A Scrotal Ultrasound is an imaging modality of the scrotum. It uses sound waves of high frequency to diagnose disorders of the male genitalia. It is a commonly performed procedure because of how safe and quick it is.
What is a Scrotal Ultrasound?
The scrotum is a male reproductive organ present under a man’s penis. Scrotal ultrasound is an imaging scan employed to check your scrotum for abnormalities. It is a non-invasive and low-risk procedure performed by a medical professional experienced in imaging, such as a radiologist, medical technologist, or nurse. It is conducted with a handheld transducer or probe held against your scrotal region. The results are displayed on a screen.
Testicular Vs. Scrotal Ultrasound — What is the difference?
Testicular and scrotal ultrasound usually refer to the same scan. However, from a literal standpoint, testicular ultrasound only visualizes your testicles, while scrotal ultrasound scans examine the other structures in your scrotum alongside your testicles.
What is a Scrotal Ultrasound with Doppler?
Doppler is a sonologic imaging technique. It is used to measure blood flow in various body parts. Scrotal ultrasound with Doppler lets medical professionals check if the blood supply in your scrotum is adequate and has normal direction.1Kühn, A. L., Scortegagna, E., Nowitzki, K. M., & Kim, Y. H. (2016). Ultrasonography of the scrotum in adults. ULTRASONOGRAPHY, 35(3), 180–197. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.15075
Indications for Scrotal Ultrasound
All scrotal conditions show different findings on the ultrasound scan and are managed accordingly after confirming their diagnosis on scrotal ultrasound. Some of the indications include:
Scrotal Pain:
Scrotal pain of all kinds, both acute and chronic, is investigated with ultrasound. This pain can be attributed to a wide variety of causes, such as:
- Testicular torsion refers to a twist in the spermatic cord and causes sudden onset of severe pain.
- Epididymitis or inflammation of the epididymis often causes gradually progressive pain.
- Varicocele, or enlargement of veins inside the scrotum, often causes a dull ache.
Scrotal Masses:
Scrotal masses can be cystic, i.e., fluid-filled or solid. They may or may not be associated with pain and tenderness. This ultrasound can differentiate between a variety of scrotal masses, such as:
- Varicocele
- Hydrocele
- Benign scrotal tumors
- Malignant scrotal tumors
Undescended Testis:
This ultrasound is a common scan for confirming undescended testis or cryptorchidism in both children and adults. When either or both of your testis cannot be seen in the scrotal sac on ultrasound, your doctor will make a diagnosis of undescended testis.2Munden MM, Trautwein LM. Scrotal pathology in pediatrics with sonographic imaging. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2000 Nov-Dec;29(6):185-205. doi: 10.1016/s0363-0188(00)90013-6. PMID: 11104171.
Scrotal Infections:
Scrotal infections are usually marked by the presence of fluid as well as increased blood flow on ultrasound. Examples include:
- Epididymitis
- Orchitis
- Fournier’s gangrene
- Scrotal abscess formation
Scrotal Trauma:
Scrotal trauma can result from injuries, surgical complications, and accidents. Ultrasound in case of scrotal trauma is only performed after pain relief medications have been provided and proper anesthesia has been achieved. It usually shows up in scans as changes in echogenicity, loss of normal contour, and parenchymal changes.

Follow-up:
Even after a diagnosis has been established, this ultrasound is a useful modality in the follow-up of patients. It helps determine if a disorder is improving or not and whether your doctors should go for a change in your treatment plan.3RSNA, A. (2024). Ultrasound – Scrotum. Radiologyinfo.org. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/us-scrotal
Importance of Scrotal Ultrasound
Scrotal ultrasound is a painless, fast, and safe medical procedure for the diagnosis of many male reproductive disorders. It has a high success rate in identifying many testicular abnormalities. For instance, out of 4088 men who underwent this scan for their infertility, around 3% were found to have a testicular mass, which prompted further medical investigation. In addition, when it comes to testicular torsion, scrotal ultrasound has 100% sensitivity, 98.1% diagnostical accuracy, and 97.9% specificity. Such statistics make this ultrasound an irreplaceable modality despite the emergence of tests like CT and MRI scans.4Liang, T., Metcalfe, P., Sevcik, W., & Noga, M. (2013). Retrospective Review of Diagnosis and Treatment in Children Presenting to the Pediatric Department With Acute Scrotum. American Journal of Roentgenology, 200(5), W444–W449. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.12.10036
Contraindications for Scrotal Ultrasound
There are no absolute contraindications that should make you or your doctors opt out of a scrotal ultrasound. These scans do not involve radiation or the use of contrast, so they are safe for all populations. Relative contraindications include:
- In conditions where you are in severe pain, such as testicular torsion, scrotal scans are avoided until adequate pain relief has been provided.
