Brachioplasty involves resectioning skin and subcutaneous fat to improve the contour of the axilla and upper limb. This procedure reshapes the arm and makes it appear smoother.
What Is Brachioplasty?
Brachioplasty, also known as the Arm lift procedure, is performed to remove excess skin and superficial tissue and destroy excessive fat in the upper arm, axilla, and lateral chest wall. It is mostly performed on old patients, pregnant women, and after massive weight loss.
According to the American Society Of Aesthetics, twenty thousand brachioplasty procedures were performed in 2015.1The Aesthetic Society’s Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank: Statistics 2019. (2020). Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 40(Suppl 1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa144
The amount of subcutaneous tissue and fat varies. Hence, the choice of procedure depends on the patient’s age and degree of skin and subcutaneous tissue.2Teimourian, B., & Malekzadeh, S. (1998). Rejuvenation of the upper arm. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 102(2), 545–553. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199808000-00041.08.004.
Indications Of Brachioplasty
There are the following indications of Brachioplasty:
- Brachioplasty is indicated in patients who have a recent massive weight loss.
- It is used to reduce skin laxity in old age.
- It reduces the elasticity or laxity of the skin after pregnancy.
- Extra skin fold thickness causes inflammation, rash, dehydration, poor hygiene, and poor self-esteem.
- People who have upper arm laxity.
- Patients who lost weight after surgery (bariatric Surgery) are now maintaining a stable weight for three to six months or, most preferably, one year.
Which Patients Are Fit For Brachioplasty?
The following patients are ideal candidates for Brachioplasty:
- It is suitable for patients having a body mass index less than 30 because if you have a body mass index greater than thirty, there are chances of complications. 3Coon, D., Gusenoff, J. A., Kannan, N., El Khoudary, S. R., Naghshineh, N., & Rubin, J. P. (2009). Body mass and surgical complications in the postbariatric reconstructive patient: analysis of 511 cases. Annals of surgery, 249(3), 397–401. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e318196d0c6
- Healthy individuals who have no other comorbidities like diabetes and hypertension.
- People who are not smokers are fit for the surgery. If the patient is a smoker, the doctor advises him/her to quit smoking at least four months before surgery because smokers have an increased risk of complications.4Coon, D., Tuffaha, S., Christensen, J., & Bonawitz, S. C. (2013). Plastic surgery and smoking: a prospective analysis of incidence, compliance, and complications. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 131(2), 385–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318277886a
- If the patient has any psychiatric illness, it should be treated first because people who have realistic expectations of the surgery are good candidates for surgery.
- Patients who do not use herbal medicines because they may impair the wound healing process.
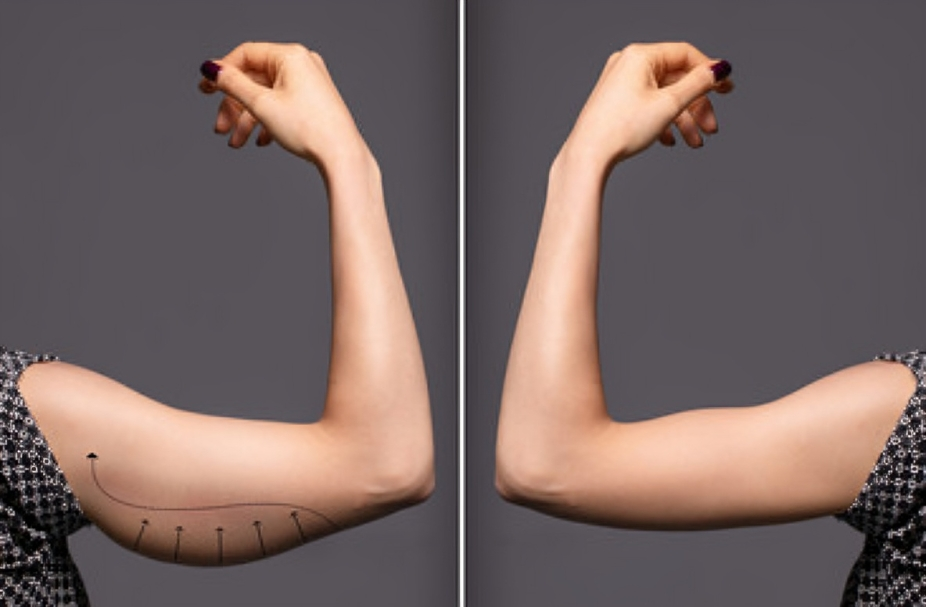
Brachioplasty before and after
How To Prepare A Patient For Brachioplasty?
