A Barium Swallow is a special type of X-ray scan that allows doctors to look inside your esophagus, a pipe-like organ connecting your mouth with your stomach. It is an important imaging modality that is used to diagnose a variety of gastrointestinal disorders. It is also called an esophagogram or barium meal.
What is Barium Swallow?
Barium swallow is a clinical investigation performed by highly trained medical imaging professionals such as radiologists and radiology technicians. It is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that helps doctors see any abnormalities in the internal structure and functioning of your upper gastrointestinal tract. This is done by making you drink a liquid with barium in it and taking X-ray films of your body in various positions while the liquid travels through your gastrointestinal system. As a result, they can diagnose disorders of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and upper part of your stomach with ease.1
Barium Swallow. (2021, August 8). Hopkinsmedicine.org. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/barium-swallow
Indications of Barium Swallow
It is indicated when you experience persistent upper gastrointestinal symptoms, such as:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Painful swallowing (odynophagia)
- Regurgitation of food back into the esophagus
- Acid reflux
- Chest pain unrelated to the heart, skeleton, and musculature
These symptoms are usually vague and can indicate a number of issues. Some disorders that are routinely diagnosed using this test are:
Motility Disorders
Esophageal motility disorders are those in which the regular peristalsis (wavelike movement of the whole gastrointestinal tract), which transfers food, is interrupted because of neurologic or muscular causes. Examples include:
- Achalasia, in which the lower sphincter of the esophagus fails to relax, shows a “bird beak” appearance on a barium swallow.
- Diffuse esophageal spasms involve irregular muscle contractions throughout the esophagus and are seen as a “rosary beads” or “corkscrew” appearance.
Strictures
Esophageal strictures are narrowings that are present in various parts of the esophagus. They halt the routine passage of food and water through the esophagus. They can exist because of benign conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disorder or malignancies of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Esophageal strictures often appear as pinches with irregular borders on barium swallow exams.
Herniations
Herniations are abnormal protrusions of the stomach and other abdominal organs, such as the sliding hiatal hernia and paraesophageal hernia. They often show up as sacs on a barium swallow or are reflected through the accumulation of air or barium in one particular region of the scan.2Yap, J. (2023, May 28). Barium swallow. Radiopaedia; Radiopaedia.org. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/barium-swallow
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications for barium swallow. However, doctors avoid it in a number of situations, such as:
- Barium sulfate can cause worsening of bowel obstruction and should be avoided.
- It is also contraindicated in cases of esophageal or other gastrointestinal perforations, as it can leak out and damage your organs.
- This test should not be performed if you have just undergone an endoscopic biopsy or another barium contrast-containing exam.
- Pregnant individuals are particularly prone to X-ray scans because of the risk of fetal abnormalities caused by radiation. Therefore, this exam is considered contraindicated.
What do I need to do for Barium Swallow Preparation?
This is a simple procedure and requires little preparation from you as a patient. Here is what you can do to prepare for a barium swallow exam:
- These exams need to be performed on an empty stomach. Therefore, you should stop eating and drinking eight hours prior to the procedure.
- Talk about your current medications with your doctor because you may need to stop taking them before your exam.
- Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, allergic to barium, or have recently had a barium swallow or endoscopy. Cancel the procedure even if it’s last minute if you have a condition that could cause complications later on. 3Clinic, C. (2022, April 21). Esophagram is a type of fluoroscopy, a video X-ray exam. It’s also called a barium swallow test. The test visualizes the inside of your esophagus as you swallow. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22766-esophagram
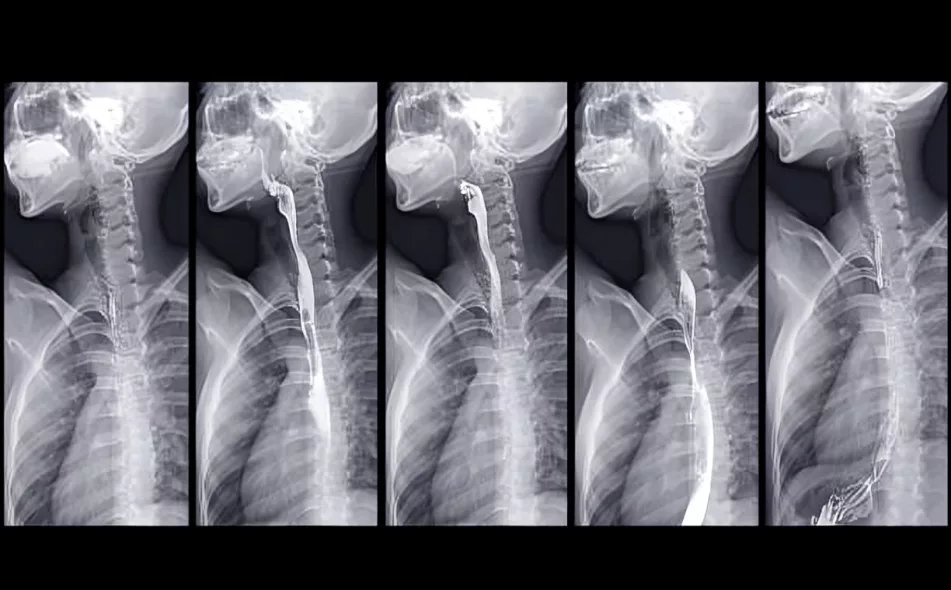
Step-by-Step Procedure for the Barium Swallow Test
This test is usually performed as an outpatient procedure. On the day of your test, you will be required to go to the radiology or gastroenterology unit of your healthcare clinic or hospital.
Preparing for a Barium Swallow
Once you are at your healthcare facility, your identity will be confirmed, and they will ask you to change into a hospital gown. You will also be asked to take off accessories like watches and jewelry that can cause artifacts during X-ray scans. In addition, a doctor or nurse will take a brief history and conduct a physical exam to make sure you are vitally stable for the barium swallow procedure.
Position during a Barium Swallow
The esophagus consists of different parts, such as the cervical esophagus, present in the head and neck; the thoracic esophagus, present in the thorax; and the abdominal thorax, present in the abdomen. You will be asked to lie in different positions depending on the type of esophagus being investigated:
- The cervical esophagus is investigated while you are sitting or standing in an upright position.
- The thoracic esophagus is investigated while you are lying on your back or on your side.
- The abdominal esophagus is investigated best when you are lying on your back, your stomach, or in a semi-upright position.
Barium Swallow Anesthesia
This exam does not require anesthesia as it is a non-invasive and simple medical procedure. You are expected to stay awake throughout the exam. Doctors avoid anesthesia and sedation during barium swallow as the administration of such drugs can result in a loss of your gag reflex and cause you to aspirate the barium liquid into your lungs.
Barium Swallow Contrast
The contrast used in this exam is usually barium sulfate. It is a thick, chalky-tasting paste or tablet that your doctor will ask you to swallow. However, it is avoided if you have a history of bowel perforation or aspiration, and a water-soluble medium is used instead. These substances cost the inner lining of your gastrointestinal tract and help capture abnormalities on x-ray films.
Barium Swallow Procedure
- Once you have been positioned on the examination table, a healthcare professional will ask you to ingest a barium compound.
- As the barium will travel through your mouth and esophagus, a doctor will take images of your body through an X-ray machine.
- You may also be given another dose of barium — which could be another liquid or a small tablet — to help visualize your organs better.
- Once the procedure is over, you will be helped off of the exam table.4Chen, A., Dawood Tafti, & Tuma, F. (2023, July 24). Barium Swallow. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493176/
What to do after the Barium Swallow Procedure?
After the procedure is over, you can go back to your daily life without any precautions. You can resume your dietary habits and continue taking most of your medications unless suggested otherwise by a doctor. In addition, you don’t need to take any time off from work or rest at home to recover as this test is not invasive and does not involve the use of anesthesia. In order to remove barium from your body, you will be asked to drink a lot of water. After a few days, you will get the results of your barium swallow procedure.
Barium Swallows Normal vs. Abnormal Results
This test may have normal results or abnormal results regarding the shape, size and function of your esophagus.
