Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), also known as follicular unit excision, is a minimally invasive hair restoration surgery. In this method, surgeons individually extract hair follicles from the scalp. They then move the extracted follicles to areas of the body where hair is thinner or absent. Typically, they harvest hair follicles from the sides and back of the scalp, although they can also extract them from the beard and other body parts.
It is usually a labor-intensive method that allows patients to keep their donor hair short without visible scarring. Surgeons use micro punches to extract and move a hair follicle. These micro punches range from 0.7 to 1.2 mm in size to get the follicular units. They also vary in their types, named robotic, motorized, and manual micro punches.1Garg, A. K., & Garg, S. (2018). Donor harvesting: follicular unit excision. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery, 11(4), 195-201.
History of FUE
A Japanese doctor, Shoji Okuda, did the first hair transplant in 1937. Then, the era of FUE began with the work of various hair surgeons, including Cole, Rassman, Rose, and Harris. But William Rassman, in 2002, coined the term FUE. Over the past 22 years, automated devices have greatly evolved to assist surgeons. Now, AI is also used for FUE.2Bansod, S., Kerure, A., Rohatgi, S., & Bilewar, U. (2021). History of follicular unit excision. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, 87(2), 315-318.
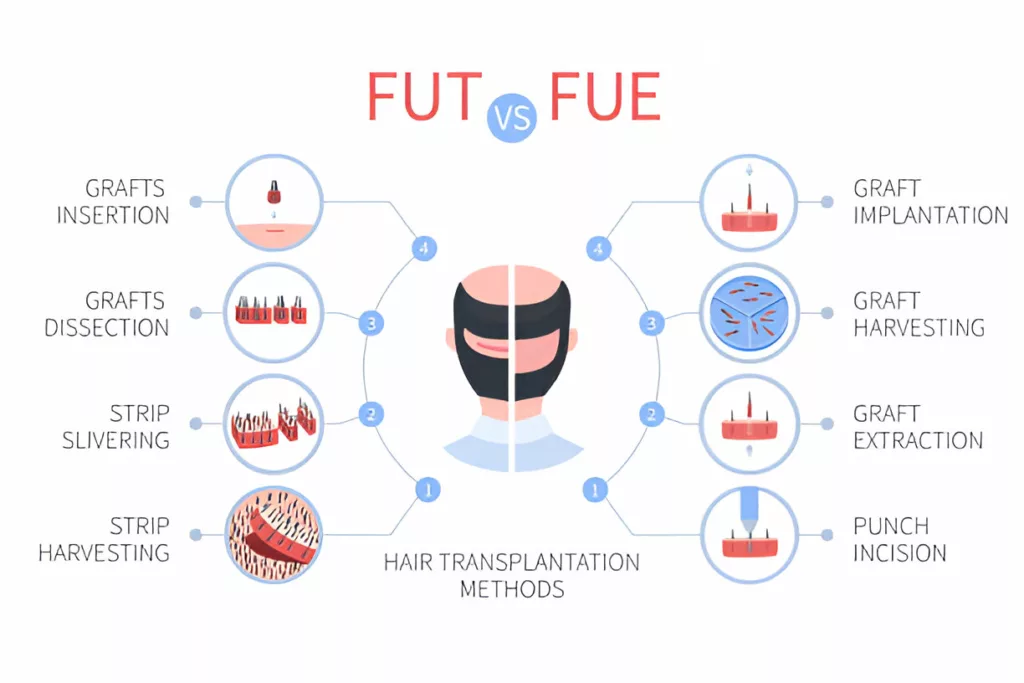
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) Vs. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
There are many differences between FUE and FUT.3DR. THOMAS BELL, M. (2024). Comparing FUE Vs. FUT Hair Transplants. https://torontoplasticsurgeon.com/blog/fue-vs-fut#:~:text=With%20a%20FUT%20hair%20transplant,an%20FUE%20transplant%20will%20look However, every surgeon prefers either one of them or both methods based on the individual case.
| Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) | Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) | |
| Extraction Method | In FUT, the surgeons remove a strip of the scalp, usually from the back of the patient’s head. | In FUE, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the scalp. |
| Surgical Technique | The area from which the strip is removed requires stitches to close it. The surgeons then separate the strip of the scalp into smaller pieces to isolate the hair follicles. | The extraction of hair follicles during FUE results in far more minimal scarring. |
| Graft Preparation | The smaller pieces are grafts. The surgeons separate the original strip of the scalp into thousands of grafts. | Each graft is extracted individually and prepared for implantation. |
| Implantation | For their next step, the surgeons need a blade or needle and a microscope. Using these things, the surgeons make very small holes in the scalp of the patient. Then, they insert hair follicles into the holes at the donor site. | Grafts are placed into the recipient sites without creating large incisions. |
| Scarring | Removing the hair strip from the back of the head results in a linear scar. | The scar resulting from the FUE hair transplant looks like very small dots. |
| Hair Length Consideration | People who have had a FUT transplant usually wish to grow their hair longer so that the longer hairs can cover the linear scars of the treatment. | Patients can keep their hair short without worrying about scars. |
| Time Requirement | A FUT transplant generally takes much less time than an FUE transplant. Time also depends on the patient and the amount of overall transplanted hairs. | Usually, it takes longer due to the individual extraction process. |
| Recommended For | Surgeons recommend FUT to those who want to achieve maximum fullness from the treatment process. | Suitable for those preferring minimal scarring. |
| Anesthesia | The patient requires local anesthesia to perform this entire process. | It also requires Local anesthesia. |
| Post-Procedure Care | The surgical site is then covered with gauze or bandages. | The surgical site is similarly covered for protection. |
Follicular Unit Extraction Machine
The surgical instrument for a FUE is a hollow, sharp instrument. Its design allows it to cut the skin around the follicular unit (FU). The following are some FUE instruments used for this procedure.
Manual Punch
It is a circular hollow scalpel. It has a diameter of 0.7 to 1.0 mm. The provider places this punch on the visible part of the FU hairs and then presses it downward with manual rotation. This will cut the dermis around the FU hairs and free it from the surrounding tissue. FUs are then extracted with forceps.
The manual FUE instruments have now been converted into mechanized components.
The SAFE System
It is a three-step manual processor. It reduces the potential for transections (unintentionally cutting hair follicles during the extraction). This system uses a piercing circular punch to cut the skin. After that, a blunted circular punch loosens the FU from its adjoining tissue. This step reduces the potential for sharp transection. The extraction of FU is the third step.
Powered SafeScribe
It is a handheld motorized device. It helps in making an appropriate selection of punches to extract the FUs. This requires the least potential for transection. SafeScribe then delivers the extracted FUs for transplantation. A variety of punch types and sizes are available. The hair restoration specialists select them according to the procedure. SafeScribe can decrease the time of FU extraction periods. It also reduces scarring. It provides undamaged FUs at a high rate.
RotoCore
This device automatically rotates the FUE sharp punch incision, relieving the physician from the need to physically move the punch. This gadget makes circular incisions around the FU. RotoCore also permits the physician to preset the punch to cut to a designated depth.
The Feller FUE
The Feller FUE pools the whole procedure into a single gadget. It means isolation, incision, and extraction through one gadget. This tool is designed to help the physician more efficiently. This will help make the work faster and more efficient.
Cole Isolation Technique
It is also known as the Follicular Isolation Technique. This technique involves the isolation and extraction of a selective FU. It improves the efficiency of the physician. In skilled hands, it increases FU harvesting in a session.
NeoGraft
The design of this mechanical device enhances the speed and efficiency of the physician. Hence, the speed of extraction and incision of FUs increases. This machine provides a rotary piercing punch to pick the skin. A suction device extracts the FUs and moves them to a collection tray. This tray can hold up to 50 FUs for transplantation.
ARTAS System
This is the most computerized FUE device. It is a complete robotic device that harvests FUs for hair restoration. Restoration Robotics, Inc. developed this device for use in surgery. This device also helped with male pattern balding. This system is run under the control of a physician. The physician uses an image-guided and computer-assisted robotic arm. This arm is equipped with Powered SafeScribe tiny punches in addition to an air suction unit. It is efficient enough to harvest one thousand FUs in one hour.4Devroye, J. (2021). U.S. Patent No. 11,071,563. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Procedure of FUE
As mentioned earlier, FUE is a sutureless method of hair restoration. This procedure requires the extraction of follicles from the back of the head. Extraction requires special micro punches and local anesthesia.
The healthcare provider shaves the donor area from the sides and back of the head to 1-2 mm in length. For this purpose, the patient lies in the inclined position on the operating table. At first, the doctor administers xylocaine, 1% diluted with saline, with local anesthesia slowly over the entire donor area.
They use 0.8 to 1 mm special micro punches to extract grafts from the donor area. The doctor usually performs this process under 2.5 to 5x magnification.
Following are the steps for the procedure:
Step 1
Scoring of scalp skin containing follicular units (FUs) with the sharp side of the micro punch.