Preparation of the patients for Brachioplasty involves the following steps:
History:
- Your doctor will ask about the history of weight loss, smoking, use of herbal medicines, and any psychiatric illness before Brachioplasty.
- He will inquire about the history of diabetes, hypertension, deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in previous surgeries, family history of deep venous thrombosis, and history of any other medical illness.
- He may discuss your expectations from this surgery and what results you expect.
Examination:
Your doctor performs a complete medical and physical examination before performing brachioplasty. The doctor will thoroughly assess your nutritional status and check your weight and body mass index.
Laboratory Investigations:
Laboratory investigations before surgery include:
- Complete blood count
- Blood glucose levels
- Urine analysis
- Coagulation profile
- Lipid profile
- Blood chemistry
- Blood glucose levels
- Echocardiography
- Lung function tests
- Kidney function tests
- Infection screening
Informed Consent:
Your doctors will counsel you about the brachioplasty procedure. After explaining the steps and any associated risks, they will ask you to sign a document as proof of your informed consent.
What Precautions Should You Follow Before Surgery?
Your doctor or nurse will counsel you about the dos and don’ts before the surgery and the diet and medicine you need to take.
- Tell all the relevant history correctly and carefully.
- Your doctor will ask you to fast for at least 6 hours before brachioplasty, so don’t have a whole meal or drink before your procedure.
- If you need to drink water, only take a small sip. Don’t drink anything 2 hours before surgery.
- Do not take meals or drinks.
- Don’t shave the site immediately before coming for surgery.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Brachioplasty
Preparation Of The Patient:
Highly experienced surgeons and their team perform Brachioplasty.
- The patient is placed supine, arms are abducted, and elbows are flexed at 90 degrees.
- The forearms and hands are covered in the drapes. It provides the desired mobility during the surgery.
- The operation theatre staff places gel pads under your arms to protect them from the injury of your arms.
- They place warm blankets, gel, and Bair huggers (warming system) and give warm intravenous fluids to prevent hypothermia.
- They will give you prophylactic antibiotics like amoxicillin-clavulanate thirty minutes before the surgery.
- The anesthesiologist will give you general anesthesia, and you will be in sedation.
- They will expose your arms, axilla, and lateral chest wall.
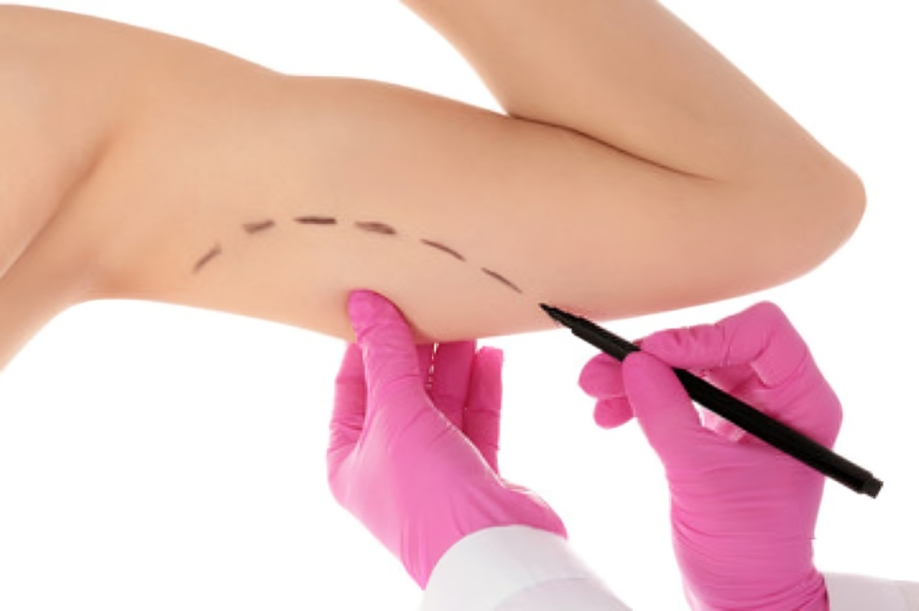
Marking for Brachioplasty
Procedure Of Brachioplasty:
The Brachioplasty procedure has the following steps:
- The surgeon accesses the area before surgery and performs liposuction of your arm, axilla, and lateral chest wall.
