Syphilis results from infection with Treponema Pallidum. Congenital Syphilis (CS) occurs when the Treponema bacterium is transmitted from the mother to the fetus (unborn baby) during pregnancy. Hence, the baby is born with Syphilis infection. Sadly, approximately half of all children with CS may not survive, either during pregnancy or shortly after birth. In surviving children, there may be signs such as “Saber Shins,” “Hutchinson teeth,” “deafness,” etc. CS is one of the TORCHes infections1Jaan A, Rajnik M. TORCH Complex. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560528/(other infections include Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, Herpes, etc.)
What causes Congenital Syphilis?
Treponema Pallidium is the cause of Congenital Syphilis. Treponema Pallidum is a spirochete bacteria. Mothers may get with Syphilis infected by coming in contact with a syphilitic sore(chancre). These chancres may be present on the penis, anus, vagina, rectum, lips, mouth, etc. Syphilis also spreads via vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can infect the baby via the mother’s placenta. CS can affect children during and after pregnancy.
What Is The Difference Between Adult And Congenital Syphilis?
The distinction between adult and congenital syphilis lies in how and when the infection is contracted. Adult syphilis typically results from sexual contact, manifesting in various stages and symptoms like sores and rashes, potentially leading to severe complications. In contrast, an infected mother transmits congenital syphilis to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth, potentially causing severe health problems and, if left untreated, even leading to the newborn’s death. The diagnosis process for adults involves blood tests, examination of sores, and an assessment of their sexual history. In the case of congenital syphilis, prenatal screening of the mother and immediate testing of the newborn after birth are crucial for early detection, even if the infant initially shows no symptoms. Treatment for both forms is Pennicllin.
How Common is Congenital Syphilis?
WHO reports that in 2016, every 7 in 1000 pregnant women had Syphilis.2Detail [Internet]. www.who.int. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/syphilis Congenital Syphilis is also rising in prevalence in the US. There were more than 2,000 cases reported in 2021 alone.3STD Facts – Congenital Syphilis [Internet]. www.cdc.gov. 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-congenital-syphilis.htm#:~:text=Congenital%20syphilis%20(CS)%20is%20a Moreover, there is a significant racial disparity in the cases as more CS cases were reported in mothers of African-American and Hispanic descent.
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Congenital Syphilis?
Infected neonates showing signs of syphilis fall into two categories: early congenital (with symptoms appearing from birth to 2 years of age) and late congenital (with symptoms emerging after two years of age).4 Congenital Syphilis – Pediatrics. MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/infections-in-neonates/congenital-syphilis Many patients may also present as asymptomatic. The symptoms of early Congenital Syphilis are:
- Macular copper-colored rash on the palm and soles
- Papular lesions around the mouth and diaper area.
- Enlarged lymph nodes and spleen.
- Hepatomegaly (liver enlargement)
- Jaundice
- Rhinitis
- Failure of the infant to thrive
- Snuffles
- Complications to the nervous system such as meningitis, seizures, and intellectual disability.
- Osteochondritis of the long bones and ribs
Late CS can lead to certain complications in the child. Some of these complications may be permanent. These signs include:
- Gummatous ulcers involving the nose, septum, and hard palate. (Gummas are soft granulomatous swellings)
- Periosteal lesions result in characteristic findings such as “Saber Shins” or Saddle Nose deformity.
- Interstitial keratitis in the eye which may lead to corneal scarring.
- Blindness due to optic atrophy
- Progressive sensory neural deafness.
- Dental anomalies like Hutchinson incisors and Mulberry molars
- Facial anomalies like “Rhadages”
- There may also be intellectual disability, which may present as delayed growth milestones.
