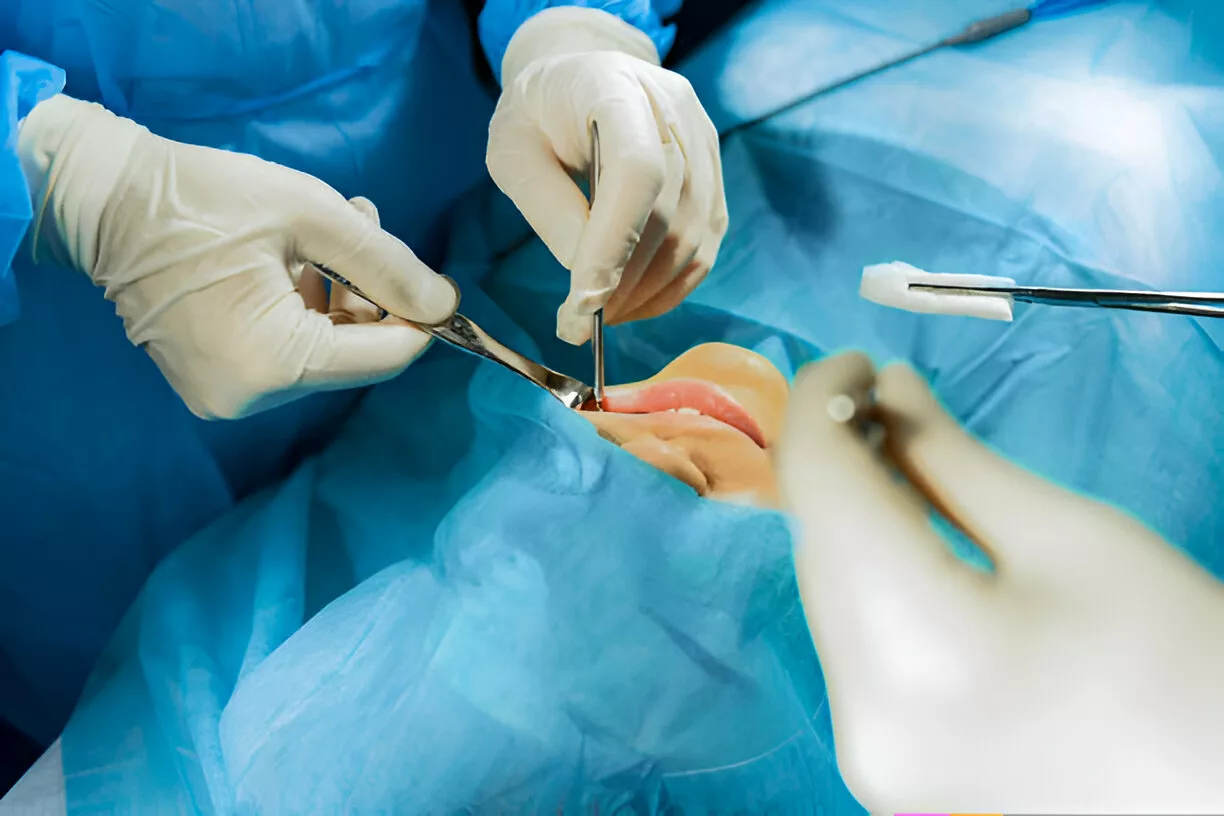
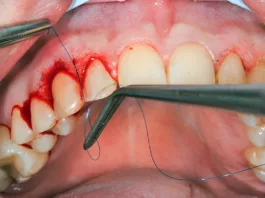
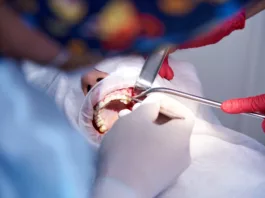
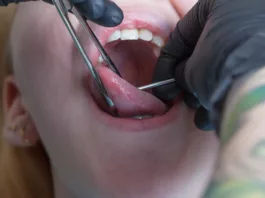
Vestibuloplasty is an oral surgical procedure to improve (deepen) the oral vestibule. The procedure is mostly done to ensure an adequate amount of soft tissue for prosthesis placement. By repositioning the soft tissue attachments, doctors aim to increase the depth of the vestibule. Research indicates that oral vestibuloplasty achieves a high implant survival rate (99%) in patients with head and neck tumors.1Wüster, J., Sachse, C., Sachse, C., Rendenbach, C., Wagendorf, O., Vach, K., … & Nahles, S. (2023). Vestibuloplasty and its impact on the long-term survival and success of dental implants in irradiated and non-irradiated patients after head and neck tumor therapy: a retrospective study. Clinical oral investigations, 27(8), 4695-4703.
