What is Lipoplasty?
Lipoplasty or Liposuction is a surgical procedure that helps eliminate undesired fat beneath your skin, permanently removing the adipose (fat) tissue from a specific area. The method is helpful for contouring body parts containing excess fat that is resistant to exercise and diet. In 2021, lipoplasty, or liposuction, was the leading cosmetic surgical procedure in the United States.1Michas, F. (2023) Top surgical cosmetic procedures U.S. 2021, Statista. Retrieved 09 August 2023 from https://www.statista.com/statistics/281224/leading-surgical-cosmetic-procedures-in-the-united-states/ Clinically, Liposuction is defined as removal of fat from deposits beneath the skin using a cannula with the assistance of a powerful vacuum.
Lipoplasty serves cosmetic purposes more than medicinal value. It is not an alternative treatment for obesity but is beneficial for people with a normal weight but excess fat deposits under the skin. The procedure is performed alone or with other cosmetic surgeries, including tummy tuck, facelift, breast reduction, etc.
Types of Lipoplasty
Lipoplasty or Liposuction can be classified based on the fluids injected and the type of technique used.
Based on techniques
Lipoplasty can be classified into the following types based on the technique used for lipolysis. The common ones are:
- Power-Assisted Liposuction (PAL)
- Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL)
- Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL)
- Traditional Liposuction (SAL)
Based on the Fluid Injected
Lipoplasty or Liposuction techniques can be categorized based on the volume of infiltration or wetting solution injected. The key difference among these liposuction techniques is the volume of infiltrating solution used and its impact on blood loss relative to the volume of aspirated fat. The Tumescent technique is considered to be the gold standard.2Sood, J., Jayaraman, L., & Sethi, N. (2011). Liposuction: Anaesthesia challenges. Indian journal of anesthesia, 55(3), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.82652
-
Dry Liposuction:
This technique does not involve a fluid injection before the fat removal process. It is less frequently used today due to its higher risk of bleeding and bruising compared to techniques that involve fluid. The estimated blood loss is around 20 to 45 % of the aspirated volume.
-
Wet Liposuction:
The Wet technique incorporates a small volume of fluid to aid fat extraction. This method helps reduce bleeding and makes the procedure somewhat easier by loosening the fat tissue before suctioning. The estimated blood loss is 4% to 30% of the aspirated volume. However, it is less effective than other techniques that use larger fluid volumes.
-
Super-wet technique:
This technique uses a larger volume of fluid than the wet technique but less than the tumescent technique (Around 1ml per estimated milliliter of aspirate). This approach enhances fat dislodgement and minimizes bleeding while being less invasive than the dry method. The estimated blood loss is 1% of the aspirated volume. It strikes a balance between fluid volume and the benefits of reduced trauma.
-
Tumescent Technique:
The Tumescent technique, described by US dermatologist Jeffery Klein in the 1980s, is the most commonly employed method in liposuction. It involves injecting a substantial volume (3-4ml per estimated milliliter of aspirate) of a saline solution mixed with lidocaine and epinephrine. The blood loss is almost 1% of the aspirated volume. This combination provides excellent pain relief, reduces bleeding, and improves the efficiency of fat removal, making it the preferred choice for many liposuction procedures.
Lipoplasty Procedure
The lipoplastic procedure may take around 1 to 2 hours. Before lipoplasty, you have to consent to the procedure. Here are a few things to consider for a successful procedure:
Patient Selection
Candidates should fulfill certain criteria to ensure a safe and effective lipoplasty procedure. Good candidates for lipoplasty should be adults and have the following:
- Good state of health
- Stubborn fat that you can’t eliminate with diet and exercise
- Average or above-average weight
- Practicable goals for the future
Preoperative Examination
Patients interested in lipoplasty must complete some medical tests to verify if they are a suitable candidate for the procedure. You must share your complete medical history with your healthcare provider for a good consultation. He might advise you to stop taking anti-inflammatory medications like aspirin, smoking, herbal supplements, contraceptives, and iron supplements. Discontinue all these at least two weeks before the surgery.
Anesthesia Options
Your surgeon will choose an appropriate anesthetic before surgery according to your condition and the requirements of the surgery. You might get a general anesthetic that is effective for 4 hours. However, epidural anesthesia is suitable if the procedure involves lower body parts. A local anesthetic will suit you best if only a small portion requires lipoplasty.
Lipoplasty Techniques
A variety of lipoplasty techniques are currently used. Some of the common ones are discussed below:
Traditional or Suction-Assisted Lipoplasty (SAL):
Traditional lipoplasty is the original and most straightforward form of liposuction. It involves inserting a thin tube (cannula) through small incisions in the skin. The cannula is manually moved back and forth to break up fat cells, which are then suctioned out. This method is effective for removing moderate amounts of fat but can cause more bruising and require a longer recovery time compared to newer techniques.
Power-Assisted Lipoplasty (PAL):
Power-assisted lipoplasty is similar to traditional liposuction but uses a specialized, vibrating cannula. The vibrations help break up fat cells more easily, reducing the surgeon’s physical effort and potentially increasing precision. This method can result in less bruising and a quicker recovery time than traditional SAL.
