Dandy-walker malformation is a congenital or inborn brain disorder in which some of your child’s brain structures remain underdeveloped (malformed). It results in neurological abnormalities. It most commonly affects the cerebellum and the spaces (ventricles) of your child’s brain. The clinical triad of this syndrome is hydrocephalus, cystic dilatation of the 4th ventricle, and posterior fossa enlargement. The symptoms of children with this syndrome include delayed motor skills and progressive skull growth due to the collection of fluid inside the skull. This problem is associated with abnormal neurological manifestations.1Incesu, L., MD. (n.d.). Dandy-Walker Malformation Imaging: practice essentials, radiography, computed tomography. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/408059-overview?form=fpf&scode=msp&st=fpf&socialSite=google&icd=login_success_gg_match_fpf#a1
What is Dandy-Walker Malformation?
Children with Dandy-Walker malformation or syndrome have abnormally developed cerebellum and 4th ventricle. The cerebellum is situated in the back of your brain and controls your balance, coordination, vision, cognition (thinking ability), and behavior.
Children with DWM usually have abnormal development of the middle part of the cerebellum, which is called the cerebral vermis. Sometimes, it remains small or absent.
The 4th ventricle is a space in your brain that is involved in circulating your cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). In Dandy walker malformation, your 4th ventricle is not fully developed, resulting in hydrocephalus and a large skull due to piling up cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in your brain.
The brainstem and cerebellum are present in the posterior part of the brain. Therefore, there is also a collection of fluid in the posterior part of the brain, resulting in posterior fossa enlargement.2Dandy-Walker malformation: MedlinePlus Genetics. (2015). Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dandy-walker-malformation/#causes
How many children are affected by this Syndrome?
The overall incidence of Dandy-Walker syndrome in the United States is about 1 in 25000-35000, out of which 1-4 % of the babies present with large heads (macrocephaly). It most commonly targets females than males. The overall survival rate of Dandy-walker malformation depends upon the severity of the disease and extracranial manifestations.3Zamora, E. A. (2023, November 12). Dandy-Walker malformation. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538197/
Types of Dandy-Walker Syndrome
There are two types of dandy-walker syndrome. These are:
Dandy-Walker Malformation:
This is the most severe form of the dandy Walker syndrome. In this syndrome, some parts of the cerebellum are not formed, and the rest of the cerebellum becomes enlarged because a large amount of fluid builds up inside the brain spaces, damaging the nearby structures. Babies with this type of Dandy-walker syndrome are presented with hydrocephalus and macrocephaly at birth and are at greater risk of having neurological abnormalities at a later age.
These babies or children require ventriculoperitoneal shunting (VP shunting) to remove extra fluid from the brain.
Dandy-Walker Variant:
This is the milder form of DWM. Babies with a variant have less fluid than those with Dandy-Walker malformation. These babies usually do not require VP shunting to remove extra fluid from their brains. Babies with this variant usually live normal lives and have a good prognosis.
Surgery can be done in some cases where fluid levels in the brain are too high.4Dandy-Walker Syndrome. (n.d.). https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/dandy-walker-syndrome
Causes of Dandy Walker’s Malformation
Your brain contains multiple foramina that drain cerebrospinal fluid through your brain. DWM usually occurs due to abnormality in foramen Luschka and foramen Magendie. However, the causes of dandy Walker malformation are as follows:
Genetic Mutations:
DWM occurs due to abnormal development of the cerebellum and other structures during embryogenesis. Some chromosomal aberrations cause dandy walker malformation. These genetic changes include mutation in the FOXC1 gene, FGF 17, NIDI, and ZIC1 and ZIC4.
Dandy-Walker malformation is also associated with other chromosomal abnormalities like trisomy 13, trisomy 18, and trisomy 21.
Environmental Factors:
Some environmental factors are involved in causing Dandy Walker’s malformation. These factors are:5National Organization for Rare Disorders. (2023, November 20). Dandy-Walker Malformation – Symptoms, causes, treatment | NORD. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dandy-walker-malformation/
- Teratogens
- Exposure to the Rubella virus
- Cytomegalovirus
- Alcohol
- Maternal diabetes
Signs & Symptoms
The clinical presentation of this syndrome depends upon the severity of the disease.6Donnelly, C. (2022, May 5). An overview of Dandy-Walker Syndrome. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/dandy-walker-syndrome-4174583
The most common findings associated with this syndrome are:
- Delayed motor development of the child (delayed walking and crawling)
- Muscle stiffness
- Fits
- Ataxia in children (abnormal walking)
- Low muscle tone or
- Breathing difficulties
- Mental abnormalities (abnormal cognition)
- The skull is larger than normal (obstructive hydrocephalus)
- Large posterior cranial fossa
- Cystic dilation of the 4th ventricle
- Irritability
- Unusual eye movement

Clinical Presentation of Dandy-Walker Syndrome
This syndrome is associated with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations, which are divided into central nervous system-associated and non-central nervous system-associated abnormalities.