- Scrotal scans are avoided if you have open or lacerating wounds in your genital region.
- Scrotal ultrasounds are also avoided right after surgery or recent trauma.5Testicle Ultrasound. (2019, August 13). Ucsfhealth.org.https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/scrotal-ultrasound
What to do for Scrotal Ultrasound Preparation?
You don’t have to do much while preparing for your scrotal ultrasound. It does not require any dietary restrictions or lifestyle modifications. You can simply visit the radiology and imaging department of the hospital where you have booked your exam, where you will be asked to wait in the Ultrasonography room’s waiting area. After that, you will be led to the examination room.
Since the procedure is painless and does not require anesthesia or sedation, you will just be asked to remove your clothing from the waist down and lie on a padded examination table. A nurse will give you a sheet to cover yourself, too.
Equipment used for Scrotal Ultrasound
This scan usually does not require a lot of equipment. The main components of a regular scrotal ultrasound setup include:
- An ultrasound machine that converts sound waves into images
- An ultrasound transducer or probe that emits sound waves towards your body parts and receives the signals that they “echo” back towards it
- An ultrasound gel that helps conduct sound waves better
- A computer monitor to display the results of the ultrasound scan
- A patient bed or examination table for you to lie down on while the ultrasound is performed
- An adjustable light source above the patient
Step-by-Step Procedure for Scrotal Ultrasound
This ultrasound procedure does not take more than half an hour. It takes place in the Ultrasonography section of a hospital’s radiology department or an imaging clinic.
Position During Ultrasound
You will be asked to lie in the supine position for your ultrasound procedure, i.e., on your back. You will be covered with a sheet or drape, leaving just your scrotum exposed to the medical professional performing the scan.
Anesthesia During Ultrasound
It does not require the use of any anesthetic or sedative drug. However, in emergency trauma cases where it is the only modality of choice, your doctors will consult your hospital’s Anesthesia and Pain Management department about what medication to offer you for pain relief prior to the ultrasound.
During the Procedure
The actual procedure is short and consists of just a few steps:
- Your doctor will place a towel underneath your scrotum for additional support. They may also ask you to hold your penis against your abdomen. This will let them have an unobstructed view of your scrotal area.
- They will apply a thin layer of ultrasound gel to your scrotum. This will improve the conduction of noise, as well as get rid of any air that can interfere with the ultrasound procedure.
- Next, they will adjust the ultrasound machine to a frequency between 7.5 and 15 MHz, as this frequency provides clear imaging of superficial body structures like the scrotum.
- Your scrotum will first be scanned transversely to check both testes. Next, longitudinal scans from top to bottom will be performed.
- Your doctor may also perform specialized Doppler scans to visualize blood supply and other soft tissues.
- Once all necessary images have been captured, your doctor will wipe the ultrasound gel off of your scrotum.6Tyloch, J. F., & Wieczorek, A. P. (2016). Standardy badania ultrasonograficznego moszny. Journal of Ultrasonography, 16(67), 391–403. https://doi.org/10.15557/jou.2016.0039
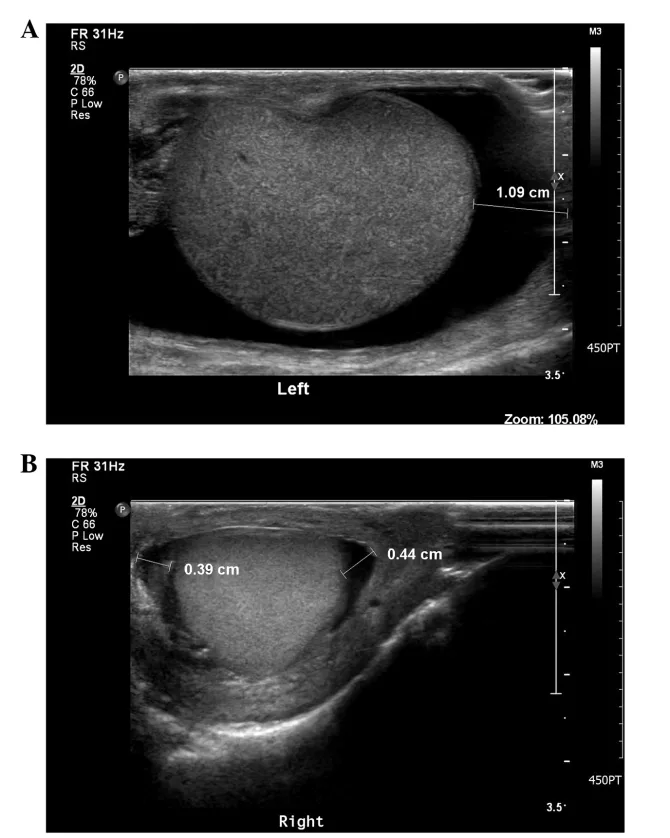
What to do after a Scrotal Ultrasound?