Laser-Assisted Lipoplasty (LAL):
Laser-assisted lipoplasty uses laser energy to liquefy fat cells before they are suctioned out. The laser also stimulates collagen production, which can help tighten the skin. Often marketed under names like SmartLipo, this method can be less invasive and result in quicker recovery times compared to traditional liposuction.3Tabbal, G.N. et al. (2013) Advances in liposuction: Five key principles emphasizing patient safety and outcomes, Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open. Retrieved 15 June 2023 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4186292/#R2
Ultrasound-Assisted Lipoplasty (UAL)
Ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty (UAL) utilizes ultrasound energy to liquefy fat cells before they are suctioned out. In this procedure, the surgeon will spot the specific area on the body from where fat will be excised. Then, an excess anesthetic solution is introduced in that area using the tumescent technique.4Sood, J., Jayaraman, L., & Sethi, N. (2011). Liposuction: Anaesthesia challenges. Indian journal of anesthesia, 55(3), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.82652 This technique involves anesthetizing skin and subcutaneous tissues locally using a large anesthetic solution that causes local swelling.
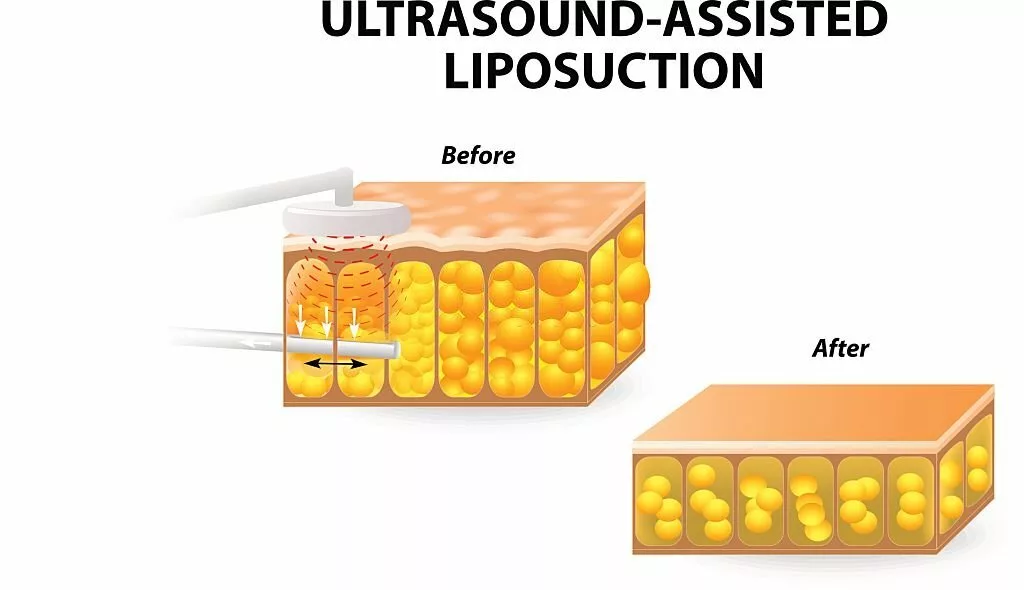
In the next step, they will insert an ultrasonic probe across the skin through an incision. The tube-like probe is moved, emitting high-frequency sound waves. These ultrasonic waves create a negative pressure that breaks and liquefies fat cells. The liquified fat is gently aspirated from that area.
AfterCare and Recovery
The doctor may advise you to:
- Wear compression garments after the surgery for the initial few days.
- Refrain from heavy exercise and physical exertion for several weeks.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle to avoid lipid accumulation in the future.
- You may not need pain medication because anesthesia may remain for 12 hours after surgery.
Recovery from lipoplasty generally involves 1 to 2 weeks of initial healing, with most people returning to light activities within 1 to 2 weeks. Full recovery and final results can take several months as swelling subsides and contouring effects become fully visible.
Will Drains Be Used After Lipoplasty?
Yes, drains or tubes are common after lipoplasty, especially in more extensive procedures. Drains remove excess fluid and reduce the risk of complications such as seromas (fluid accumulation).5Taha, A. A., Wahba, M. M., & Tahseen, H. (2020). Liposuction: Drains, Are They Adequate? Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open, 8(3), e2677. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002677 Your surgeon will typically place these drains during the procedure, and they will be removed once the drainage decreases and the risk of fluid buildup is minimized, usually within a few days to a week after surgery. The removal is usually painless.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any other surgery, lipoplasty accompanies some risks and complications. However, it is possible to minimize the potential risk by selecting a well-trained plastic surgeon. Complications are less likely if a small portion of the body is operated. Some of the potential risks include:
- Bleeding6Karmo FR, Milan MF, Silbergleit A. Blood loss in major liposuction procedures: a comparison study using suction-assisted versus ultrasonically assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001 Jul;108(1):241-7; discussion 248-9. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200107000-00039. PMID: 11420531.
