What is Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Carotid artery stenosis refers to the narrowing of the carotid artery, typically caused by a buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) along the artery walls. There are two carotid arteries, one on each side of the neck, and they play a vital role in maintaining the brain’s blood supply. Carotid artery stenosis makes stroke more likely. Untreated, the stroke can lead to death.
Carotid artery stenosis is often asymptomatic until a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke occurs, making early detection crucial. When they occur, symptoms may include sudden weakness, numbness, difficulty speaking, or loss of vision in one eye. Managing the condition involves lifestyle changes, medications, and, in severe cases, surgical procedures like carotid endarterectomy or stenting to restore blood flow and reduce stroke risk.1Rerkasem A, Orrapin S, Howard DP, Rerkasem K. Carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 12;9(9): CD001081.
How Common is Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Carotid Artery Stenosis makes strokes more likely. Almost six cases per 100,000 experience symptoms from internal carotid artery occlusion. In the US, internal carotid artery occlusion contributes to one-third of all stroke cases. Stroke ranks as the third leading cause of death in the United States, trailing behind heart disease and cancer. Nearly 60% of all stroke-related deaths occur among females.2Qaja E, Tadi P, Theetha Kariyanna P. Carotid Artery Stenosis. PubMed. Published 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442025/ African Americans and Mexican Americans face a higher stroke risk compared to Caucasians.
Causes of Carotid Artery Stenosis
Narrowing(stenosis) of carotid arteries is usually caused by “Atherosclerosis.” Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of plaque deposits.3 Carotid Artery Disease – Health Encyclopedia – University of Rochester Medical Center. www.urmc.rochester.edu. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p08248 These plaques are a mix of cholesterol, fatty substances, calcium, fibrin, etc. Plaque buildup narrows the arterial lumen, restricting blood flow to the brain. This reduces the oxygen supply to brain cells. Brain cells are highly dependent on oxygen, and deprivation for just a few minutes can lead to irreversible damage or brain cell death. Moreover, this narrowing may lead to clot formation. If a clot (thrombus) breaks off (embolizes) and travels to smaller brain arteries, it can completely block blood flow, leading to an ischemic stroke.
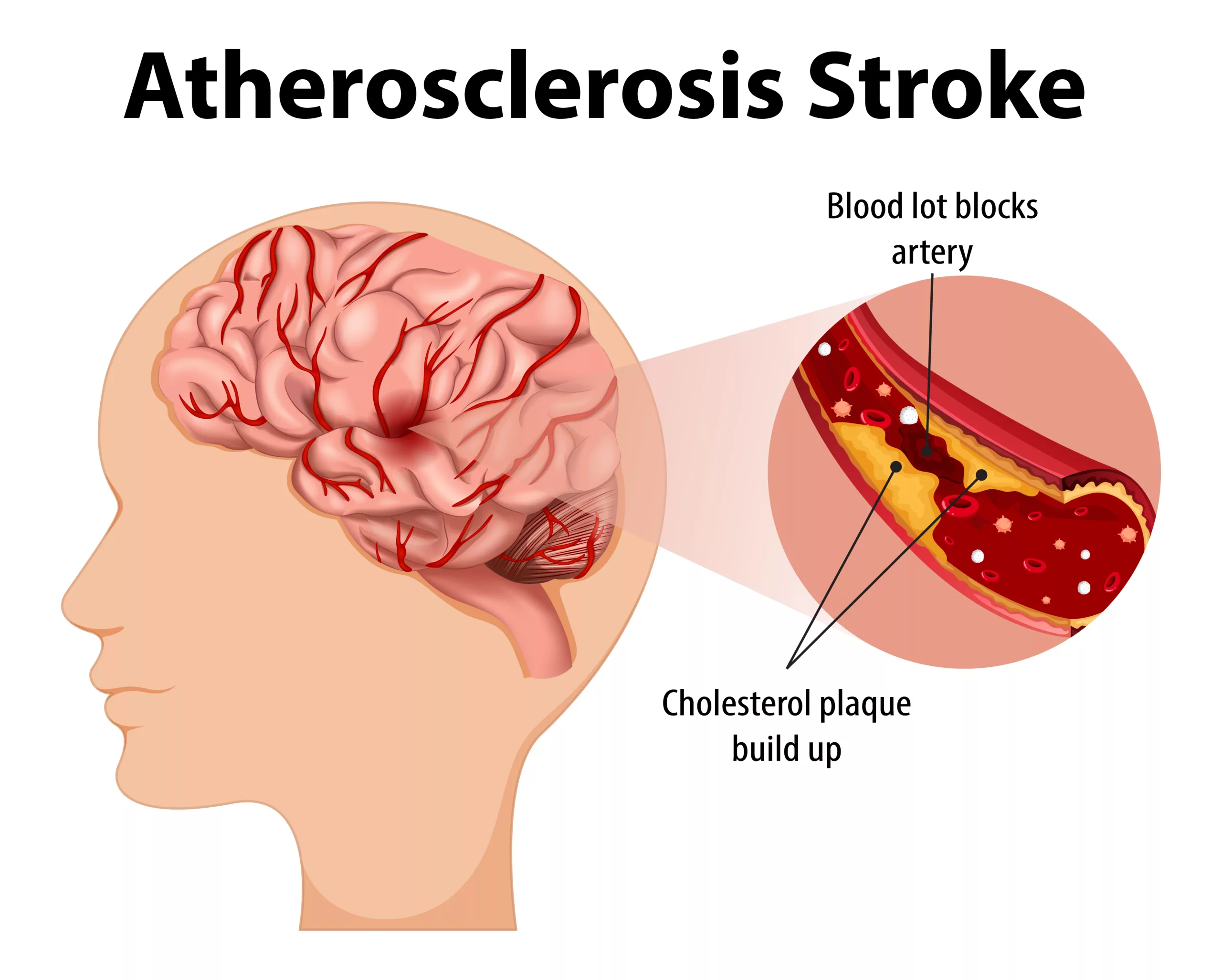
Risk Factors of Carotid Artery Stenosis
Carotid Artery Stenosis is more likely in certain conditions.4Carotid Artery Disease. Pennmedicine.org. Published 2022. https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/carotid-artery-disease These include:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Family history of stroke
- Elevated blood pressure (Hypertension)
- Increased cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
- Advanced age, especially in males
- Smoking or Alcohol use
- Recreational drug use
- Injury to the neck
- Sleep apnea
- Lack of exercise
Symptoms Of Carotid Artery Stenosis
Early stages of the disease are generally asymptomatic. However, as the condition progresses, patients may experience Transient Ischemic Attacks. TIAs are brief episodes of neurologic dysfunction. They usually result from reduced blood flow to the brain. In some people, the condition remains asymptomatic until they have a stroke. Symptoms of TIA include.
- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face or limbs, often on one side of the body.
- Trouble speaking and understanding speech.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness or loss of balance.
- Severe headache with no known cause.
Complications of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease causes about 10% to 15% of strokes. A stroke is a medical emergency that can cause brain damage, muscle weakness, and possibly death.
Carotid artery disease can lead to stroke through:
Reduced Blood Flow
A carotid artery might get so narrow because of atherosclerosis that insufficient blood reaches parts of the brain.
Ruptured Plaques
A piece of plaque can break off and travel to smaller arteries in the brain. The piece of plaque can get stuck in one of these smaller arteries. This blockage cuts off blood supply to part of the brain.
Blood Clot Blockage
Some plaques are prone to cracking and forming irregular surfaces on the artery wall. The body reacts as it does to an injury. It sends blood cells that help the clotting process to the area. The result can be a large clot that blocks or slows blood flow to the brain, causing a stroke.
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Stenosis
To diagnose Carotid Artery Stenosis, the doctor can perform physical exams to hear for a bruit. They may also check for the signs of stroke and ask you questions regarding fainting spells, temporary loss of vision, or cognitive ability. Physicians might also request blood tests to examine your sugar levels, cholesterol, and triglycerides to evaluate your general health and the possibility of carotid artery narrowing. Doctors may also order certain tests like:
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound
Carotid Duplex Ultrasound is a non-invasive scanning test that uses sound waves to produce images of the carotid arteries. The word Duplex refers to the use of two technologies: Doppler (for visualizing blood flow) and B-mode transducer (for visualizing the blood vessels).5 Duplex ultrasound. stanfordhealthcare.org. https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-tests/u/ultrasound/procedures/duplex-ultrasound.html#:~:text=Duplex%20ultrasound%20involves%20using%20high It is often the first test prescribed. If the physician suspects a diagnosis of Carotid Stenosis, then CTAs or other contrast tests may be ordered.
MR Angiography (MRA)
Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) employs strong magnetic fields and radio frequency waves instead of X-ray radiation to assess blood vessels for abnormalities. Gadolinium-based contrast may be administered via an IV catheter in the arm during the procedure to enhance imaging. Unlike iodinated contrast used in CTA (Computed Tomography Angiography), Gadolinium is less allergic.6Radiology (ACR) RS of NA (RSNA) and AC of. MR Angiography (MRA). Radiologyinfo.org. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiomr Hence, MRA may be preferred in patients where CTA is contraindicated.
Cerebral Angiography
This is an invasive procedure used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain. A catheter is inserted into an artery, usually in the leg or arm, and then guided up to the blood vessels in the brain. Contrast dye is then injected through the catheter, and X-ray images are taken. Conventional Angiography is the gold standard for diagnosis of Carotid Artery Stenosis.
