Wound dehiscence occurs when a surgical incision reopens either internally or externally. Dehiscence is the partial or complete separation of wound edges that were previously closed, resulting from a failure in the normal wound healing process. It is a surgical complication where a wound comes apart entirely or partially. Surgical wound dehiscence usually occurs at the early stages of wound healing, within 5 to 8 days after surgery.1Rosen RD, Manna B. Wound Dehiscence (2022 May 8). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan. Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551712/
Although wound disruption may occur after any surgery, it is most common in abdominal and cardiac surgeries. According to the Tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), the code for surgical wound dehiscence is T81.31. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies this condition under the category of injury, poisoning, and other external factors.
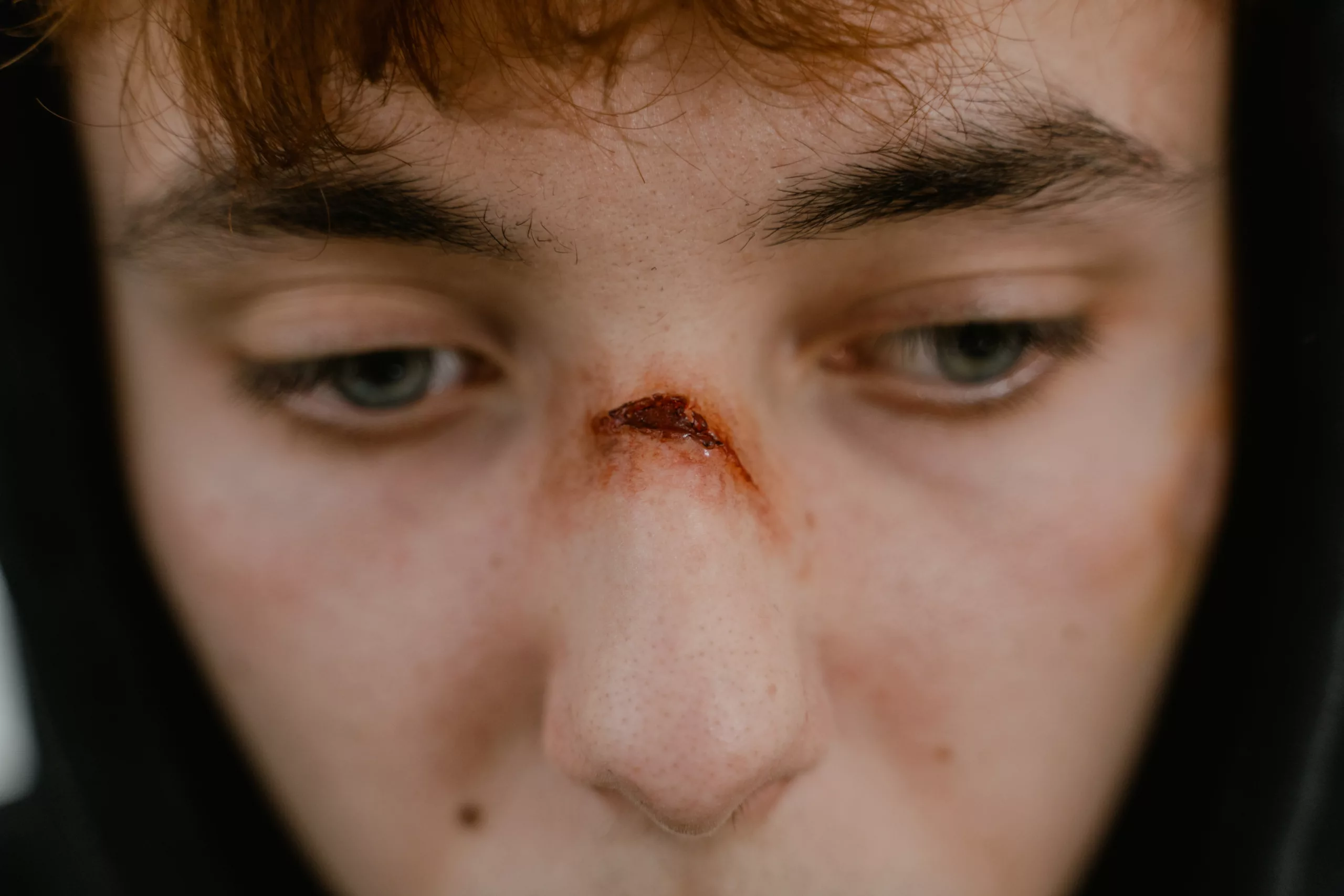 Types of Wound Dehiscence
Types of Wound Dehiscence
- Partial Dehiscence: It refers to pulling apart a small wound area.