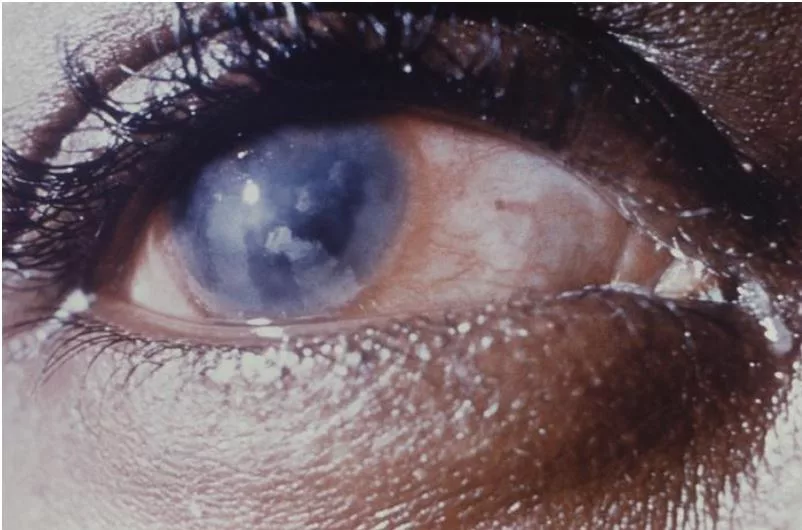
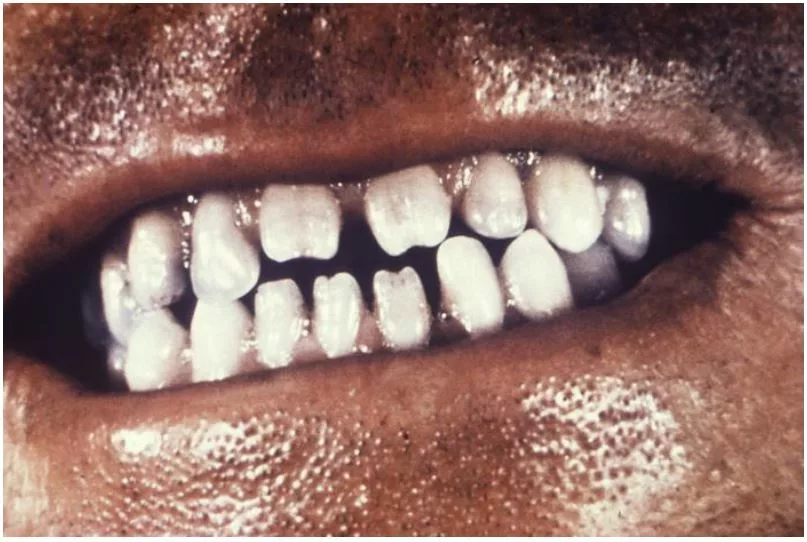
The Characteristic Clinical Signs Of Congenital Syphilis
Congenital Syphilis presents with certain characteristic clinical signs, which may present as:
- Saber shins refer to anterior tibial bowing.
- Hutchinson’s teeth are small, widely spaced, peg-shaped, notched upper incisors with thin, discolored enamel.
- Mulberry molars are molars with many small cusps.
- Rhagades are deep fissuring of mucocutaneous junctions in the nares, lips, and anus.
- Snuffles are mucopurulent blood-stained discharge from the nose.
- Hutchinson’s Triad refers to interstitial keratitis, Hutchinson incisors, and 8th cranial nerve deafness. This finding is diagnostic for congenital syphilis. It is a common presentation of late congenital syphilis.
How Do You Diagnose Congenital Syphilis?
Testing for CS differs for mothers and neonates. Healthcare providers typically screen pregnant mothers for congenital syphilis, adhering to local laws and regulations. These screenings occur at various intervals, both early in pregnancy and later. Neonates born to mothers with a positive Syphilis serology should undergo clinical evaluation for the disease. Testing for mothers and neonates involves
Testing for Mothers
Syphilis screening for pregnant women is a two-step process. The first test is a non-treponemal test like RPR or VDRL. If serology for expectant mothers screened for the disease is positive, healthcare providers perform a treponemal test such as FTA-ABS.
1. Non-Treponemal tests
Doctors use non-treponemal tests like RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagent) or VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Laboratory) for the initial screening of syphilis. These tests detect antibodies that are not specific to Treponema pallidum. A positive result indicates potential exposure to syphilis, but you’ll need further confirmatory tests for a definitive diagnosis. At times, non-treponemal tests may produce false negatives.
2. Treponemal Tests
Treponemal tests, like FTA-ABS, confirm syphilis by detecting specific antibodies to Treponema pallidum. They are highly sensitive and can detect syphilis antibodies even in the early stages. FTA-ABS involves mixing blood with syphilis antigens and fluorescent tags to detect antibodies. A positive result indicates syphilis exposure, while a negative result suggests no syphilis antibodies.
Neonatal Testing
This is done for children born to mothers who are positive for syphilis. Clinical evaluation of neonates includes non-treponemal tests, dark-field microscopy, or immunofluorescent staining of skin or mucosal lesions.5Brown DL, Frank JE. Diagnosis and management of syphilis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(2):283-290. Infants and young children exhibiting CS symptoms or having suggestive serologic test results undergo a lumbar puncture. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) extracted is then analyzed for cell count, VDRL, and protein levels.