What Is The Oral Vestibule, And What Causes Its Loss?
It refers to the space located between your lips/cheeks (externally) and the teeth/gums (internally). The horseshoe-shaped area surrounds your teeth and gums. It plays an essential role in speech, mastication, and overall oral health. Moreover, an optimal vestibule height is required for prostheses (implants and dentures) placement. Multiple reasons can lead to loss of the oral vestibule:
Trauma/Injury
Direct physical injury to the vestibule can lead to subsequent inflammation and ulceration, which eventually result in tissue loss. Bites, falls, accidents, and brawls can potentially damage the region.
Burns
Thermal and chemical burns can also contribute to a shortening of the oral vestibule, thereby making it impossible to place a good denture. Very hot foods (pizza) and hot beverages can induce pizza burns that can have long-lasting effects.
Periodontitis And Tooth Loss
Periodontists observe several edentulous patients with vestibule loss in their daily practices. This is because severe gum disease and associated loss of teeth potentially cause detachment of soft tissues (from the teeth), which leads to loss of vestibule depth.
Excessive Ridge Resorption
Your alveolar bone (that surrounds the tooth roots) undergoes negative reshaping after the extraction of a tooth. In some cases, there is excessive residual ridge resorption that decreases the height and width of the ridge, which reciprocates in the oral vestibule as well.
Sometimes, chronic infections and auto-immune pathologies (like oral lichen planus) can also lay the foundation for vestibule loss.
Indications For Vestibuloplasty
Oral vestibulopathy is indicated in the following cases:
Prosthesis Preparation
Doctors most commonly advise a vestibuloplasty to patients who have a shallow vestibule and want to have a prosthesis. A pre-prosthetic vestibuloplasty surgery is needed to ensure a stable base for removable dentures. Dentures rest on your ridge (and gums), and denture extensions take support from your vestibule. Therefore, a significant height of the vestibule is a must for good support and retention of a denture. The repositioning of the soft tissues aids in improving the denture seal.
Clinical studies reveal that vestibuloplasty is an effective method of increasing vestibule height that helps enhance denture stability, especially in completely edentulous patients.2Fokam, S. T., Ntep, D. B. N., Bohimbo, J. E., Abena, M. E. N., & Messanga, C. B. (2022). Vestibuloplasty to enhance denture stability: About two observations. Advances in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 6, 100288. Moreover, the increase in vestibular depth helps edentulous patients improve their oral hygiene.
The adoption of advanced systems like CAD/CAM and implant-retaining splints, along with vestibuloplasty, has proven to evidently increase mandibular implant survival rates. Patients also report better oral hygiene post-vestibuloplasty.3Van Der Kelen, L., Ureel, M., Denoiseux, B., Boderé, P. J., Matthys, C., Vermeersch, H., & Coopman, R. (2025). Enhancing Implant Success in Mandibular Reconstruction: A Novel Approach Combining Implant-Retained Splint and Vestibuloplasty—A Case Series. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1298.
Weak Gingiva
Another condition that warrants vestibuloplasty is a lack of keratinized gingiva. Microscopic analyses have revealed that keratinized gingiva is strong and plays a significant role in protecting the underlying structures (soft tissues and bone). Your periodontist may advise a vestibuloplasty if the present keratinized layer is inadequate. At times, doctors combine vestibuloplasty with free gingival grafting to increase sulcus depth and amount of keratinized gingiva.4Yüce, Z., Düger, N., & Sağsöz, A. (2024). Combined application of vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft. International Dental Journal, 74, S247.
Poor Oral Hygiene
A shrunken oral vestibule tends to make oral hygiene maintenance an arduous task. Therefore, several patients undergo vestibuloplasty to minimize hindrance in oral hygiene maintenance. In a clinical study, a 29-year-old male underwent vestibuloplasty (and free gingival grafting) to manage gingival recession (and associated bleeding) and reduce difficulty in cleaning teeth. The procedure helps increase the vestibular depth and attain a thick gingival phenotype. The patient was satisfied with the results, as he was now able to maintain routine oral hygiene with a deeper vestibule. Moreover, there was minimal plaque deposition.5Gogoi, A. (2022). Enhancing gingival phenotype with vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft: improving maintenance of regular oral hygiene. Cureus, 14(3).
