Jaw clicking or popping, also known as temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJD), is a crepitus or jaw clicking and cracking sound produced during jaw movement. The temporomandibular joint is one of the most commonly used joints of the orofacial region in speaking, eating or chewing, singing, and yawning. You can feel jaw-clicking or popping with all of these movements. It is usually associated with painful sensations.
Jaw clicking is the 2nd most common joint disorder after lower back pain. It can occur at any age, but the peak incidence of this disorder is about 20-40 years. Women are affected more than men. 60 to 70% of people have jaw clicking, and about 5 to 12% of the patients report to clinical settings and require definite treatment. 1Maini, K. (2023, January 30). Temporomandibular Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551612/
This blog will discuss signs and symptoms, causes and risk factors, diagnostic tests, and treatment options for jaw clicking. Let’s get straight into the details of jaw-popping!
Signs & Symptoms of Jaw-Clicking
Jaw popping is asymptomatic in some people but can be painful in severe cases. The most common signs and symptoms of jaw clicking are:
- Pain during movement of the jaw
- Crepitus or clicking sound on opening or closing the mouth
- Facial tenderness and swelling
- Ear aches
- Difficulty eating
- Toothaches
- Difficulty opening the mouth wide open
- Pain in neck
- Discomfort
- Headaches
- Ringing in the ears
- Dizziness, hearing loss
Causes & Risk Factors of Jaw-Clicking
Jaw clicking usually occurs due to temporomandibular joint disorders. According to the National Institute of Dental and craniofacial research, jaw clicking is more common in females than males. 2TMD (Temporomandibular Disorders). (n.d.). National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/tmd
The etiology of this disease is not well understood, but several risk factors contribute to temporomandibular joint problems. These factors include:
- Arthritis (degenerative bone disease)
- Bruxism (the phenomenon of clenching and grinding teeth, especially during sleep)
- Malpresentation of your teeth
- Mayo facial problems
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Psychological stress
- Tumors
- Infections
- Trauma
- Positive family history
- Injury to the jaw or facial trauma
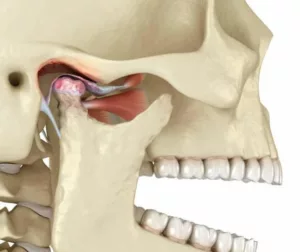
How Is Jaw-Clicking Diagnosed?
Jaw popping or jaw clicking is diagnosed clinically by history, examination, psychological, and radiological assessments.
History and Physical Examination
Your doctor may ask you about the onset of pain, location of pain, aggravating or relieving factors, nature of pain (whether it radiates to other parts of the body), past medical and family history, treatment history, and history of any other joint disorder.
During a physical examination, your doctor may ask you to perform various jaw movements to assess the severity of the disease.
Psychological Assessment
Your physician may ask questions about psychological or emotional stress. Chronic stress and other mental health problems are risk factors for jaw clicking.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging for jaw clicking or temporomandibular joint disorder include X-ray, CT scan, Ultrasound screening, and MR imaging. MR imaging is the modality of choice for jaw clicking.
When to See Your Doctor for Jaw-Clicking?
It is not an alarming condition. In case of severe pain, you may need to visit a hospital on an emergency basis. If you observe the following symptoms, book an appointment with your doctor:
- Persistent pain on opening and closing of the mouth
- Tenderness over the affected area
- Swelling
- Trouble eating and breathing
- Radiating pain in your ears
- Jaw-clicking associated with headache
- Jaw locking
How Can You Fix or Prevent Jaw-Clicking?
First, conservative management at home is used to overcome it. 50-90% of cases show an improvement with conservative management. In asymptomatic cases, reassurance and patient education play a critical role. Your doctor may guide you about jaw relaxing exercises, jaw strengthening exercises, and jaw massage techniques. You can fix jaw clicking with the following measures:
- Improving your head posture
- Eating soft diet
- Jaw relaxing exercises exercises
- Jaw strengthening exercises
- Jaw massage, intra-oral and external massage
- Warm or cold compresses on the affected area
- Stretching
- Acupuncture (needling)
- By using splints
Which Exercises Reduce Jaw-Clicking?