Darkfield Microscopy
Dark-field microscopy highlights transparent specimens like microorganisms using angled light, creating contrast. This makes such organisms visible against a dark background. It’s frequently used in microbiology for studying specimens like spirochetes that don’t stain well.
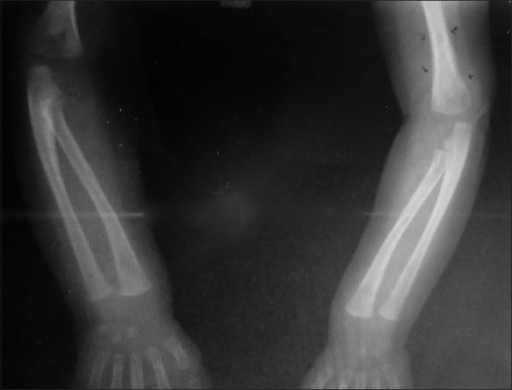
Additionally, physicians may order complete blood count (CBC) with platelet count, liver function tests, and long-bone X-rays. Physicians may also order Chest X-rays, Neuroimaging, and Auditory brain stem response tests. Physicians conduct the Auditor Brain Response test to assess the functionality of the inner ear and auditory brain pathways. Healthcare providers may also order long-bone X-rays to potentially uncover various abnormalities associated with syphilis, including:
- Periosteal reactions6Rathod S, Shah B. Early prenatal syphilis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2010;1(1):39-41. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.73259 such as in the following image.
- Diffuse or localized osteitis
- Metaphysitis
Late congenital syphilis can be diagnosed via clinical history, distinct signs, and serology testing. The triad of Hutchinson teeth, interstitial keratitis, and deafness are usually enough to make a diagnosis.
How Do You Treat Congenital Syphilis?
The preferred treatment for all stages of Syphilis is Penicillin. Treatment of Congenital Syphilis depends on when the disease is confirmed.7Arnold SR, Ford-Jones EL. Congenital syphilis: A guide to diagnosis and management. Paediatr Child Health. 2000;5(8):463-469. doi:10.1093/pch/5.8.463
For patients who are infants to up to 4 weeks of age:
Administer IV Crystalline Penicillin G every 12 hours for seven days. After the initial seven days, switch to giving the IV dosage every eight hours for 10 to 14 days. Alternatively, use Procaine Penicillin G for intramuscular administration for 10 to 14 days. Set the dosage for both IV and IM at 50,000 units/kg.8Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, July 22). Congenital syphilis – STI treatment guidelines. Retrieved August 1, 2024, from https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm
For patients older than four weeks:
Physicians administer IV aqueous Penicillin G at 6-hour intervals, continuing for 10 to 14 days. The dosage is set at 50,000 units/kg. Asymptomatic patients suspected of Syphilis exposure receive a single IM dose of Benzathine Penicillin G.
Before treating pregnant women allergic to Penicillin with Penicillin G, doctors ensure they undergo desensitization. These women are identified through either skin testing or oral oral-graded Penicillin challenge. Infants with congenital syphilis and a Penicillin allergy also undergo desensitization followed by Penicillin G. However, it’s important to note that skin testing is not available in this age group.
What Is The Jarischx Herhiemer Reaction?
Patients infected with spirochetes who undergo antibiotic treatment may experience the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (JHR).9Dhakal A, Sbar E. Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction. 2023 Apr 24. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 32491752. This is a transient clinical phenomenon. The reaction typically occurs within 24 hours of administering antibiotics to treat spirochete infections. The reaction occurs because the body responds to dying spirochetes. Spirochete infections include syphilis, leptospirosis, Lyme disease, and relapsing fever. The JHR commonly presents with fever, chills, rigors, nausea and vomiting, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperventilation, flushing, myalgia, and exacerbation of skin lesions. Severe JHR may lead to death.
What Is The Prognosis Of Congenital Syphilis?
The prognosis is excellent, with an early diagnosis of CS. However, the following groups10Hussain SA, Vaidya R. Congenital Syphilis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537087/ of patients have an increased risk of adverse complications:
- Premature infants
- Those with severe Jarichx Herhiemer Reactions after treatment.