- After that, they will make an incision on the back of your arm, start dissecting, and remove extra fat from that area.
- The surgeons remove the superficial layer of fat and preserve the deep fascia, which protects the medial brachial cutaneous and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves.
- After the fat and the target skin area have been removed for Brachioplasty, the surgeons place a scar medially in the bicipital groove. These scars have different shapes, including W, S, and L-shaped scars and Z plasties.5Miotto, G., & Ortiz-Pomales, Y. (2018). Arm Contouring: Review and Current Concepts. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 38(8), 850–860. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx218
- In the final step, the surgeons secure hemostasis and close the wound after that.
- First, they approximate the layers of the deep fascia, then they close the superficial fascia and the layers of skin and apply sutures in the final step. In this process, they close the skin using a three-point closure technique because it reduces dead space.6Egrari S. (2016). Brachioplasty: A Personal Approach. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 36(2), 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjv146
- The surgeons apply a tube in your arm to drain the surgical wounds. Then, they dress the wound and apply compression garments over the limb.
- They give deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis to the patient using anticoagulant drugs and post-operative antibiotics to the patients.
- The doctor advises regular check-ups, and they discharge patients on the same day as the surgery.
Technique For Brachioplasty/ Types Of Brachioplasty:
Some techniques for brachioplasty include the following:
Posterior Arm Brachioplasty:
Some doctors perform posterior arm brachioplasty in which the surgeon places the scars in the brachial sulcus. They do it for cosmetic reasons because the scar is less visible from the front.
Brachioplasty With Minimal Scar:
For cosmetic reasons, surgeons perform minimal access Brachioplasty, where a small scar is concealed in the axilla (armpit).7Reed L. S. (2014). Brachioplasty with a limited scar. Clinics in plastic surgery, 41(4), 753–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2014.06.009
Patients with massive weight loss are unfit for this surgery. Minimal Scar Brachioplasty is a successful alternative to traditional long scar brachioplasty.
L Shaped Brachioplasty:
In L-shaped brachioplasty, your doctor makes an incision in a curvilinear pattern extendable from the axilla to the lateral chest wall.
Post Operative Care