Sometimes, health professionals carry out procedures like this to correct anatomical abnormalities and thus, improve aesthetics.
Vestibuloplasty Types
There are different types of vestibuloplasty procedures:
Submucosal Vestibuloplasty
This technique aims to reposition the soft tissues to increase sulcular depth. Further subclassifications of the technique include:
Closed Submucosal Vestibuloplasty
The doctor accesses the soft tissues via a “tunneling” technique, i.e., surgical instruments are inserted via a small vertical incision.
Open Submucosal Vestibuloplasty
As the name indicates, the surgeon makes an open, horizontal incision along the mucogingival junction and performs dissection of the supra-bone (supraperiosteal) tissues. With this dissection, he then elevates a thin mucosal flap and excises underlying muscles/subcutaneous tissues to increase the vestibule height. The surgeons are cautious to preserve the periosteum. The mucosal flap is then fixed to the periosteum (deep in the vestibule) with the help of sutures. The free flap is returned and sutured to its normal position.
Maxillary Pocket Inlay Vestibuloplasty
This technique is employed to improve maxillary denture retention. Here, the surgeon creates pockets around the thick bone part of the maxilla (aka maxillary buttress) and the piriform aperture regions.
Secondary Epithelialization Vestibuloplasty
As the name indicates, this technique aims to improve the epithelial layers of the vestibule. It is a commonly adopted technique, but has the drawback of post-operative scarring. There are various techniques of secondary epithelialization with slight differences:
Kazanjian Technique
Used in mandibular vestibuloplasties, it involves creating a mucosal flap from the inner aspect of the lower lip. The surgeon carries out supra-periosteal dissection to increase the height. The raw area on the lip is not sutured and heals by secondary epithelialization.
Godwin’s Modification
It is similar to Kazanjian’s. The only difference here is that the doctor doesn’t dissect the supra periosteal structures and rather performs sub-periosteal stripping to push down (or excise) the periosteum.
Transpositional Flap Vestibuloplasty