CT Angiography (CTA)
This is a non-invasive imaging test. In this procedure, contrast dye is injected into a vein in the arm. After which, a series of X-ray images are taken at different angles. The test uses computed tomography to produce detailed images of blood vessels in the body.7 Silvennoinen HM, Ikonen S, Soinne L, Railo M, Valanne L. CT angiographic analysis of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of manual assessment, semiautomatic vessel analysis, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(1):97-103. 8Szczerbo-Trojanowska M, Jargiełło T, Drelich-Zbroja A. Management of carotid stenosis. History and today. J Ultrason. 2013;13(52):6-20. doi:10.15557/JoU.2013.0001
How Do You Classify Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Carotid Artery Stenosis can be classified into mild, moderate, and severe. These refer to the percentage of occlusion. Mild blockage is under 50%, Moderate is 50-79%, and Severe is 80-99% artery blockage.
Treatment Of Carotid Artery Stenosis
The goal of treating carotid artery disease is to prevent stroke. Treatment depends on how blocked the carotid arteries are, whether the blockage is causing symptoms, and the age and other illnesses of the person who has the blockage.
Treatment for mild to moderate blockage:
This involves lifestyle changes to slow the buildup of fatty deposits. These might include quitting smoking, losing weight, eating healthy foods, reducing salt, and exercising regularly. Medicines to control blood pressure or lower cholesterol. This might include taking a daily aspirin or other blood-thinning medicine to prevent blood clots.
Treatment for Severe Blockages or Patients with a history of TIAs and Stroke:
For these patients, two treatment modalities are available. Treatment may involve removing the blockage or relieving the occlusion.
1. Carotid Endarterectomy
This is the most common treatment for severe carotid artery disease. After cutting along the front of the neck, a surgeon opens the blocked carotid artery and removes the plaques. The surgeon uses stitches or a graft to repair the artery.
2. Carotid Angioplasty & Stenting
This treatment is for blockages too hard to reach with carotid endarterectomy or for people who have other health conditions that make surgery too risky. This involves a local numbing medicine known as anesthesia. A surgeon then uses a tube, known as a catheter, to send a tiny balloon to the area of the clog. The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery. Then, a small wire mesh coil, known as a stent, is placed inside to keep the artery from narrowing again.
What Are Lifestyle Modifications For Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of Carotid Artery Stenosis include:
- Increase consumption of fresh fruits, vegetables, lean meats (like poultry and fish), and low-fat or non-fat dairy products.
- Limit intake of salt, sugar, processed foods, saturated fats, and alcohol.
- Aim for 40 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity at least 3 to 4 days per week.
- Quit smoking and manage stress.
Conclusion
Carotid artery stenosis refers to the narrowing of the carotid artery, which can lead to reduced blood flow, increasing the risk of strokes and potential fatality if left untreated. The primary cause is atherosclerosis, which leads to narrowing the artery and reducing blood supply to the brain. Risk factors for Carotid Artery Stenosis include diabetes, high blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, and advanced age, among others. While early stages often have no symptoms, Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) may be seen as the condition progresses.
Diagnosis involves physical examinations, blood tests, and various imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT angiography, and MRI to evaluate artery narrowing. Treatment aims to reduce clotting and clear blockages. Blood thinners like aspirin may be prescribed. For more severe cases, urgent revascularization procedures such as carotid endarterectomy or carotid artery stenting may be necessary. Lifestyle modifications like dietary changes, exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management are crucial in reducing the risk of carotid artery stenosis.
Refrences
- 1Rerkasem A, Orrapin S, Howard DP, Rerkasem K. Carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 12;9(9): CD001081.
- 2Qaja E, Tadi P, Theetha Kariyanna P. Carotid Artery Stenosis. PubMed. Published 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442025/
- 3Carotid Artery Disease – Health Encyclopedia – University of Rochester Medical Center. www.urmc.rochester.edu. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=85&contentid=p08248
- 4Carotid Artery Disease. Pennmedicine.org. Published 2022. https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/carotid-artery-disease
- 5Duplex ultrasound. stanfordhealthcare.org. https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-tests/u/ultrasound/procedures/duplex-ultrasound.html#:~:text=Duplex%20ultrasound%20involves%20using%20high
- 6Radiology (ACR) RS of NA (RSNA) and AC of. MR Angiography (MRA). Radiologyinfo.org. https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/angiomr
- 7Silvennoinen HM, Ikonen S, Soinne L, Railo M, Valanne L. CT angiographic analysis of carotid artery stenosis: comparison of manual assessment, semiautomatic vessel analysis, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28(1):97-103.
- 8Szczerbo-Trojanowska M, Jargiełło T, Drelich-Zbroja A. Management of carotid stenosis. History and today. J Ultrason. 2013;13(52):6-20. doi:10.15557/JoU.2013.0001