- Total Dehiscence: Complete dehiscence is when the whole cut reopens across all layers of skin and muscles.
- Abdominal Wound Dehiscence: It occurs when the layers of an abdominal wound separate due to improper healing. It is a life-threatening cause of morbidity and mortality following a surgical procedure.2Sandy-Hodgetts, K., Carville, K., & Leslie, G. D. (2013). Determining risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence: a literature review. International Wound Journal, 12(3), 265–275. Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12088
- Perineal Wound Dehiscence: Perineal wound dehiscence is caused by the breakdown of sutures. It might happen due to pressure on sutures or an infection leaving the wound open.
- Wound Dehiscence C-section: It is also known as postpartum uterine dehiscence. It occurs when the surgical incision opens after a cesarean section.
Phases of Wound Healing
Wound healing commonly occurs in the following four phases:3Ozgok Kangal MK, Regan JP. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): May 1, 2023. Wound Healing.
- Hemostasis: Blood vessels contract to reduce bleeding. Platelets form a blood clot together with fibrin to avoid further blood loss.
- Inflammation: Blood vessels dilate to remove bacteria and debris from the injury site.
- Proliferation: New tissues and blood vessels are formed to replace the ones damaged due to injury.
- Maturation: The remodeling phase where newly formed tissues strengthen and become elastic enough to heal the wound.
Causes of Wound Dehiscence
It occurs due to an improper healing process.4Wernick B, Nahirniak P, Stawicki SP. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Aug 28, 2023. Impaired Wound Healing. Wounds may pull apart during any phase of healing, mainly due to the following factors:
Infection
An infected wound remains in the inflammatory phase to remove bacteria from the site of infection. Therefore, the newly formed tissues do not mature and remain weak.
Poor Suture Technique
Suturing material and technique have an impact on wound healing. Inappropriately applied sutures neither provide enough mechanical support nor closure to the wound.
Pressure on Sutures
Activities that strain sutures may break them. For instance, coughing, lifting weights, and vomiting put pressure on sutures. Splitting a single suture can lead to the opening of surgical cuts.
Decreased Blood Flow
Adequate blood supply is vital to the wound because cells require oxygen and nutrition for repair. Damaged cells and debris are also removed from the wound site through blood. Factors that hinder blood supply to a wound may lead to its disruption.
Risk Factors of Wound Dehiscence
Various factors make a person susceptible to dehiscence. Some of the common risk factors associated with the condition are as follows:5Sandy-Hodgetts, K., Carville, K., & Leslie, G. D. (2015). Determining risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence: a literature review. International Wound Journal, 12(3), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12088
- Age
- Infection6Walming, S., Angenete, E., Block, M., Bock, D., Gessler, B., & Haglind, E. (2017). Retrospective review of risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence and incisional hernia. BMC Surgery, 17(1). Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-017-0207-0
- Obesity
- Malnutrition
- Emergency surgery7Teklemariam, B. T., Biyana, C. F., & Asfaw, S. A. (2022). Determinants of Postoperative Abdominal Wound Dehiscence among Patients Operated in a Tertiary Hospital. Ethiopian journal of health sciences, 32(4), 739–746. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v32i4.10
- Gender
- Respiratory or cardiovascular disorders
- Steroids
Wound Dehiscence Symptoms
Wounds may split open even if they seem to be healing. Check your wound regularly to ensure it is healing correctly. If you notice any of the following signs or symptoms, immediately seek medical help.
- Pulling sensation and pain
- Signs of infection (redness, pus, swelling, heat, etc.)
- Bleeding
- Fever
- Broken sutures
- Open Wound
- Fluid leakage
Complications of Wound Dehiscence
If left unchecked, wound dehiscence may cause severe complications and life-threatening infections. Seek immediate medical help even if you notice minor dehiscence signs; otherwise, wounds will worsen. Severe cases of complete dehiscence may lead to the excision of organs through the open wound.
How is Wound Dehiscence Treated?