You can get dressed and go home immediately after this procedure. It is an outpatient procedure, so you don’t need to stay at the hospital. In addition, as it is a non-invasive and risk-free procedure, you can resume your daily activities right after a scrotal ultrasound.
Result Interpretation for Scrotal Ultrasound
The results of this ultrasound will be announced depending on the urgency of your scan. The report may be available instantly or in a few days and may have normal or abnormal findings.
Normal Scrotal Ultrasound Findings:
Normal scrotal ultrasound findings show that your tested and their surrounding structures are in sound health, such as:
- Testes are symmetrical in size and shape and have a homogenous echotexture
- Epididymis is similar in shape and echotexture to the testes
- The scrotal wall is thin and uniform and does not have any irregularities or thickenings
- If performed, Doppler shows normal, low resistance flow of arterial and venous blood throughout the scrotal sac and its components
Abnormal Scrotal Ultrasound Findings
In contrast, abnormal scrotal ultrasound findings show deviations from normal results. For example:7Sharma, R. (2024). Testicular and scrotal ultrasound. Radiopaedia. https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-33262′
| Condition | Scrotal Ultrasound Findings |
| Testicular torsion | Enlarged and heterogeneous testis
Reduced or absent blood flow in the testis that is affected |
| Epididymitis | Enlarged and hypoechoic testis with increased blood flow |
| Varicocele | Dilated scrotal veins larger than 2-3 mm in diameter, paired with a characteristic “bag of worms” look |
| Hydrocele | Fluid-filled, anechoic space surrounds the testis |
| Spermatocele | Well-defined, anechoic epididymal cyst with posterior acoustic enhancement se |
| Testicular tumor | Irregularly shaped hypoechoic or heterogeneous mass, with increased blood flow in case of malignant tumors |
| Undescended testis | The absence of testis in the scrotal sac appears as a homogeneously hypoechoic oval-shaped stricture |
| Scrotal abscess | Accumulation of fluid in a mass, hypoechoic region in the scrotum |
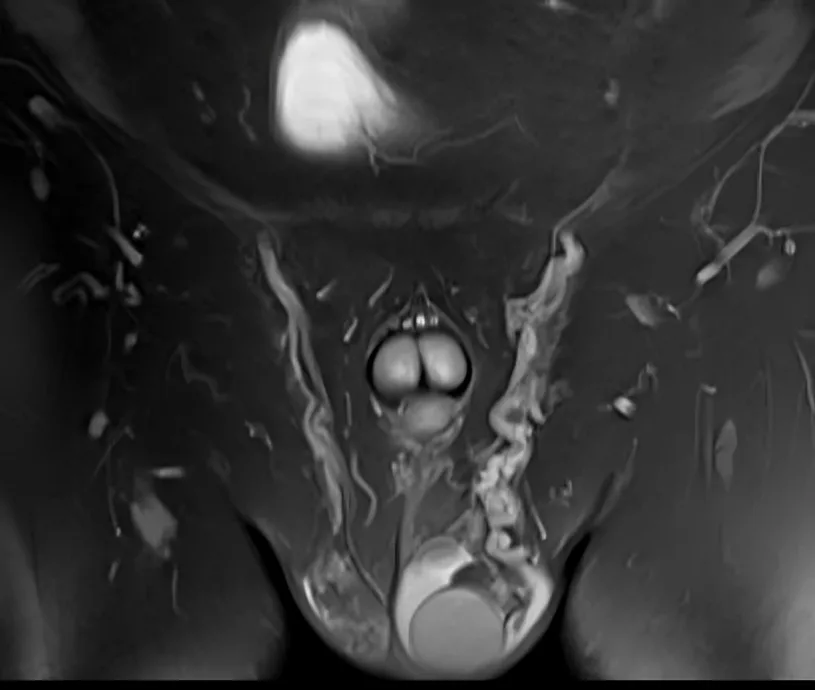

Side Effects of Scrotal Ultrasound
There are no risks for the ultrasound scan, and only a small number of patients experience side effects such as:
- Mild discomfort from coming into skin-to-skin contact with an ultrasound probe in a sensitive body region
- Skin irritation from prolonged contact with ultrasound gel
- Some patients may experience psychological stress or anxiety from an ultrasound scan of such nature.8Clinic, C. (2024, June 13). A testicular ultrasound is a noninvasive imaging test. Healthcare providers use it to diagnose and treat conditions that affect your testicles and surrounding areas. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/testicular-ultrasound
Is Scrotal Ultrasound Painful?
