McCune-Albright Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder affecting the skin, bones, and endocrine glands. It is clinically defined by a triad of fibrous dysplasia of bone (FD), skin pigmentation (café-au-lait skin spots), and endocrine abnormalities. Clinically, this syndrome is characterized by multiple bone disorders, bony lesions, scoliosis, and brown patches on the skin. This syndrome also affects the neuroendocrine system, leading to abnormal production of hormones in the body. There is currently no standard treatment for McCune-Albright syndrome.
As we have discussed earlier, McCune-Albright syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, so the prevalence of this syndrome ranges from 1/100000 to 1/1000000.1Dumitrescu, C. E., & Collins, M. T. (2008). McCune-Albright syndrome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-3-122Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. >https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
What is McCune-Albright Syndrome?
McCune-Albright syndrome presents with three hallmark features: fibrous dysplasia, pigmentary skin changes, and endocrine dysfunction.
Fibrous Dysplasia:
Fibrous dysplasia involves the replacement of normal bone with fibrous tissue, resulting in weakened and deformed bones. In most MAS cases, multiple bones are affected, a form known as polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Patients may present with bone pain, visible lumps, and pathological fractures. These lesions typically appear on one side of the body. Scoliosis (a sideways curvature of the spine) is a common skeletal feature. Frequently involved bones include the femur, tibia, ribs, and facial bones.
Skin Pigmentation:
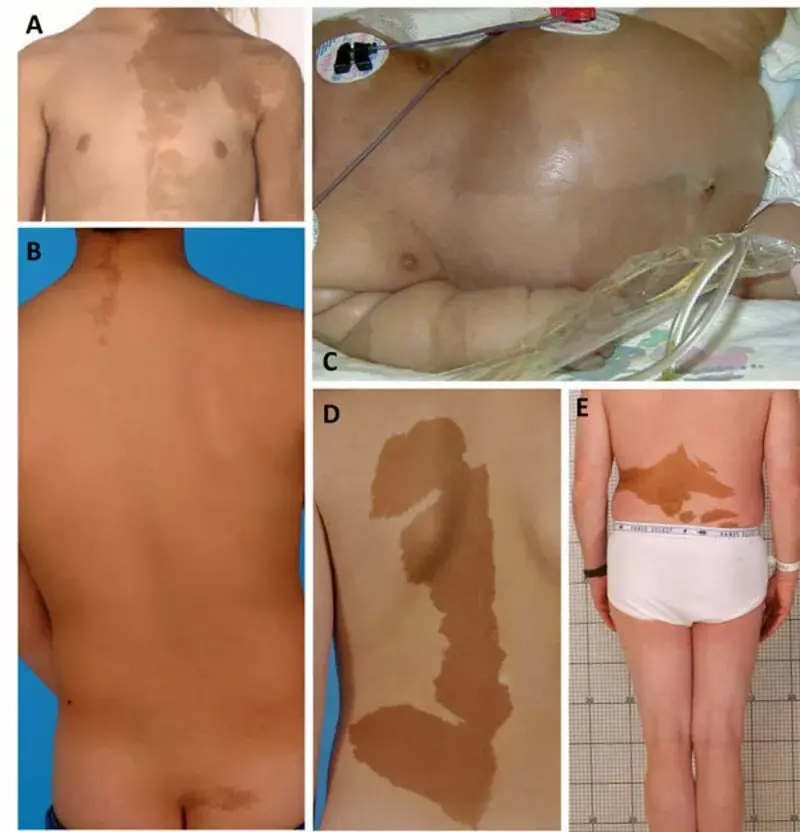
MAS also causes light brown, irregularly bordered skin patches known as café-au-lait macules. These lesions are often present at birth and, like fibrous dysplasia, tend to occur unilaterally (on one side of the body). Unlike the smoother borders seen in café-au-lait spots from neurofibromatosis type 1, the borders in MAS are typically jagged or “coast of Maine” shaped.
Endocrine Abnormalities:
McCune-Albright syndrome also disrupts the body’s endocrine system, leading to a range of hormone-related conditions. Precocious puberty is one of the most common manifestations, especially in young girls, where early estrogen production causes premature physical development. Some patients may also develop hyperthyroidism due to autonomous thyroid activity, as well as abnormal growth hormone secretion that results in features of acromegaly. Additionally, cortisol-producing adrenal lesions may lead to Cushing syndrome. These hormonal imbalances vary from person to person and often require individualized treatment to manage their effects on development, metabolism, and overall health.
Causes of McCune-Albright Syndrome
McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by a postzygotic (after fertilization) somatic mutation in the GNAS gene, most commonly at arginine 201 (Arg201) or glutamine 227 (Gln227). This gene encodes the alpha subunit of the G protein (Gsα), which plays a key role in intracellular signal transduction.
The G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) pathway is active in multiple tissues, including bone, skin, and endocrine glands. The activating mutation in GNAS leads to constitutive (always on) activation of the Gsα protein, causing persistent stimulation of adenylate cyclase. This results in elevated intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels.