Multiple treatment options are available according to the cause of dehiscence. Your doctor will choose any method according to the severity and cause of wound disruption. The most common methods are:
Management of Risk Factors
Your doctor will identify and try to minimize the factors contributing to dehiscence. For instance, if dehiscence occurs due to pus accumulation, he can remove excess fluid from the wound. Similarly, he can control blood sugar levels if you are a diabetic patient.
Pain Management
Your physician might prescribe you a painkiller to relieve pain due to wound disruption. He might use a different type of dressing that reduces pain. The doctor can suggest ways to preserve the wound that causes less pain.
Antibiotics
Your doctor will prescribe antibiotics if a bacterial or viral infection causes wound dehiscence or if infection is possible. Antibiotics are medications that slow down or inhibit the growth of microorganisms that cause infection. They also help heal wounds.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) treats wounds draining fluid. It involves a closed wound dressing fastened to a vacuum pump. It is used to suck the fluid away from the wound. Your doctor may use NPWT to promote wound healing and reduce the chances of infection.8Sandy-Hodgetts K, Leslie GD, Parsons R, Zeps N, Carville K. Prevention of postsurgical wound dehiscence after abdominal surgery with NPWT: a multicentre randomized controlled trial protocol. J Wound Care. 2017 Feb;26(Sup2):S23-S26. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.Sup2.S23. PMID: 28182535.
Removal of Dead Tissue
Any dead tissue present at the site of the wound slows down the healing process and increases the likelihood of infection. Your doctor might use a special dressing on your wound that helps remove dead cells from it. However, if the dead tissue is large and deep, he will go for a surgical procedure for its removal.
Closure
The doctor might close the disrupted wound again using stitches. Otherwise, he may leave the wound open and let it heal independently. In case of complete dehiscence, you may require surgery to restore the dehisced wound.
When to Contact Your Physician?
You need immediate medical assistance if you face any of the symptoms mentioned above. Moreover, contact your physician for consultation if you feel fever, nausea, vomiting, or severe pain. Notice your wound for any fluid leakage or bleeding.
Prevention of Wound Dehiscence
Taking some precautions to enhance wound healing can prevent the risk of dehiscence. Some preventive measures you can adopt are:
- Use antibiotics before and after surgery to reduce the likelihood of infection.
- Restrain from exercise or any activity that strains the wound.
- Keep your wound clean and change the dressing regularly.
- Apply your dressing using an appropriate technique.
- Take a nutritious diet particularly rich in proteins.
Conclusion
Wound dehiscence is a surgical complication that usually occurs during the early phases of wound healing. It happens when a surgical wound fails to heal, and the incision reopens. Wound disruption may lead to severe complications if the condition is left unchecked. Closely monitor the healing of wounds and adopt specific preventive measures to avoid this situation. Still, if you notice signs of dehiscence, seek immediate medical help.
Refrences
- 1Rosen RD, Manna B. Wound Dehiscence (2022 May 8). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan. Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551712/
- 2Sandy-Hodgetts, K., Carville, K., & Leslie, G. D. (2013). Determining risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence: a literature review. International Wound Journal, 12(3), 265–275. Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12088
- 3Ozgok Kangal MK, Regan JP. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): May 1, 2023. Wound Healing.
- 4Wernick B, Nahirniak P, Stawicki SP. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Aug 28, 2023. Impaired Wound Healing.
- 5Sandy-Hodgetts, K., Carville, K., & Leslie, G. D. (2015). Determining risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence: a literature review. International Wound Journal, 12(3), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12088
- 6Walming, S., Angenete, E., Block, M., Bock, D., Gessler, B., & Haglind, E. (2017). Retrospective review of risk factors for surgical wound dehiscence and incisional hernia. BMC Surgery, 17(1). Retrieved 2023 April 20 from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-017-0207-0
- 7Teklemariam, B. T., Biyana, C. F., & Asfaw, S. A. (2022). Determinants of Postoperative Abdominal Wound Dehiscence among Patients Operated in a Tertiary Hospital. Ethiopian journal of health sciences, 32(4), 739–746. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v32i4.10
- 8Sandy-Hodgetts K, Leslie GD, Parsons R, Zeps N, Carville K. Prevention of postsurgical wound dehiscence after abdominal surgery with NPWT: a multicentre randomized controlled trial protocol. J Wound Care. 2017 Feb;26(Sup2):S23-S26. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.Sup2.S23. PMID: 28182535.