Step 2
To loosen the FU, the doctor twists the dull side of the punch while the surgical assistant applies counter-traction. This action will help the punch penetrate into the dermis.
Step 3
In the third step, the assistant softly takes out the FUs with forceps. The extracted grafts need preservation in cool Ringer’s lactate or saline solution. The extracted grafts consist of 4 or rarely 5 to 6 hairs. It is the most time-consuming plus tiresome part of the process.5Dua, A., & Dua, K. (2010). Follicular unit extraction hair transplant. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery, 3(2), 76-81.

Step 4
After preparing the extracted grafts, the surgeon prepares the recipient area (the area where the hair will be implanted) by making small incisions or slits in the scalp. After that, he carefully inserts the prepared grafts into the recipient sites.
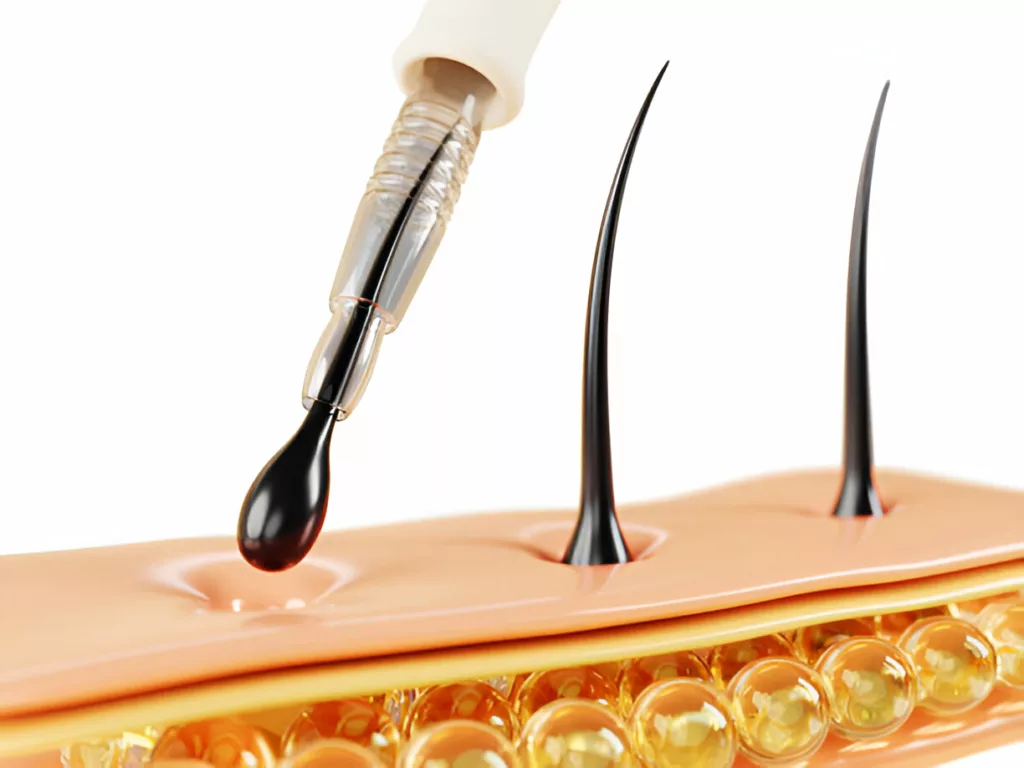
After the grafts are implanted, the surgeon provides post-operative care instructions, including medication for pain relief and scalp care guidelines. Patients may initially experience shedding of the transplanted hair, but new growth typically begins within several months. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing and assess the results of the transplant, ensuring everything is progressing as expected.
FUE Recovery
FUE’s recovery process is faster and less uncomfortable in most cases. The doctor performs the procedure in a trimmed area, leaving small scars in the donor and recipient areas that remain until they are rubbed away. Within one to two weeks after the procedure, scabs typically fall off, leading patients into what is often referred to as an ‘invisible state’ or ‘Shock Loss,’ during which transplanted grafts may shed, making way for new hair to grow in their place. In this state, hair grafts fall out, and they wait for the transplanted hair to grow. The transplanted hair grows 1 cm per month. Normal hair growth can take several months. In some cases, the results take more than one year to appear fully.
The use of postoperative sprays, bandages, etc., varies among surgeons. Other policies, like water exposure and return to exercise, also vary among surgeons. It is important to follow the instructions given by your surgeon.
Advantages of FUE
FUE holds several advantages. Some of them are the following:
- The more rapid healing process in the donor area.