- Patients with severe spread of disease or multi-organ failure
- Delayed diagnosis and treatment present with signs of late CS. Below is a man with characteristic complications from a Congenital Syphilis infection.
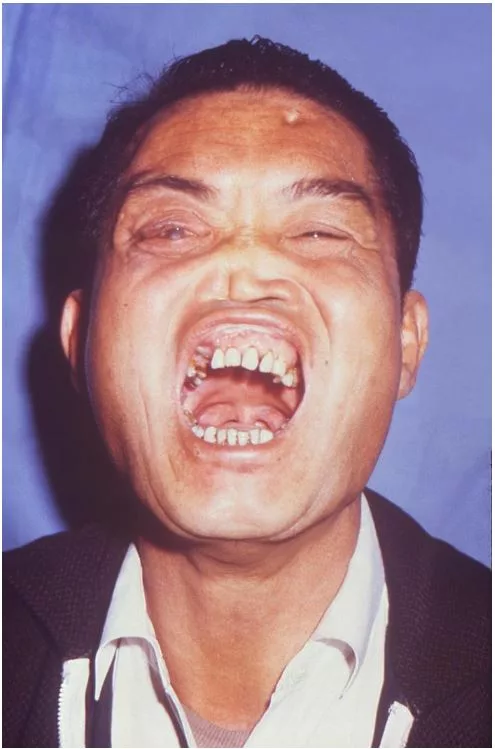
How to Prevent Congenital Syphilis?
Syphilis transmission can be prevented via increased awareness. Other methods to prevent Syphilis spread by not having multiple sex partners, using Condoms, and screening blood transfusions. (There have been rare cases of people acquiring Syphilis via blood transfusions.)11Owusu-Ofori AK, Parry CM, Bates I. Transfusion-transmitted syphilis in teaching hospital, Ghana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(11):2080-2082. doi:10.3201/eid1711.110985
Congenital Syphilis can also be prevented by routine health screenings of pregnant women.12Prenatal Syphilis Screening Laws. www.cdc.gov. Published August 4, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/syphilis-screenings.htm These screenings in the US are done in the 1st trimester. In areas with a higher prevalence of Syphilis, healthcare providers perform repeat screenings for women in the 3rd trimester and at the time of delivery. Adequate treatment during pregnancy effectively cures both the mother and fetus in nearly all cases. When diagnosing congenital syphilis, it is crucial to examine other family members for physical and serologic signs of infection.
Conclusion
Treponema pallidum causes Congenital Syphilis (CS) and is transmitted to the fetus through the placenta. CS is a multi-system disorder. Most cases exhibit early signs like skin lesions, lymphadenopathy, and neurological issues, while later symptoms include ulcers, dental deformities, sensory problems, etc. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and confirmation through serology or microscopy. Treatment of CS involves penicillin. Desensitize infants and pregnant women who are allergic to Penicillin before initiating antibiotic therapy. Screenings of Pregnant mothers are highly effective for the prevention of congenital syphilis.
Refrences
- 1Jaan A, Rajnik M. TORCH Complex. [Updated 2023 Jul 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560528/
- 2Detail [Internet]. www.who.int. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/syphilis
- 3STD Facts – Congenital Syphilis [Internet]. www.cdc.gov. 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-congenital-syphilis.htm#:~:text=Congenital%20syphilis%20(CS)%20is%20a
- 4Congenital Syphilis – Pediatrics. MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/infections-in-neonates/congenital-syphilis
- 5Brown DL, Frank JE. Diagnosis and management of syphilis. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(2):283-290.
- 6Rathod S, Shah B. Early prenatal syphilis. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2010;1(1):39-41. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.73259
- 7Arnold SR, Ford-Jones EL. Congenital syphilis: A guide to diagnosis and management. Paediatr Child Health. 2000;5(8):463-469. doi:10.1093/pch/5.8.463
- 8Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021, July 22). Congenital syphilis – STI treatment guidelines. Retrieved August 1, 2024, from https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/congenital-syphilis.htm
- 9Dhakal A, Sbar E. Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction. 2023 Apr 24. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 32491752.
- 10Hussain SA, Vaidya R. Congenital Syphilis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537087/
- 11Owusu-Ofori AK, Parry CM, Bates I. Transfusion-transmitted syphilis in teaching hospital, Ghana. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17(11):2080-2082. doi:10.3201/eid1711.110985
- 12Prenatal Syphilis Screening Laws. www.cdc.gov. Published August 4, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/syphilis-screenings.htm