Central Nervous System Associated:
These abnormalities include the following presentation.
- Dysgenesis or absence of corpus callosum
- Holoprosencephaly and porencephaly(failure of development of embryonic forebrain reported in 25% of the cases)
- Dermoid cyst
- Macrocephaly (Large head)
- Spina bifida
- Malformation of cerebellar folia
- Spinal lipoma
Non-CNS Associated Abnormalities:
The non-CNS-associated abnormalities include the following:
- Cleft lip and cleft palate
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Cataract formation in eyes
- Facial hemangioma
- Cardiac defects
- Polydactyly (one or more extra fingers) and syndactyly (webbed or fused fingers)
How to Diagnose Dandy-Walker Malformation?
DWS is diagnosed by taking a detailed history of the mother, conducting a clinical examination of the baby or child, and conducting a laboratory investigation followed by imaging.
History:
The patient’s history remains the prime part of the diagnosis. During the history, your doctor will ask questions about your disease to determine the exact cause of DWS. He may ask about your history of diabetes, gestational diabetes, smoking during pregnancy, alcohol intake during pregnancy, medications during pregnancy, and family history of DWM.
Physical Examination:
After the history, your doctor will examine your child’s head and measure its size. The clinical presentation of this disease is non-specific and depends upon the severity of the disease and other comorbidities. Most of the time, patients present with a large head with increased intracranial pressure.
On examination, the baby or child has a large head (macrocephaly). It is the most common presentation of this disease that affects 90 percent of babies during the first month of their life. Hydrocephalus is also the most common presentation of this disease; however, some patients with this syndrome present with cleft lips and cleft palates.
Laboratory Investigations:
Laboratory investigations are advised for the genetic testing of the fetus.
Cell-Free Fetal DNA Testing
In this test, blood is drawn from the mother and is evaluated to check for any abnormality in the baby’s DNA.
Amniocentesis
In this test, fluid is taken from the amniotic cavity and is checked for abnormality.
Fetal Blood Testing
Fetal blood is used for karyotyping to check chromosomal abnormality.7Fletcher, J. (2022, December 16). What to know about Dandy-Walker syndrome. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/dandy-walker-syndrome#diagnosis
Imaging:
Imaging helps to see your child’s internal structure. These studies include the following imaging modalities:
Ultrasound
This imaging modality, readily accessible and commonly used, enables prenatal diagnosis of multiple anomalies in your baby. It assesses the head size and internal brain structure effectively. Moreover, patients with this syndrome have heads that are larger than normal in size.
Radiography
Plain radiography helps your doctor see any bony abnormalities and the position of the ventriculoperitoneal shunt. On a radiograph, the posterior fossa is typically enlarged, followed by occipital protuberance.
Doctors notice the following changes on radiographs:
- Hypoplasia or agenesis of the foramen of Luschka and foramen of Magendie (they do not form)
- Partial or complete absence of cerebellar vermis
- Weakened occipital bones
- Tentorium elevation
- Brain stem compression
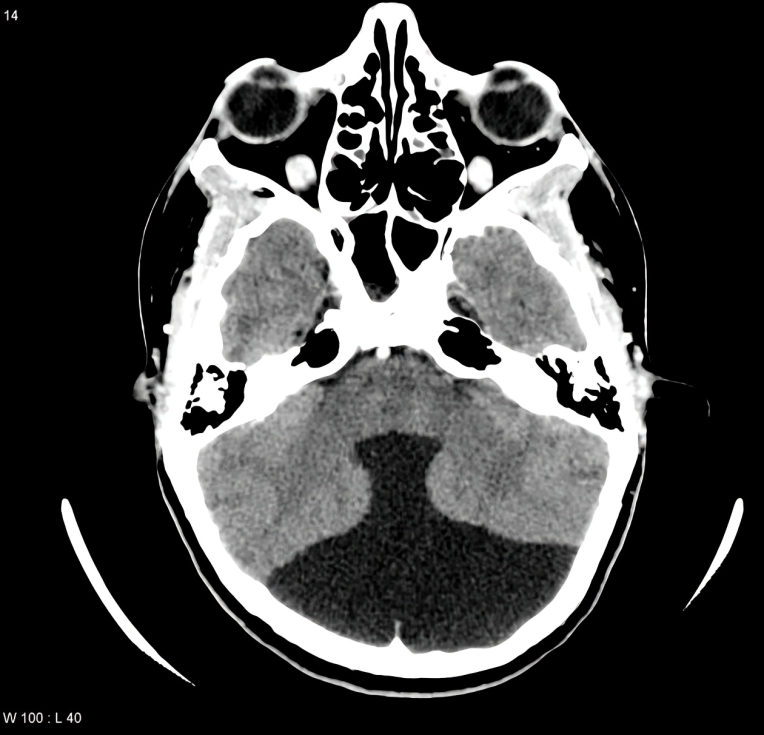
MRI
MRI can more accurately demonstrate CNS malformation than ultrasound, making it the most reliable test for checking for CNS malformation. Doctors advise an MRI after the 20th week of gestation when there is suspicion of Dandy-Walker syndrome on the ultrasound scan.