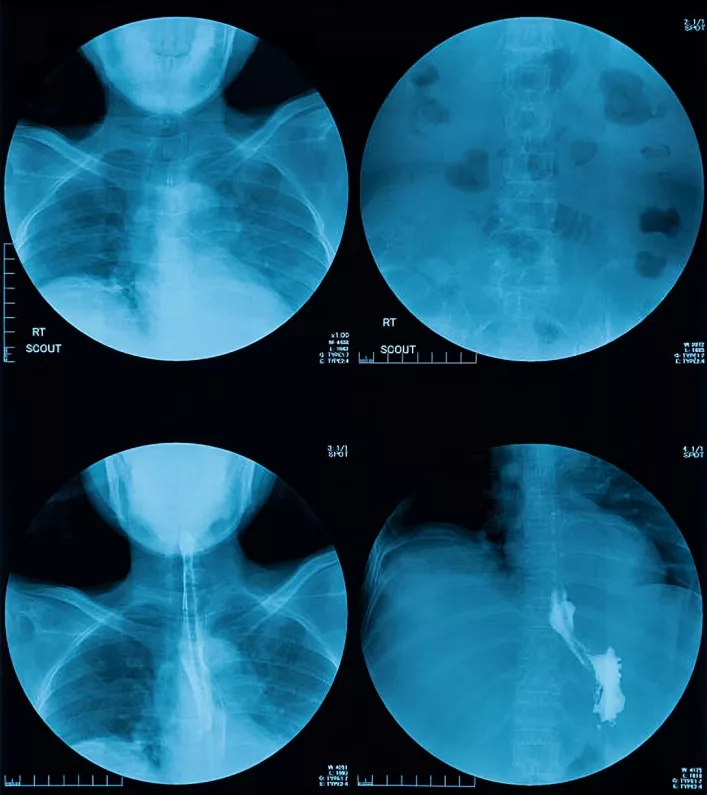
Normal Results:
Normal results include:
- Smooth walls of the esophagus without any bulges, constrictions, or tears.
- Normal, rhythmic peristalsis that pushes food from your mouth towards your stomach.
- No defects in your gastrointestinal system, which result in the improper filling of your organs with barium.
Abnormal Results
Abnormal results refer to pathologic findings that indicate something is wrong with your gastrointestinal tract. These include:5Barium Swallow: Test Preparation, Side Effects, vs. Upper GI Series. (2023, November 16). City of Hope. https://www.cancercenter.com/diagnosing-cancer/diagnostic-procedures/barium-swallow
| Findings | Appearance |
| Bird’s beak appearance | Achalasia |
| Corkscrew appearance | Esophageal spasm |
| Narrowed esophagus | Esophageal stricture |
| Pouches in the esophagus | Diverticula, hernia |
| Growths in the esophagus | Polyps |
| Enlarged veins | Esophageal varices |
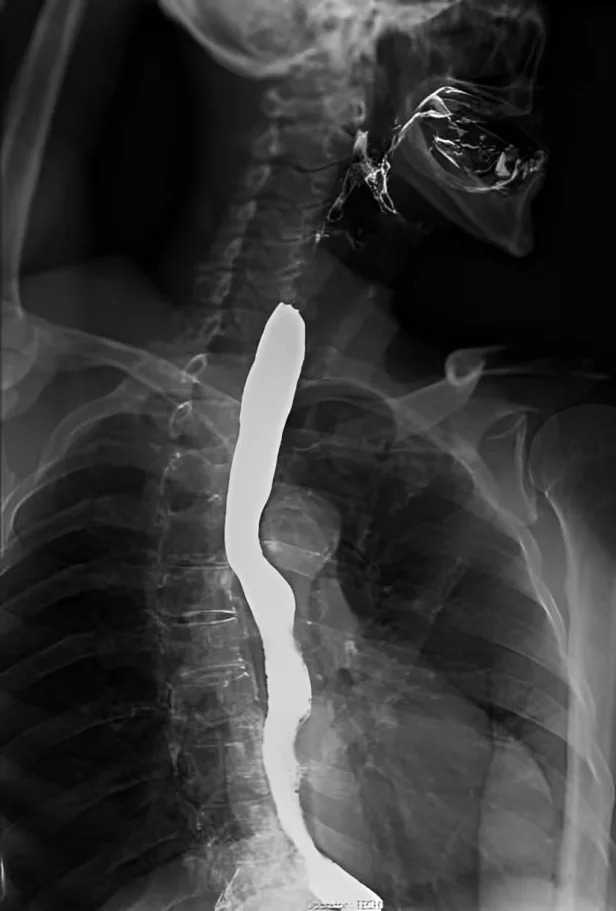
Side Effects
This is a low-risk procedure. It does not have any serious risks associated with it as it does not involve the administration of any equipment into your body except barium contrast. However, it may have unpleasant side effects, such as:
- Mild abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Indigestion
- Nausea
Among the side effects, there are certain red flags that should make you contact your doctor to confirm if something happened during your procedure:
- Bowel obstruction
- Not being able to pass flatus even after days
- Signs of infection, such as fever, pain and chills
- Bleeding from your mouth or rectum
How will a Barium Swallow Test affect my stool?