- In endocrine tissues, high cAMP levels cause overproduction of hormones, leading to endocrine abnormalities such as precocious puberty, thyrotoxicosis, and Cushing syndrome.
- In bone, elevated cAMP stimulates osteoclast activity, leading to fibrous dysplasia—a condition in which normal bone is replaced by structurally weak fibrous tissue.
- In the skin, increased cAMP promotes melanocyte activity, which results in the development of café-au-lait macules (hyperpigmented patches).3Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
Symptoms of McCune-Albright Syndrome
There can be multiple symptoms of McCune-Albright syndrome because of the involvement of different tissues. The most common symptoms, according to the pathology, are:
Symptoms of Endocrinopathy:
There are various signs and Symptoms of McCune-Albright endocrinopathy. These symptoms are different in males and females.4Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
In Males
The following are symptoms of endocrinopathy in males:
- Large testes
- Pubic hair
- Axillary hairs
- The smelly odor from the body
In Females
- Vaginal bleeding
- Development of breast tissue before the age of puberty (precocious puberty)
- Ovarian cyst
Other symptoms common in both genders are:
- Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
- Symptoms of Cushing syndrome
- Symptoms of excessive growth hormone
Symptoms of Fibrous Dysplasia:
Fibrous dysplasia most commonly affects your bone tissues. It replaces your bone marrow with fibrous tissue, resulting in bone weakness. Symptoms of fibrous dysplasia include the following:5 Dumitrescu, C. E., & Collins, M. T. (2008). McCune-Albright syndrome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-3-126Department of Health & Human Services. (n.d.). McCune-Albright syndrome. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/mccune-albright-syndrome
- Bone pain
- Pathological bone fracture
- Facial asymmetry
- Rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults
- Scoliosis
- Loss of mobility
- Lump formation
Dermatological Manifestation:
McCune-Albright syndrome causes skin pigmentation known as café-au-lait skin spots. These skin spots have irregular borders.
McCune-Albright Syndrome vs Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is a rare genetic disorder that causes the formation of benign tumors on your skin and nerve tissues. However, neurofibromatosis differs from McCune-Albright syndrome based on the appearance of café-au-lait skin spots.
While both McCune-Albright Syndrome (MAS) and Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) can cause café-au-lait skin spots, MAS typically presents with irregular, jagged-edged spots that do not cross the midline (“coast of Maine”), whereas NF1 features smooth-edged spots that often cross the midline (“coast of California”). MAS is also associated with fibrous dysplasia and endocrine disorders, which are not seen in NF1.
How to diagnose McCune-Albright Syndrome?
McCune-Albright Syndrome (MAS) is primarily diagnosed based on clinical findings, supported by biochemical tests and imaging. Diagnosis generally includes the following steps:
History:
A detailed medical history is essential for initial suspicion. Your doctor may ask:
- Patient name, age, and weight
- Any previous history of illness?
- Do you have pain in your bones?
- Any genetic disease?
Physical Examination:
After taking a detailed history, a general physical exam is conducted to look for hallmark features of the syndrome, such as:
- Skin examination for café-au-lait spots (typically with irregular borders and limited to one side)
- Skeletal abnormalities, including limb asymmetry or scoliosis
- Abdominal or pelvic masses in cases of ovarian cysts
- Signs of endocrine dysfunction (e.g., breast development in young girls, goiter, or Cushingoid features)
Laboratory Evaluation:
Your doctor may order several lab tests to assess endocrine function and rule out other conditions:
- CBC (Complete Blood Count): To screen for anemia or infection.
- Genetic Testing (GNAS Mutation): This is the most definitive test, detecting postzygotic activating mutations in the GNAS gene at Arg201 or Gln227.7Lo FS, Chen TL, Chiou CC. Detection of Rare Somatic GNAS Mutation in McCune-Albright Syndrome Using a Novel Peptide Nucleic Acid Probe in a Single Tube. Molecules. 2017 Nov 1;22(11):1874. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111874. PMID: 29104223; PMCID: PMC6150203.
- Hormonal Assays:
- Estradiol or Testosterone – For precocious puberty
- Growth Hormone and IGF-1 – If acromegaly is suspected
- Cortisol and ACTH – If Cushing syndrome is suspected
- Calcium, Phosphate, and Vitamin D Levels: To rule out rickets, osteomalacia, or other metabolic bone diseases.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): May be used to assess for growth hormone suppression in suspected acromegaly.8Akirov A, Masri-Iraqi H, Dotan I, Shimon I. The Biochemical Diagnosis of Acromegaly. J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 9;10(5):1147. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051147. PMID: 33803429; PMCID: PMC7967116.
Radiological Evaluation:
Radiological studies are the investigation of choice. The radiological examination includes X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, CT scan, biopsy, and bone scan.
Xray
X-ray is the first-line imaging to identify bony lesions with the characteristic “ground-glass” appearance, cortical thinning, and deformity.

Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is performed to rule out other causes.
CT Scan
CT scan of the skull indicates craniofacial abnormalities and diagnoses pituitary lesions.
MRI
MRI is only indicated in the case of soft tissue involvement.
