2023, June 1). Acne conglobata. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459219/
- 3Silcock F. A. (1937). Acne Conglobata. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine, 31(2), 82–84.
- 4Mph, R. a. S. M. (n.d.). Acne conglobata differential diagnoses. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1072716-differential#1?form=fpf
- 5Palmer, A. (2024, January 26). How to identify and treat acne conglobata. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/acne-conglobata-overview-4158219
- 6Gerd Plewig, & Kligman, A. M. (1975). Acne Conglobata. Springer EBooks, 168–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-96246-2_11
- 7Canpolat, F., Kurmuş, G. I., & Gönül, M. (2018). Acne conglobata. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324532340_Acne_Conglobata
- 8Camisa C. Squamous cell carcinoma arising in acne conglobata. Cutis. 1984 Feb;33(2):185-7, 190. PMID: 6230214.