The lip switch technique is performed when a minimum bone height of 15 mm is available between the two mental foramina. In this technique, doctors raise a mucosal flap similar to Kazanjian/Godwin.
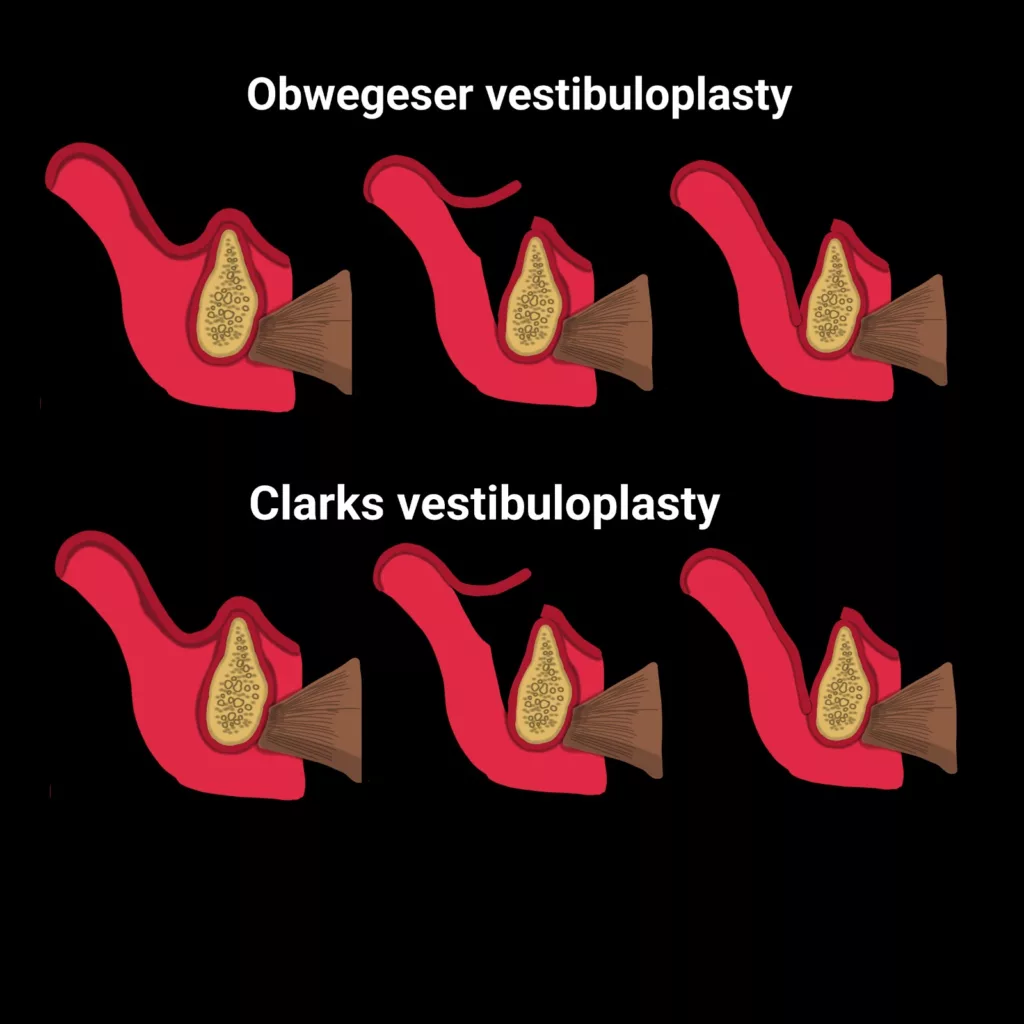
Clark’s Technique
It is the reverse of Kazanjian’s vestibuloplasty technique, where the surgeon starts an incision on the alveolar ridge, i.e., labial to the crest of the ridge (instead of the lip). The surgeon continues incising until he reaches the vermillion border while undermining the mucosal flap on the inner aspect of the lip. This technique preserves the periosteal layer. Therefore, quicker healing is seen. In a clinical case of mandibular gingival recession, doctors combined mandibular gingival advancement with Clark’s technique to ensure better brushing and gingival health.6Paramashivaiah, R., Anusha, S., & Prabhuji, M. (2023). Vestibuloplasty with coronal advancement in mandibular gingival recession defects-A Case Report. J Dent Maxillofacial Res, 6(3), 78-79.
Lingual Vestibuloplasty
This type of vestibuloplasty aims at increasing the depth of the lingual sulcus instead of the buccal vestibule in the lower jaw. In this technique, the surgeon repositions the lingual muscles to create a deeper sulcus. There are different modifications of lingual vestibuloplasty:
- Cooley (anterior lingual sulcoplasty) is characterized by reattachment of the genioglossus muscle to a new position and probable removal of large genial tubercles.
- In Trauner’s technique, the mylohyoid muscle is attached at a lower level, i.e., equal to the level of the residual alveolar ridge.
- The Caldwell’s technique is more extensive, in which doctors give an incision from the posterior mandibular ridge to the molar region. In this particular technique, the surgeon removes the mylohyoid muscle (and the mylohyoid ridge) and reduces the genial tubercle.
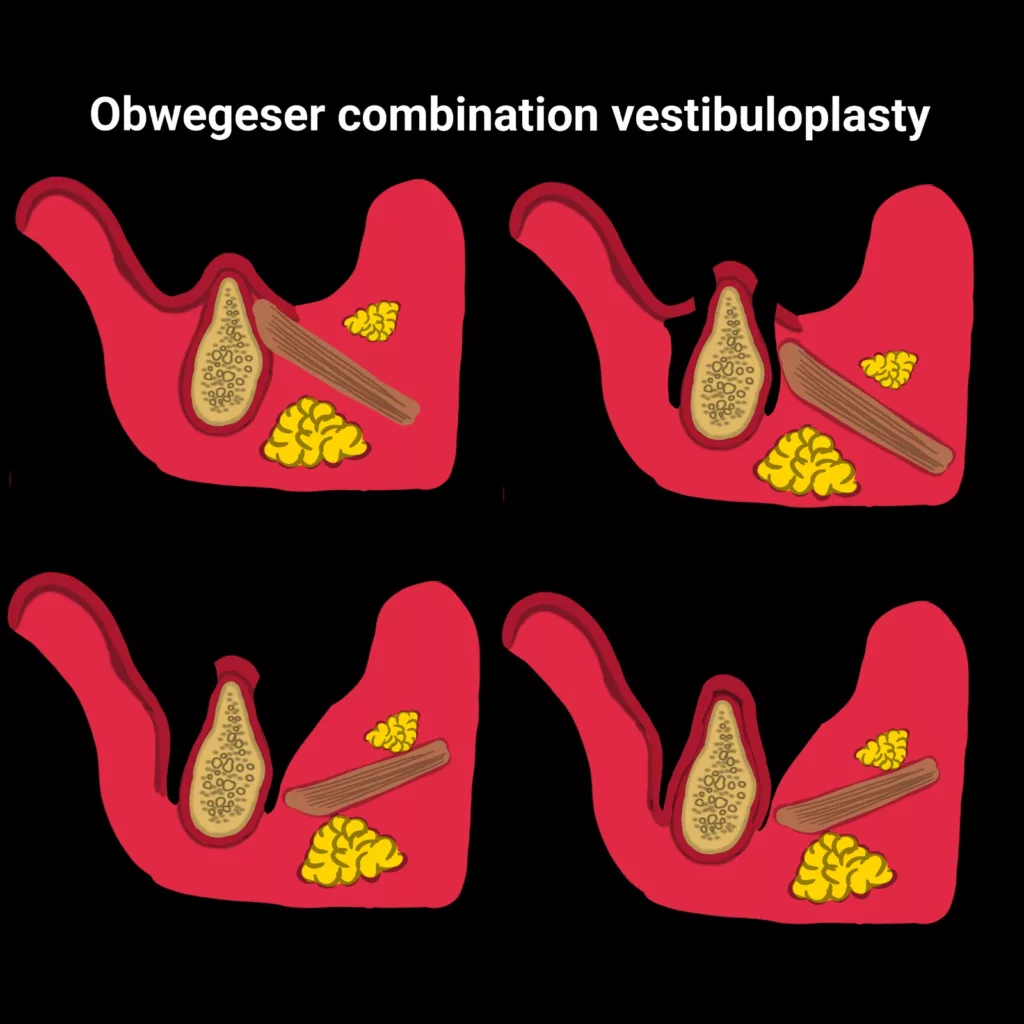
- Obwegeser’s technique increases buccal and lingual vestibule height. An incision is given at the crest of the ridge, and extensions are made on both sides, i.e., labial and lingual ridge. The exposed raw bone is covered with a skin graft, and a surgical stent is placed over it to ensure increased height in the buccal vestibule and lingual sulcus. Modified Obwegeser’s vestibuloplasty successfully increases keratinized gingiva and improves conditions for prosthesis.7Rajashri, R., MP, S. K., & MUTHUSEKHAR, M. (2020). Modified Obwegeser’s Vestibuloplasty: A Case Report. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (09752366), 12(1).