Post-operative care for Brachioplasty includes the following measures:
- Your doctor will advise you to use oral analgesics for two weeks. Use your medications as advised.
- Do not do strenuous exercise for two weeks.
- Avoid driving for two weeks.
- Use compression garments for four weeks.
- Take prophylactic antibiotics for two weeks as advised by your doctor.
- Take good care of the wound and maintain hygienic measures.
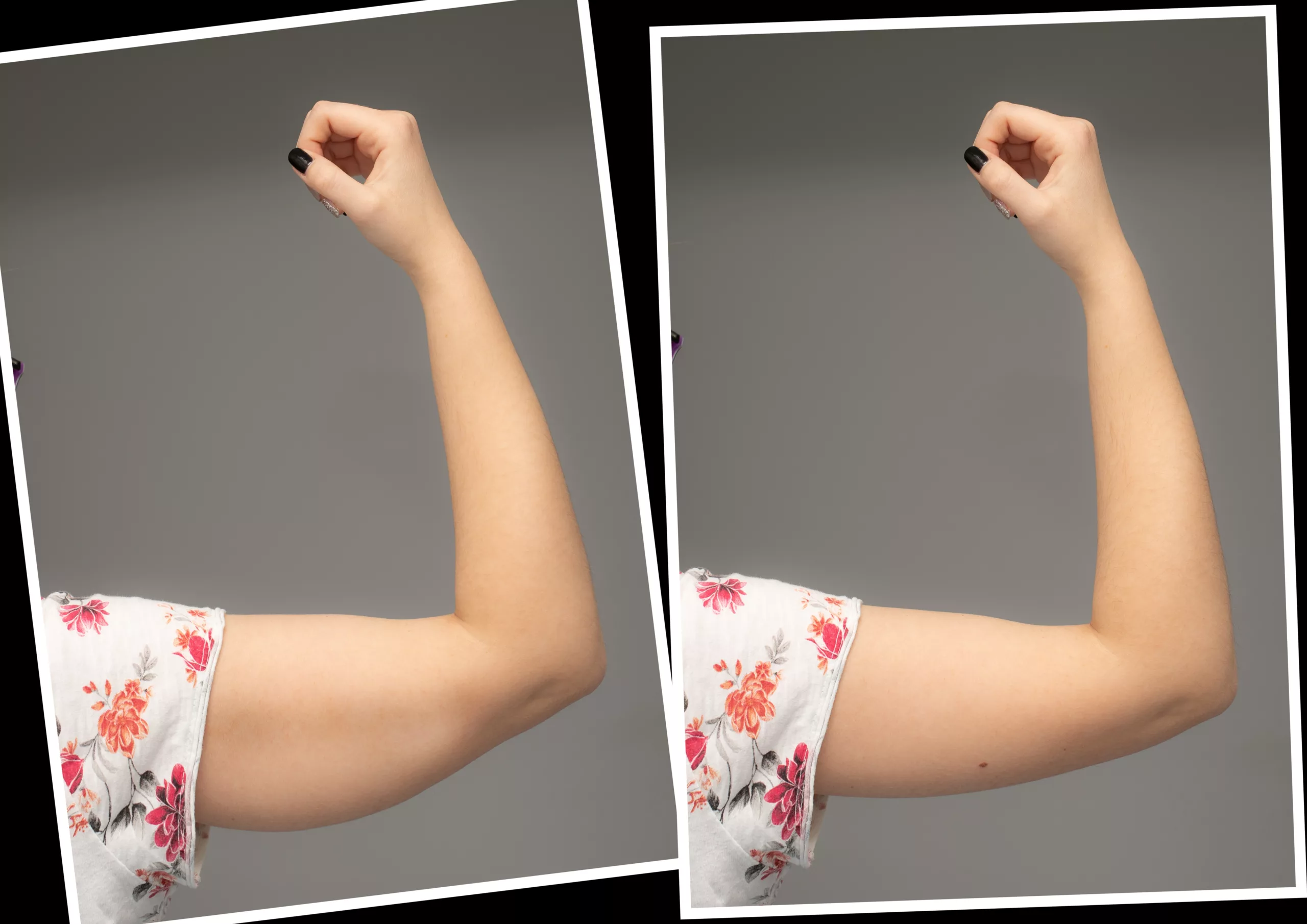
Before and after Brachioplasty
Complications Of Brachioplasty
Brachioplasty has the following complications:
- Infections can disrupt wound healing, and unfavorable scarring may occur.
- Wound dehiscence may occur if you don’t properly care for your wound or do not use prophylactic antibiotics.
- There is a chance of recurrence of fat deposition, and you may need a second surgery for that.
- Infections may occur. They usually occur if you don’t use antibiotics or you do not take care of your wound.
- A seroma is a fluid collection in the wound area surrounded by skin. It is one of the common complications of brachioplasty.
- Lymphedema is the collection of lymphatic fluid around the wound, and it may occur after brachioplasty.
- Hematoma (collection of blood) may form after brachioplasty.
How To Prevent Complications Of Brachioplasty?
To avoid complications during Brachioplasty, highly skilled surgeons should not prolong the duration of surgery unnecessarily. Follow your doctor’s instructions. If you have massive weight loss, your doctor may divide Brachioplasty into multiple stages to prevent operative complications, complications of anesthesia, blood loss, and other complications.8Kokosis, G., & Coon, D. (2019). Safety in Body Contouring to Avoid Complications. Clinics in plastic surgery, 46(1), 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2018
Compartment Syndrome After Brachioplasty
Acute compartment syndrome is a serious complication of Brachioplasty, but it is rare. It occurs due to excessive pressure over the skin, which compresses underlying muscles, nerves, and vessels, resulting in their necrosis. The symptoms of compartment syndrome include pain, skin pallor, weakness, and inability to move the limbs.
Excess skin or fat removal tightens the remaining skin and causes compartment syndrome. Another reason behind compartment syndrome is the long duration of surgery. If the surgeon takes too long for the surgery, your arm will swell too much to close it. Afterward, when the surgeon forcefully pushes the skin, it exerts pressure on underlying structures, leading to compartment syndrome. Sometimes, it can occur itself despite the correct procedure for surgery.