Imaging Criteria for DWM:
Barkovich et Al. proposed the imaging criteria for this malformation in 2003. It includes8Zamora, E. A. (2023, November 12). Dandy-Walker malformation. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538197/
- Posterior fossa cyst in continuation with the 4th ventricle
- Agenesis or absence of cerebellar vermis
- Hypoplasia of the vermis
- The angle of fastigium is absent
- Elevated torcula
- Hypoplastic cerebellar hemisphere
During imaging, measuring the size of the brain-stem vermian angle and brain-stem tentorium angle is crucial to diagnosing the dandy Walker malformation. These angles increase with the severity of the disease. Brain stem vermian angle greater than 18 is suggestive of dandy Walker malformation. The brain-stem tentorium angle between 21-44 suggests Dandy Walker’s malformation.9Dandy-Walker Malformation Diagnosis during Pregnancy. (2017, September 22). Fetal Health Foundation. https://www.fetalhealthfoundation.org/fetal-syndromes/dandy-walker-malformation/
How to treat Dandy-Walker Malformation?
The treatment of this syndrome is based on the severity of the disease. A careful examination is necessary before starting treatment. Treatment aims to remove the extra amount of fluid from your brain.
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting (VP shunting):
Hydrocephalus is the most common presentation of DWM. In hydrocephalus, fluid accumulates in the patient’s brain. Your doctor will place a hollow tube (shunt) in the brain that helps remove extra fluid from the brain and decrease the pressure on the brain. VP shunting prevents continuous damage to your child’s brain. This hollow tube is placed for the rest of your Child’s life.
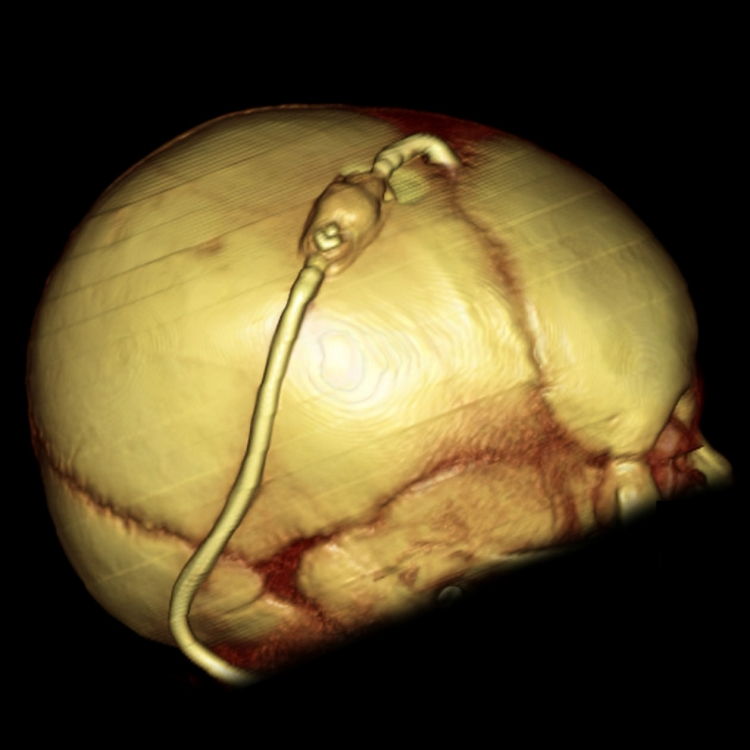
This surgery is possible soon after birth or later, depending upon the severity of the disease. Some people have Dandy-Walker syndrome but no signs of hydrocephalus. They can be discharged and followed up, and parents are also advised to check for signs of hydrocephalus. Your doctor will tell you the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus that you have to notice in your child.
Some complications can occur after the surgery. These include infections due to the tube’s blockage. However, the blockage requires surgical intervention to replace the old tube with a new one.
How do I care for my child after the surgery?