It is not a painful procedure. However, it may be painful depending on the discomfort you are already experiencing because of a scrotal disorder. In addition, some individuals have sensitive skin and may feel some pain upon the application of ultrasound gel or ultrasound probe on their skin.
Is it normal to get erect during a Testicular Ultrasound?
A penile erection is a normal body response of the male genitalia to physical touch, so it is completely normal if you get erect during a testicular ultrasound procedure. It is also not a shock for your medical team as they routinely see patients experience erections during various exams of the scrotal region.
Can Scrotal Ultrasound detect Infection?
These ultrasound scans can detect and differentiate between a wide variety of testicular disorders, including infections of the scrotum. Infections usually show up as hypoechoic, edematous swellings on the ultrasound scans.
Do I need to shave before the Scrotal Ultrasound?
It is not necessary to shave before this ultrasound. However, some healthcare setups require patients to shave their genital regions, as this improves contact and reduces friction between your skin and the ultrasound probe. The absence of hair in your scrotal region also reduces the chances of artifacts showing up in your exam findings.
Conclusion
A scrotal ultrasound is a readily available ultrasound of the scrotal region. It allows medical experts to visualize the internal structure of your male genitalia. It is used to diagnose conditions such as testicular torsion, undescended testis, and epididymitis. Moreover, this ultrasound is also used as a go-to follow-up scan in the management of testicular disorders. It is a safe and fast outpatient procedure, and you can go home immediately once it is over.
Refrences
- 1Kühn, A. L., Scortegagna, E., Nowitzki, K. M., & Kim, Y. H. (2016). Ultrasonography of the scrotum in adults. ULTRASONOGRAPHY, 35(3), 180–197. https://doi.org/10.14366/usg.15075
- 2Munden MM, Trautwein LM. Scrotal pathology in pediatrics with sonographic imaging. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2000 Nov-Dec;29(6):185-205. doi: 10.1016/s0363-0188(00)90013-6. PMID: 11104171.
- 3RSNA, A. (2024). Ultrasound – Scrotum. Radiologyinfo.org. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/us-scrotal
- 4Liang, T., Metcalfe, P., Sevcik, W., & Noga, M. (2013). Retrospective Review of Diagnosis and Treatment in Children Presenting to the Pediatric Department With Acute Scrotum. American Journal of Roentgenology, 200(5), W444–W449. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.12.10036
- 5Testicle Ultrasound. (2019, August 13). Ucsfhealth.org.https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/scrotal-ultrasound
- 6Tyloch, J. F., & Wieczorek, A. P. (2016). Standardy badania ultrasonograficznego moszny. Journal of Ultrasonography, 16(67), 391–403. https://doi.org/10.15557/jou.2016.0039
- 7Sharma, R. (2024). Testicular and scrotal ultrasound. Radiopaedia. https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-33262′
- 8Clinic, C. (2024, June 13). A testicular ultrasound is a noninvasive imaging test. Healthcare providers use it to diagnose and treat conditions that affect your testicles and surrounding areas. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/testicular-ultrasound