Your doctor will perform a fasciotomy to treat it. Immediate fasciotomy is essential.
What Are The Alternatives To Brachioplasty?
BodyTite:
BodyTite is a less invasive arm lift procedure. In this process, the BodyTite probe emits radiofrequency radiations that heat your body to 65 degrees Celsius, which destroys the fat and skin and improves the contour of your arms. It has relatively fewer complications and is an easy procedure with a few skin incisions. However, it can not be performed in very obese people.
Renuvion (Skin Tightening):
In this process, your doctor shrinks the saggy skin and coagulates fats using thermal energy. Surgeons make small skin incisions that heat tissues to 85 Celsius. It is a relatively easy procedure with fewer complications. Bruising and swelling can occur, and the results take almost six months to show.
Laser Liposuction:
Laser liposuction is a relatively harmless procedure. Your doctor will make a few tiny incisions in your skin, and laser energy will be used to remove the extra fat. It lifts the saggy skin more effectively and tightens it. However, if you had bariatric surgery earlier, your doctor will prefer brachioplasty over laser liposuction.
Cool Sculpting:
Cool sculpting uses Cryo lipolysis, a fast-freezing technology that targets fat and freezes it. Some patients complain it is painful, but there is no need for skin incisions. Its side effects are bruising, pain, and discomfort.
VASER Liposuction:
VASER liposuction breaks down excess fats by using a hollow vacuum tube that emits acoustic waves to melt the fat in your arms. It does not tighten your saggy arms, but surgeons consider it a gold standard for burning fat.
Liposuction Vs. Brachioplasty
Liposuction and brachioplasty are similar in that both of them improve the contour of your arms. In brachioplasty, doctors make incisions on the skin, which can leave large scars. Complications after the surgery include wound infection, hematoma, seroma, and compartment syndrome. Comparatively, liposuction removes large pockets of fats from your arms without large skin incisions. It involves the use of laser beams to destroy unnecessary fats. Liposuction is relatively harmless compared to brachioplasty as there is no risk of incision leaving a large scar or post-surgical complications. It is an easy and less time-consuming procedure compared to brachioplasty. Moreover, liposuction is a short procedure, while brachioplasty can have many stages.
Which Procedure Is Preferred For Obese People?
Liposuction is less effective for removing fat from the arms of very obese people. Moreover, there are more chances of recurrence of laxity and arm folds after liposuction in obese people than after brachioplasty. Brachioplasty is preferred for obese people as it gives the expected results in people with high BMI. If you are not obese, you can go for a liposuction process like laser liposuction.
Conclusion
Brachioplasty, or arm lift, is an effective way of removing excessive fat from your arms. It is a surgery that requires expertise and care to avoid complications. If an experienced team of surgeons performs it, it gives effective results and improves the contour of your arm. Compartment syndrome is the major complication of this surgery, but experienced surgeons take less time to perform Brachioplasty to prevent this complication. It has excellent results.
Refrences
- 1The Aesthetic Society’s Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank: Statistics 2019. (2020). Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 40(Suppl 1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa144
- 2Teimourian, B., & Malekzadeh, S. (1998). Rejuvenation of the upper arm. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 102(2), 545–553. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199808000-00041.08.004.
- 3Coon, D., Gusenoff, J. A., Kannan, N., El Khoudary, S. R., Naghshineh, N., & Rubin, J. P. (2009). Body mass and surgical complications in the postbariatric reconstructive patient: analysis of 511 cases. Annals of surgery, 249(3), 397–401. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e318196d0c6
- 4Coon, D., Tuffaha, S., Christensen, J., & Bonawitz, S. C. (2013). Plastic surgery and smoking: a prospective analysis of incidence, compliance, and complications. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 131(2), 385–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318277886a
- 5Miotto, G., & Ortiz-Pomales, Y. (2018). Arm Contouring: Review and Current Concepts. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 38(8), 850–860. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx218
- 6Egrari S. (2016). Brachioplasty: A Personal Approach. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 36(2), 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjv146
- 7Reed L. S. (2014). Brachioplasty with a limited scar. Clinics in plastic surgery, 41(4), 753–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2014.06.009
- 8Kokosis, G., & Coon, D. (2019). Safety in Body Contouring to Avoid Complications. Clinics in plastic surgery, 46(1), 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2018