Grafting Vestibuloplasty
Vestibuloplasty is paired with grafting to compensate for an inadequate amount of bone. Relapse is seen in several cases of vestibular height increase procedures, so it is essential to ensure a good height of the alveolar bone. Therefore, in some cases, doctors place a bone graft at the surgical site during the vestibuloplasty procedure. Different types of grafts are used for the purpose, including xenografts, autografts, skin grafts, and mucosal grafts etc.
The use of platelet-rich fibrin as a graft has proven to have great results in root coverage. It can also serve as an alternative to conventional secondary epithelialization techniques.8Salgado‐Peralvo, A. O., Uribarri, A., Kewalramani, N., Peña‐Cardelles, J. F., & Liñares, A. (2023). The use of platelet‐rich fibrin in vestibuloplasty: A 36‐month follow‐up technique report. Clinical advances in periodontics, 13(1), 33-37. The use of grafts not only strengthens the gingiva but has also been shown to improve oral hygiene maintenance among the patients.9Gogoi, A. (2022). Enhancing gingival phenotype with vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft: improving maintenance of regular oral hygiene. Cureus, 14(3).
Vestibuloplasty Procedure
The first step in vestibuloplasty is anesthesia. Your doctor will give you local anesthesia, and after the area goes numb, he will start the process of cutting through the tissues. The conventional method of vestibuloplasty requires using a scalpel to cut through the connective tissue and muscle attachments. However, now doctors use medical-grade lasers to remove the muscle fibers and deepen the vestibule.
Laser vestibuloplasty (diode or carbon dioxide laser) has numerous advantages over the conventional scalpel method. As the cutting with a laser is fine and precise, there is no need for extensive stitching. Laser cutting significantly reduces localized bleeding. So, it can be used effectively in patients with bleeding disorders. Moreover, clinicians have noted a lesser degree of scarring in patients with laser vestibuloplasty.