Bone scan
A bone scan (Technetium-99m) identifies the extent of bone involvement in polyostotic disease.
Biopsy or Histopathology:
In uncertain cases, a bone biopsy may be done. Histological features typically show irregular, thin trabeculae of woven bone within a fibrous stroma. Marrow spaces are replaced by fibroblastic tissue, confirming fibrous dysplasia.
How to treat McCune-Albright Syndrome?
There are different treatment options for McCune-Albright syndrome according to the severity of the disease.
Treatment of Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone:
In this case, your doctor prescribes medicine to treat your bone pain and bone abnormalities. These medications are:
- Painkillers to reduce bone pain
- Bisphosphonates are also used for pain relief and to treat osteoporosis
- Analgesics
- Vitamin D supplements
- Calcium supplements
- Physical therapy to improve joint mobility
Treatment of Endocrinopathies:
Treatment varies depending on the specific hormone abnormality:
- Pituitary adenomas: Managed through medication, radiation, or surgical resection depending on tumor size and hormone secretion.9Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf.
- Precocious puberty: In gonadotropin-independent cases (common in girls with MAS), aromatase inhibitors and tamoxifen are used. Aromatase inhibitors block the conversion of androgens into estrogens, while tamoxifen acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator. For central precocious puberty, GnRH analogs (e.g., leuprolide) are used to suppress pituitary gonadotropin secretion.
- Hyperthyroidism: Managed with antithyroid drugs such as methimazole to reduce thyroid hormone levels.
- Growth hormone excess (acromegaly): Treated with somatostatin analogs like octreotide or lanreotide to suppress GH secretion.
- Hyperprolactinemia: Treated with dopamine agonists such as bromocriptine or cabergoline.
- Ovarian or testicular cysts: May resolve spontaneously, but surgical intervention might be required in symptomatic or persistent cases.
Prognosis of McCune-Albright Syndrome
The prognosis of this disease depends on the severity of the disease. Patients with renal phosphate wasting and fibrous dysplasia are at greater risk of bone pain and bone fractures. Moreover, the primary goal is to prevent precocious puberty because if it remains neglected, growth plates close earlier, resulting in short stature.
Furthermore, there may be a risk of malignancy of polyostotic cells, so make sure that you or your child schedules visits with your doctor. However, Early screening of women suffering from this syndrome is essential to avoid breast cancer. Comparatively, women with McCune-Albright syndrome are at higher risk of getting breast cancer than others.10Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
When to see your doctor?
You have to schedule your appointment with your healthcare provider if you or your child has these symptoms:
- Sleeping difficulty
- Bone deformity
- Frequent bone fractures
- Severe bone aches
- Early menarche (early menses before the age of 8)
Complications of McCune-Albright Syndrome
McCune-Albright syndrome can lead to several complications involving the bones, endocrine system, and nervous system:
- Osteoporosis (brittle bones)
- Rickets in children or osteomalacia in adults due to poor bone mineralization
- Vision loss occurs if fibrous dysplasia compresses the optic nerve
- Hearing loss due to craniofacial bone involvement affecting the vestibulocochlear nerve
- Joint stiffness or deformities
- Adrenal tumors, which can lead to endocrine abnormalities
- Cushing syndrome, caused by cortisol overproduction due to adrenal hyperplasia or tumors
Symptoms of Cushing Syndrome
This syndrome causes the enlargement of adrenal glands and results in the overproduction of cortisol, leading to Cushing syndrome. The symptoms of this syndrome are:
- Truncal Obesity / central obesity
- Wasting of the muscle
- Facial plethora (red, rounded face)
- Diabetes
- Skin pigmentation
- Stunted growth
Conclusion
To conclude, McCune-Albright syndrome is a rare genetic but not inherited disorder that affects your bones, endocrine glands, and skin. It has a prevalence of 1:100000. Moreover, this syndrome is diagnosed by radiological investigations and genetic testing. Treatment of this disease is symptomatic. The prognosis depends upon the severity of the disease. If you or your loved ones have symptoms, consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and management.
Refrences
- 1Dumitrescu, C. E., & Collins, M. T. (2008). McCune-Albright syndrome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-3-12
- 2Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. >https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
- 3Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
- 4Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/
- 5Dumitrescu, C. E., & Collins, M. T. (2008). McCune-Albright syndrome. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-3-12
- 6Department of Health & Human Services. (n.d.). McCune-Albright syndrome. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/mccune-albright-syndrome
- 7Lo FS, Chen TL, Chiou CC. Detection of Rare Somatic GNAS Mutation in McCune-Albright Syndrome Using a Novel Peptide Nucleic Acid Probe in a Single Tube. Molecules. 2017 Nov 1;22(11):1874. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111874. PMID: 29104223; PMCID: PMC6150203.
- 8Akirov A, Masri-Iraqi H, Dotan I, Shimon I. The Biochemical Diagnosis of Acromegaly. J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 9;10(5):1147. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051147. PMID: 33803429; PMCID: PMC7967116.
- 9Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf.
- 10Holbrook, L. (2022, July 12). McCune-Albright Syndrome. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537092/