- No or very minimal scarring in the extraction area. This is beneficial for patients who wear short hairstyles.
- Greater comfort in the donor area.6Jiménez-Acosta, F., & Ponce-Rodríguez, I. (2017). Follicular unit extraction for hair transplantation: an update. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (English Edition), 108(6), 532-537.
- There is no need to limit the exercise schedule after this procedure.
- Provide an alternative solution to linear strip harvesting.
- Provide the theoretical possibility of harvesting hairs other than the scalp. These can be hairs from the beard or body hairs.
- The doctor can also harvest very fine hair from the nape of the neck for eyebrows or hairlines.
The FUE is useful for patients with a high risk of scarring, such as:
- Younger patients
- Muscular patients
- Athletes
- Patients with extra loose or tight scalp skin
Disadvantages of FUE
The following are the disadvantages of the FUE:
- FUs are harvested from a much vaster donor area than the traditional method.
- Maximum yield is lower than traditional hair transplantation.
- Graft quality is low, but the follicular transection rate is high.
- Extracted FUs often lack protection from the fat and dermis after dissection under a microscope.
- It is difficult to grasp an entire FU, resulting in lower density.
- Grafts of low quality do not grow well.
- New scarring arises at every transplantation session. For example, if the first session involves 2000 grafts, the scars will be 2000. However, with a second 2000-graft session, the total scars will be 4000.
- The number of grafts in a single setting is limited.
- FUE is a slower process than the strip harvesting method.7Garg, A., & Garg, S. (2021). Overview of follicular extraction. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, 54(04), 456-462. Transplants involving many grafts need more time. Grafts spend more time outside the body, leading to suboptimal growth.
- FUE is more expensive than traditional hair transplant methods.
Complications of FUE
With FUE, you may not experience more scars. Tiny white dots will appear only where the doctor takes out the follicles. Or these dots will fade with time. But there are some possible and rare side effects. See your doctor if you experience any of them.
- Drainage at the surgical site
- Symptoms of infection
- Folliculitis (Swelling of follicles)
- Swelling or pain in or around the surgery site
- Bleeding from the site of surgery
- Tingling or numbness around the surgical site
- Thinning or balding continues even after the hair transplant.8Avram, M. R., Rogers, N., & Watkins, S. (2014). Side-effects from follicular unit extraction in hair transplantation. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 7(3), 177-179.
Cost of the FUE Procedure
An estimated FUE hair transplant cost is between $4000 and $15000 per session. The multiple-session procedure costs more than $50,000. The ultimate cost of a FUE transplant depends on various factors such as:
- Number of Grafts extracted and transplanted
- Experience of the surgeon
You will need to cover the prescribed medications for possible side effects.
Conclusion
FUE is an exciting and advanced hair transplant method. It is propelling the field of hair transplant one step closer to the elite minimally invasive prominence. Being a promising scarless surgery is attractive for both patients and surgeons. This transplant method is normally a pain-free procedure. FUE serves as an imperative alternative to traditional hair transplantation methods. Risks and complications are few and rare.
FUE is becoming a popular choice among people due to various reasons. These include the numerous benefits and natural-looking results of FUE. If you are considering a hair restoration surgery, first consult with a highly qualified hair restoration specialist. He will help you determine whether FUE is right for you or not.
Refrences
- 1Garg, A. K., & Garg, S. (2018). Donor harvesting: follicular unit excision. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery, 11(4), 195-201.
- 2Bansod, S., Kerure, A., Rohatgi, S., & Bilewar, U. (2021). History of follicular unit excision. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, 87(2), 315-318.
- 3DR. THOMAS BELL, M. (2024). Comparing FUE Vs. FUT Hair Transplants. https://torontoplasticsurgeon.com/blog/fue-vs-fut#:~:text=With%20a%20FUT%20hair%20transplant,an%20FUE%20transplant%20will%20look
- 4Devroye, J. (2021). U.S. Patent No. 11,071,563. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
- 5Dua, A., & Dua, K. (2010). Follicular unit extraction hair transplant. Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery, 3(2), 76-81.
- 6Jiménez-Acosta, F., & Ponce-Rodríguez, I. (2017). Follicular unit extraction for hair transplantation: an update. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (English Edition), 108(6), 532-537.
- 7Garg, A., & Garg, S. (2021). Overview of follicular extraction. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery, 54(04), 456-462.
- 8Avram, M. R., Rogers, N., & Watkins, S. (2014). Side-effects from follicular unit extraction in hair transplantation. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 7(3), 177-179.