- Infection
- Bruising
- Contour deformities
- Change in skin color
- Nerve damage due to compression or trauma
Pros and Cons of Lipoplasty
Before consenting to this procedure, you should be aware of all the pros and cons of lipoplasty. Consult an experienced plastic surgeon and consider every good or bad aspect of surgery. Here are a few pros and cons that might accompany lipoplasty:
Pros
- You can eliminate stubborn fat from the abdomen, thighs, arms, hips, etc.
- Lipoplasty helps expose your perfectly toned muscles as a result of the workout.
- Recovery time is short compared to other surgical procedures. After one week, you can resume your daily tasks.
- Lipoplasty is a versatile procedure that can involve many body parts in a single procedure or be combined with other procedures to create the body that you desire.
Cons
- Potential complications might follow surgery, e.g., infections, bleeding, anesthesia-related problems, etc.7Dixit VV, Wagh MS. Unfavourable outcomes of liposuction and their management. Indian J Plast Surg. 2013 May;46(2):377-92. doi: 10.4103/0970-0358.118617. PMID: 24501474; PMCID: PMC3901919.
- Lipoplasty does not manage problems associated with loose skin. Your skin should have good elasticity to contour after the surgery. If you have loose skin, you need to integrate other techniques with lipoplasty.
- You have to continue with a healthy lifestyle after surgery to avoid weight gain in the future.
- There might be swelling on the site of the surgery. However, it subsides with time.
Injection Lipolysis Vs. Lipoplasty
Lipoplasty and Injection lipolysis are two distinct fat reduction methods. Injection lipolysis, often referred to as “fat dissolving injections,” involves the injection of substances like deoxycholic acid into targeted fat deposits, which breaks down fat cells that the body then naturally eliminates. This non-surgical approach is best suited for small areas of fat and offers minimal downtime.8Plastic Surgery. (n.d.). Injection Lipolysis. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/cosmetic-procedures/nonsurgical-fat-reduction/injection-lipolysis
What is VASER liposuction?
VASER liposuction is a specialized form of liposuction that utilizes third-generation ultrasound technology VASER® to break apart fat cells and loosen them from deeper tissues, enhancing the effectiveness of fat removal. The acronym VASER stands for Vibration Amplification of Sound Energy at Resonance. This method employs powerful sound waves to disrupt fat cell bonds, making the procedure more controlled and gentle.9Massignan, Felipe. (2018). Safety Evaluation of Vaser® in Body Contouring Improvement Liposuction. Surgery: Current Research. 08. 10.4172/2161-1076.1000308.
Unlike traditional Ultrasound-Assisted Lipoplasty (UAL), which also uses ultrasound to remove fat, VASER liposuction offers more precise and targeted fat disruption. This distinction allows for better contouring and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues.
The Bottom Line
Lipoplasty is a relatively safe procedure that helps eliminate excess fat from different body areas. However, it is not a substitute for weight loss treatment; it helps contour and shape your body. Consult and choose a skilled plastic surgeon to ensure good results and minimize the risks associated with surgery. Make sure to maintain healthy conduct following this surgery to maintain a good body posture.
Refrences
- 1Michas, F. (2023) Top surgical cosmetic procedures U.S. 2021, Statista. Retrieved 09 August 2023 from https://www.statista.com/statistics/281224/leading-surgical-cosmetic-procedures-in-the-united-states/
- 2Sood, J., Jayaraman, L., & Sethi, N. (2011). Liposuction: Anaesthesia challenges. Indian journal of anesthesia, 55(3), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.82652
- 3Tabbal, G.N. et al. (2013) Advances in liposuction: Five key principles emphasizing patient safety and outcomes, Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open. Retrieved 15 June 2023 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4186292/#R2
- 4Sood, J., Jayaraman, L., & Sethi, N. (2011). Liposuction: Anaesthesia challenges. Indian journal of anesthesia, 55(3), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.82652
- 5Taha, A. A., Wahba, M. M., & Tahseen, H. (2020). Liposuction: Drains, Are They Adequate? Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open, 8(3), e2677. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002677
- 6Karmo FR, Milan MF, Silbergleit A. Blood loss in major liposuction procedures: a comparison study using suction-assisted versus ultrasonically assisted lipoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001 Jul;108(1):241-7; discussion 248-9. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200107000-00039. PMID: 11420531.
- 7Dixit VV, Wagh MS. Unfavourable outcomes of liposuction and their management. Indian J Plast Surg. 2013 May;46(2):377-92. doi: 10.4103/0970-0358.118617. PMID: 24501474; PMCID: PMC3901919.
- 8Plastic Surgery. (n.d.). Injection Lipolysis. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/cosmetic-procedures/nonsurgical-fat-reduction/injection-lipolysis
- 9Massignan, Felipe. (2018). Safety Evaluation of Vaser® in Body Contouring Improvement Liposuction. Surgery: Current Research. 08. 10.4172/2161-1076.1000308.