Sparing 2-5 minutes daily to do the following exercises can help reduce the pain and overall symptoms:
Jaw Relaxing Technique
In this exercise, you must close your mouth by touching your teeth ( upper and lower), not clenching. After this, relax your jaw muscles, touch your tongue to the floor ( hard palate of your mouth), and move it forward behind your upper teeth and backward towards your soft palate.
In an active manner, continuously touch your tongue to your soft palate while slowly opening your mouth, causing the tongue to move away from the soft palate. Keep it up for 5 seconds and repeat the same exercise.
Chin Tucks
Maintain your posture, move your chin downwards, and touch it to your neck, creating a double chin.
Jaw-Strengthening
In this exercise, you must resist jaw movement by applying force with your hand. Place your hand on the jaw and apply force inward while moving your jaw outward. (resist opening and closing movement of the mouth)
Repeat these exercises daily for 2-3 weeks, and you are going to be click-free. During these exercises, follow these precautions for better results:
- Do not clench your teeth
- Do not bite your nails
- Do not bite your lips
- Make sure that your upper and lower teeth are apart during rest
- Do not cross your exercise limits
Pharmacological Approach to Treat Jaw-Clicking
When conservative measures fail, healthcare professionals consider the pharmacological approach an alternative. The drug of choice to treat this pain is Non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They alleviate pain and reduce the severity of symptoms. 3Maini, K. (2023b, January 30). Temporomandibular Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551612/
Benzodiazepines also help in treating severe pain due to muscular spasms (bruxism). Tricyclic antidepressants are given in severe conditions when the muscle and nerves are involved. They also manage jaw clicking due to chronic stress.
Surgical or Invasive Approaches
Surgical approaches or invasive techniques are used when all treatment modalities fail to treat it. The surgical procedure involved in the management of jaw popping is:
Steroids Injections
Intra-articular steroid injections treat the temporomandibular joint disorder. The use of steroids should not be more than one week because they can destroy the cartilage. Intra-articular steroid injection at the affected site alleviates the symptoms of TMJ disorders. Steroids resemble cortisol in nature which is a hormone released by the adrenal glands. Steroids act as immunosuppressive agents. It blocks the activity of phospholipase A2, thus declining the production of leukotrienes and prostaglandins that acts as inflammatory marker.
Botulinum Toxin
In treating severe muscle spasms in bruxism, healthcare providers utilize botulinum toxins as trigger point injections. Botulinum toxin is a biological drug that halts the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in maintaining the activity of skeletal muscle. This toxin is used to treat hyperactivity disorders such as temporomandibular joint disorders.
Radio Wave Therapy
In this procedure, healthcare providers actively use a beam of waves to increase blood supply to the affected area and alleviate pain severity. Radio waves are bombarded from outside at the trigger area. These waves stimulate joint activity and increase blood flow toward the affected area, which alleviates the pain sensation.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Test
This procedure uses an electrical impulse to relax the affected muscle by releasing endorphins that reduce pain severity. The transcutaneous nerve stimulation test is a treatment modality that alleviates the pain of TMJ disorder. A controlled exposure to electrical impulses is given from outside to the affected area, which relaxes the hyperactivity of the muscles and alleviates the pain.
Conclusion
Jaw-clicking is a temporomandibular joint disorder. The temporomandibular joint is characterized by a clicking sound when moving, jaw pain, facial swelling, and, in severe cases, jaw locking. If you have these symptoms, consult your physician for detailed examination, diagnosis, and treatment. Performing jaw-strengthening exercises helps reduce the severity of the disease. Surgical interventions are used to resist it.
Refrences
- 1Maini, K. (2023, January 30). Temporomandibular Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551612/
- 2TMD (Temporomandibular Disorders). (n.d.). National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/health-info/tmd
- 3Maini, K. (2023b, January 30). Temporomandibular Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551612/