Your surgeon can opt for any of the vestibuloplasty types mentioned above. Depending on the type of vestibuloplasty selected, the doctor keeps the wound open (in case of secondary epithelialization), covers the surgical site with a splint, or closes it with sutures. Sometimes, surgeons add graft materials (like collagen membranes) to speed up healing.
Vestibuloplasty Recovery
Vestibuloplasty recovery time usually ranges from 4 to 6 weeks. You can see initial healing during this phase. However, complete healing is achieved anywhere between 6 weeks to several months, depending on the type of vestibuloplasty done. Patient factors like age, generalized health, and lifestyle habits also play a role in the duration of recovery.
Vestibuloplasty Post-Op Care
An oral vestibuloplasty is an outpatient procedure, and patients can return home on the same day. However, it is important to follow the post-op instructions for quicker and uneventful healing. You should follow these steps:
- Take over-the-counter pain-killer medications to manage post-operative pain and swelling (during the first 24-48 hours).
- Shift to a softer diet for the first few days.
- If stitches are placed, get them removed after 7-10 days (or as instructed by your doctor).
- Regularly follow-up appointments with your doctor.
Prostheses like removable dentures and implants are placed after the wound has completely healed.
Vestibuloplasty Complications
Though rare, complications can arise after a vestibuloplasty surgery. Just like any other surgical process, vestibuloplasty can lead to post-operative issues like infection, swelling, and bleeding. Nerve damage occurs very rarely, but there is a chance.
Final Word
Vestibuloplasty is an oral surgical procedure to increase the depth of the oral vestibule for better prosthesis retention. Patients with short vestibules due to infection, trauma, bone loss, or periodontitis need to undergo vestibuloplasty before denture or implant placement. Performed under local anesthesia, there are different types of vestibuloplasties, including submucosal, secondary epithelialization, and grafting vestibuloplasty. Doctors may use a scalpel or laser to cut vestibular soft tissues and reattach them to a lower level, thereby increasing the vestibular height. Sometimes, doctors keep the surgical wound open, while other times they close it with sutures or cover it with a splint. Healing usually takes 4 weeks to several months.
Refrences
- 1Wüster, J., Sachse, C., Sachse, C., Rendenbach, C., Wagendorf, O., Vach, K., … & Nahles, S. (2023). Vestibuloplasty and its impact on the long-term survival and success of dental implants in irradiated and non-irradiated patients after head and neck tumor therapy: a retrospective study. Clinical oral investigations, 27(8), 4695-4703.
- 2Fokam, S. T., Ntep, D. B. N., Bohimbo, J. E., Abena, M. E. N., & Messanga, C. B. (2022). Vestibuloplasty to enhance denture stability: About two observations. Advances in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 6, 100288.
- 3Van Der Kelen, L., Ureel, M., Denoiseux, B., Boderé, P. J., Matthys, C., Vermeersch, H., & Coopman, R. (2025). Enhancing Implant Success in Mandibular Reconstruction: A Novel Approach Combining Implant-Retained Splint and Vestibuloplasty—A Case Series. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(4), 1298.
- 4Yüce, Z., Düger, N., & Sağsöz, A. (2024). Combined application of vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft. International Dental Journal, 74, S247.
- 5Gogoi, A. (2022). Enhancing gingival phenotype with vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft: improving maintenance of regular oral hygiene. Cureus, 14(3).
- 6Paramashivaiah, R., Anusha, S., & Prabhuji, M. (2023). Vestibuloplasty with coronal advancement in mandibular gingival recession defects-A Case Report. J Dent Maxillofacial Res, 6(3), 78-79.
- 7Rajashri, R., MP, S. K., & MUTHUSEKHAR, M. (2020). Modified Obwegeser’s Vestibuloplasty: A Case Report. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (09752366), 12(1).
- 8Salgado‐Peralvo, A. O., Uribarri, A., Kewalramani, N., Peña‐Cardelles, J. F., & Liñares, A. (2023). The use of platelet‐rich fibrin in vestibuloplasty: A 36‐month follow‐up technique report. Clinical advances in periodontics, 13(1), 33-37.
- 9Gogoi, A. (2022). Enhancing gingival phenotype with vestibuloplasty and free gingival graft: improving maintenance of regular oral hygiene. Cureus, 14(3).