You can care for your child after the surgery according to the doctor’s advice. After the surgery, your baby will be shifted to the NICU. The ventilator will help your child breathe until full recovery. Post-operative care includes:
- Mobilize your child in bed to avoid bed sores
- Interact with your baby
- Clean your baby’s wound regularly to avoid infection
Immediately consult with your doctor when you see the following signs or symptoms.
- Breathing difficulty
- High-grade fever
- Increase in size of your Child’s head after the surgery
Medication:
Your doctor will advise on some medications to treat the symptoms of the dandy walker malformation. It includes anti-seizure medications.
Physiotherapy:
In this condition, the muscle strength of your child decreases. Moreover, your doctor will advise physiotherapy to improve your child’s muscle strength.
Speech therapy:
Some patients with DWM also have speech problems. Therefore, your doctor may advise speech therapy that helps improve language and speech development.10Dandy-Walker malformation. (n.d.). Children’s Hospital Colorado. https://www.childrenscolorado.org/conditions-and-advice/conditions-and-symptoms/conditions/dandy-walker/
Prognosis:
The survival rate of the patient with this syndrome depends upon the severity of the disease, associated comorbidities, timely diagnosis, and treatment. Patients with less severe forms of Dandy-Walker syndrome, where the cerebellar vermis is present and less affected, show a good prognosis and can live normal lives. However, in a severe form of dandy Walker malformation where the cerebellar vermis is absent, the patient is at a higher risk of having neurological abnormalities.
50 percent of the patients die in their early life (2-3 years) and remain untreated, and 20-30 percent of the children will reach adulthood and have neurological abnormalities (motor delay, auditory deficit, and visual impairment)
The prognosis of the patient also depends upon the diameter of the 4th ventricle. Therefore, 21% of Patients with a diameter between 11-15 mm show developmental delay and later ages. At the same time, 50% of the patients are at risk of having motor abnormalities and have a diameter greater than 15 mm.
How can I Prevent Dandy Walker’s Malformation?
You can not prevent it. However, you can avoid risk factors that increase the chance of having this condition. It includes:
- Controls your blood sugar level because maternal diabetes increases the risk of having dandy walker malformation
- Avoid drinking alcohol
- Genetic counseling is compulsory
Although the best prenatal care for your child depends on your health, a physician can make your pregnancy safe.
Dandy-Walker malformation vs Joubert
Dandy-Walker malformation is a genetic disease in which the development of the brain is compromised. In this syndrome, the cerebellum is normal or diminished in size. Cerebellar vermian is small in size or absent with rotation greater than 45 degrees and large cisterna magna. A molar tooth sign is not present on the MRI.
Joubert syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects brain development. In this syndrome, the cerebellum and cisterna magna are normal in size. Cerebellar vermis is small or absent. Molar tooth sign is a characteristic finding of Joubert syndrome on MRI.
Conclusion
To conclude, Dandy walker malformation is a brain defect in which an infant’s brain does not develop completely. Symptoms of Dandy-Walker syndrome manifest as delayed walking and running, delayed speech, fits, ataxia, difficulty breathing, large skull size due to collection of excess fluid, and abnormal eye movements. Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is the treatment of choice for Dandy-Walker syndrome. The prognosis of this condition depends on the extent of the disease and associated features.
Refrences
- 1Incesu, L., MD. (n.d.). Dandy-Walker Malformation Imaging: practice essentials, radiography, computed tomography. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/408059-overview?form=fpf&scode=msp&st=fpf&socialSite=google&icd=login_success_gg_match_fpf#a1
- 2Dandy-Walker malformation: MedlinePlus Genetics. (2015). Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/dandy-walker-malformation/#causes
- 3Zamora, E. A. (2023, November 12). Dandy-Walker malformation. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538197/
- 4Dandy-Walker Syndrome. (n.d.). https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/dandy-walker-syndrome
- 5National Organization for Rare Disorders. (2023, November 20). Dandy-Walker Malformation – Symptoms, causes, treatment | NORD. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dandy-walker-malformation/
- 6Donnelly, C. (2022, May 5). An overview of Dandy-Walker Syndrome. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/dandy-walker-syndrome-4174583
- 7Fletcher, J. (2022, December 16). What to know about Dandy-Walker syndrome. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/dandy-walker-syndrome#diagnosis
- 8Zamora, E. A. (2023, November 12). Dandy-Walker malformation. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538197/
- 9Dandy-Walker Malformation Diagnosis during Pregnancy. (2017, September 22). Fetal Health Foundation. https://www.fetalhealthfoundation.org/fetal-syndromes/dandy-walker-malformation/
- 10Dandy-Walker malformation. (n.d.). Children’s Hospital Colorado. https://www.childrenscolorado.org/conditions-and-advice/conditions-and-symptoms/conditions/dandy-walker/