Barium can cause your stool to become lighter in color. In addition, it can also make your stool harder and more difficult to pass. These changes will wear off once the barium from the barium swallow has been removed from your gut.6Barium X-Rays (Upper and Lower GI). (2024, July 2). Hopkinsmedicine.org. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/barium-xrays-upper-and-lower-gi
Is Barium Sulfate safe for Pregnancy?
Barium sulfate is a contrast medium and is generally considered safe for pregnancy despite its few known side effects. However, damage to a growing fetus may occur through X-ray scans, which can cause developmental problems. For this reason, these tests are avoided in pregnancy even though barium sulfate is safe for pregnancy.
Is Barium Swallow a form of Fluoroscopy?
Barium swallow is a form of fluoroscopy. Fluoroscopic procedures involve the use of an imaging modality such as X-ray scans as well as the use of fluorescent dyes or contrast media that can highlight different structures of your body on these films. Your bodily functions are then viewed in real-time— as barium swallow involves these steps, it is considered a fluoroscopy.
Barium Swallow vs. Endoscopy
Barium swallow and endoscopy are both procedures that are commonly used to identify abnormalities in your gastrointestinal tract. A barium swallow is a simple and safe series of contrast X-ray scans that identify the disorders of the gastrointestinal system. However, for more complex disorders, invasive procedures that employ the use of a camera or endoscope to look at the inside of your esophagus, stomach, and intestines may be used. Both have their advantages as well as limitations and are used for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders.
| Barium Swallow | Endoscopy |
| Employs X-ray scan | Employs endoscope camera |
| Identifies abnormalities of the gastrointestinal system | Visualises the gastrointestinal system |
| Does not allow doctors to take biopsies | Allows doctors to take biopsies |
| Noninvasive procedure with lower risks and side effects | Invasive procedure with considerable risks and adverse effects |
| Less expensive and needs less prep | More expensive and needs more prep |
Barium Swallow vs. Barium Enema
A barium swallow is a procedure that shows doctors the abnormalities of your upper gastrointestinal tract. Barium is administered orally. On the other hand, a barium enema is used for abnormalities in your lower gut, such as your colon and rectum. It involves the administration of barium through the anorectal route.7Barium Radiology. (2024). Muschealth.org. https://muschealth.org/medical-services/ddc/patients/medical-tests/barium-radiology/
Conclusion
This is a noninvasive outpatient procedure used to diagnose a variety of esophageal conditions. Patients are required to ingest a barium-containing substance, which highlights different abnormalities as it travels down their gastrointestinal tract. Results are shown on X-ray films. It does not have any known absolute contraindications or serious side effects in non-pregnant individuals.
Refrences
- 1
Barium Swallow. (2021, August 8). Hopkinsmedicine.org. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/barium-swallow
- 2Yap, J. (2023, May 28). Barium swallow. Radiopaedia; Radiopaedia.org. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/barium-swallow
- 3Clinic, C. (2022, April 21). Esophagram is a type of fluoroscopy, a video X-ray exam. It’s also called a barium swallow test. The test visualizes the inside of your esophagus as you swallow. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22766-esophagram
- 4Chen, A., Dawood Tafti, & Tuma, F. (2023, July 24). Barium Swallow. Nih.gov; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493176/
- 5Barium Swallow: Test Preparation, Side Effects, vs. Upper GI Series. (2023, November 16). City of Hope. https://www.cancercenter.com/diagnosing-cancer/diagnostic-procedures/barium-swallow
- 6Barium X-Rays (Upper and Lower GI). (2024, July 2). Hopkinsmedicine.org. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/barium-xrays-upper-and-lower-gi
- 7Barium Radiology. (2024). Muschealth.org. https://muschealth.org/medical-services/ddc/patients/medical-tests/barium-radiology/

